
- 684 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About This Book
This book focuses on those organic chemicals that are regulated by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs). as well as organic chemical with the attributes of being persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic to ecosystem and human beings, criteria used by the Stockholm Convention for screening POP candidates. Because of the unfavourable properties of POPs, numerous research efforts have been directed toward investigating their input sources, fate, and effects, with the help of continuously improving analytical technologies. The contributors to this book provide an integrated assessment of existing data, which will benefit both the scientific and management communities in planning further research projects and/or pollution control measures.
- Comprehensive overview of recent advances in analyzing persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
- Covers input sources, fate and biological effects of POPs
- Contains essential information for environmental management
Frequently asked questions
Information
Analytical Methods for the Measurement of Legacy and Emerging Persistent Organic Pollutants in Complex Sample Matrices
1 Corresponding author: E-mail: [email protected]
Abstract
Keywords
GC with MS detectors; LC with MS detectors; Persistent organic pollutants analysis; Sample collection; Sample extraction; Sample purification1. Introduction
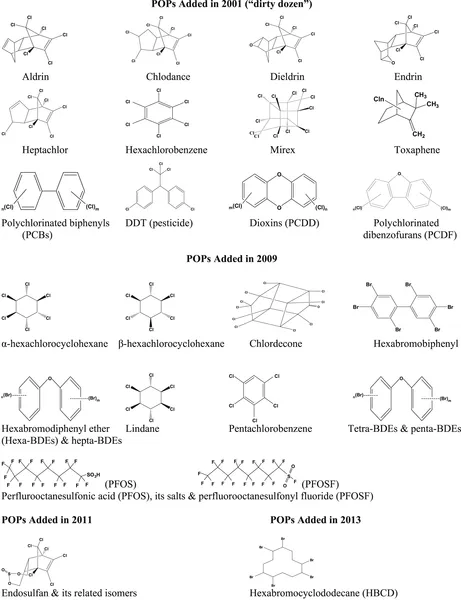
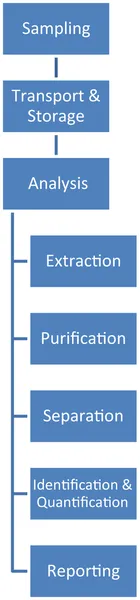
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Advisory Board
- Copyright
- Contributors to Volume 67
- Series Editor’s Preface
- Volume Editor’s Preface
- Chapter 1. Analytical Methods for the Measurement of Legacy and Emerging Persistent Organic Pollutants in Complex Sample Matrices
- Chapter 2. Bioanalytical Approaches to Understanding Toxicological Implications of Mixtures of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Marine Wildlife
- Chapter 3. Fast Analytical Techniques Based on Microextraction
- Chapter 4. Application of Passive Sampling Techniques in Measurement of HOCs in Aquatic Environments
- Chapter 5. Assessment of Sediment Toxicity with SPME-Based Approaches
- Chapter 6. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in the Environment and Their Removal from Wastewater through Constructed Wetlands
- Chapter 7. Occurrence and Fate of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Wastewater
- Chapter 8. Atmospheric Deposition of POPs: Implications for the Chemical Pollution of Aquatic Environments
- Chapter 9. Electronic Waste: A New Source of Halogenated Organic Contaminants
- Chapter 10. Occurrence and Human Health Risk of Emerging Organic Contaminants in E-Waste
- Chapter 11. Long-Range and Regional Atmospheric Transport of POPs and Implications for Global Cycling
- Chapter 12. Occurrence and Ecological Risk of Halogenated Flame Retardants (HFRs) in Coastal Zones
- Chapter 13. Atmospheric Long-Range Transport of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) into Polar Regions
- Chapter 14. Bioaccumulation and Biotransformation of Brominated Flame Retardants
- Chapter 15. Bioavailability of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Soils: Concept, Analytical Tools, and Application in the Risk Assessment
- Chapter 16. Benzotriazoles: History, Environmental Distribution, and Potential Ecological Effects
- Chapter 17. QSARs on the Thyroid Hormone Effects of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether (PBDE) Derivatives
- Chapter 18. The Toxicity of Persistent Organic Pollutants to Aquatic Organisms
- Chapter 19. Health-Based Risk Assessment of PBDEs
- Index