
Electrical Drives for Direct Drive Renewable Energy Systems
- 280 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Electrical Drives for Direct Drive Renewable Energy Systems
About This Book
Wind turbine gearboxes present major reliability issues, leading to great interest in the current development of gearless direct-drive wind energy systems. Offering high reliability, high efficiency and low maintenance, developments in these direct-drive systems point the way to the next generation of wind power, and Electrical drives for direct drive renewable energy systems is an authoritative guide to their design, development and operation.Part one outlines electrical drive technology, beginning with an overview of electrical generators for direct drive systems. Principles of electrical design for permanent magnet generators are discussed, followed by electrical, thermal and structural generator design and systems integration. A review of power electronic converter technology and power electronic converter systems for direct drive renewable energy applications is then conducted. Part two then focuses on wind and marine applications, beginning with a commercial overview of wind turbine drive systems and an introduction to direct drive wave energy conversion systems. The commercial application of these technologies is investigated via case studies on the permanent magnet direct drive generator in the Zephyros wind turbine, and the Archimedes Wave Swing (AWS) direct drive wave energy pilot plant. Finally, the book concludes by exploring the application of high-temperature superconducting machines to direct drive renewable energy systems.With its distinguished editors and international team of expert contributors, Electrical drives for direct drive renewable energy systems provides a comprehensive review of key technologies for anyone involved with or interested in the design, construction, operation, development and optimisation of direct drive wind and marine energy systems.
- An authorative guide to the design, development and operation of gearless direct drives
- Discusses the principles of electrical design for permanent magnet generators and electrical, thermal and structural generator design and systems integration
- Investigates the commercial applications of wind turbine drive systems
Frequently asked questions
Information
Electrical generators for direct drive systems: a technology overview
Abstract:
Key words
1.1 Introduction
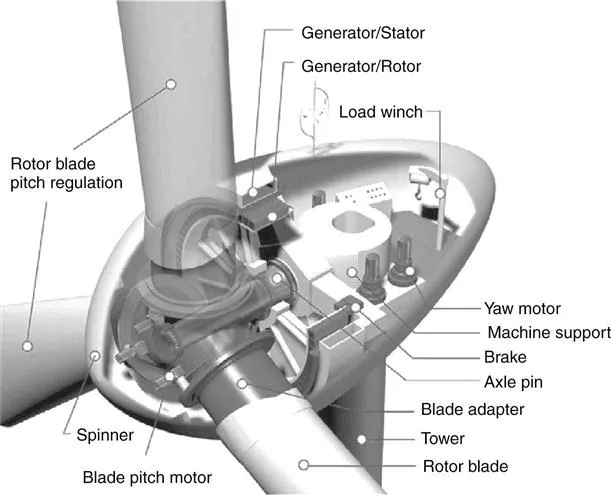
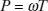
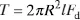
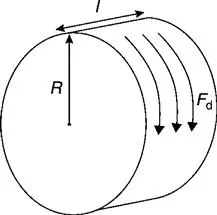
1.2 Excitation methods
1.2.1 Electrically excited direct drive (EEDD) generators
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Contributor contact details
- Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy
- Part I: Electrical drive technology
- Part II: Applications: wind and marine
- Index