
Integrated Design and Simulation of Chemical Processes
- 886 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Integrated Design and Simulation of Chemical Processes
About This Book
This comprehensive work shows how to design and develop innovative, optimal and sustainable chemical processes by applying the principles of process systems engineering, leading to integrated sustainable processes with 'green' attributes. Generic systematic methods are employed, supported by intensive use of computer simulation as a powerful tool for mastering the complexity of physical models.
New to the second edition are chapters on product design and batch processes with applications in specialty chemicals, process intensification methods for designing compact equipment with high energetic efficiency, plantwide control for managing the key factors affecting the plant dynamics and operation, health, safety and environment issues, as well as sustainability analysis for achieving high environmental performance. All chapters are completely rewritten or have been revised.
This new edition is suitable as teaching material for Chemical Process and Product Design courses for graduate MSc students, being compatible with academic requirements world-wide. The inclusion of the newest design methods will be of great value to professional chemical engineers.
- Systematic approach to developing innovative and sustainable chemical processes
- Presents generic principles of process simulation for analysis, creation and assessment
- Emphasis on sustainable development for the future of process industries
Frequently asked questions
Information
Integrated Process and Product Design
Abstract
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 Motivation
1.1.2 The road map of the book
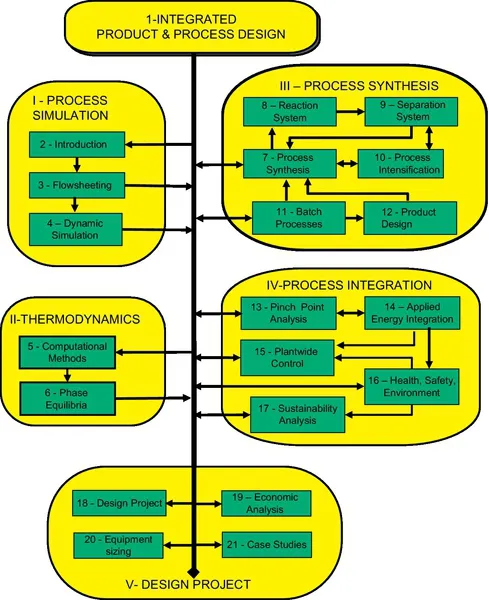
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- Chapter 1: Integrated Process and Product Design
- Chapter 2: Introduction in Process Simulation
- Chapter 3: Steady-State Flowsheeting
- Chapter 4: Dynamic Simulation
- Chapter 5: Generalised Computational Methods in Thermodynamics
- Chapter 6: Phase Equilibria
- Chapter 7: Process Synthesis by the Hierarchical Approach
- Chapter 8: Synthesis of Reaction Systems
- Chapter 9: Synthesis of Separation Systems
- Chapter 10: Process Intensification
- Chapter 11: Batch Processes
- Chapter 12: Chemical Product Design
- Chapter 13: Pinch Point Analysis
- Chapter 14: Applied Energy Integration
- Chapter 15: Plantwide Control
- Chapter 16: Health, Safety and Environment
- Chapter 17: Sustainability Analysis
- Chapter 18: Process Design Project
- Chapter 19: Economic Evaluation of Projects
- Chapter 20: Equipment Selection and Design
- Chapter 21: Case Studies
- Appendices
- Index