
- 160 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Mathematical Modelling
About this book
Mathematical modelling modules feature in most university undergraduate mathematics courses. As one of the fastest growing areas of the curriculum it represents the current trend in teaching the more complex areas of mathematics. This book introduces mathematical modelling to the new style of undergraduate - those with less prior knowledge, who require more emphasis on application of techniques in the following sections: What is mathematical modelling?; Seeing modelling at work through population growth; Seeing modelling at work through published papers; Modelling in mechanics.Written in the lively interactive style of the Modular Mathematics Series, this text will encourage the reader to take part in the modelling process.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
What is Mathematical Modelling?
1.1 Modelling with data
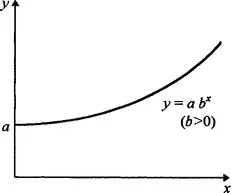

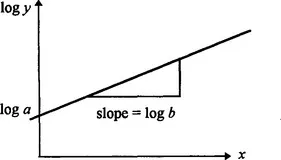
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Other titles in this series
- Copyright
- Series Preface
- Preface
- Chapter 1: What is Mathematical Modelling?
- Chapter 2: Modelling Population Growth
- Chapter 3: Mathematical Modelling in Action
- Chapter 4: Developing Modelling Skills
- Answers to Selected Problems
- Index of Modelling Problems
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
