
- 272 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Advanced Fixed Income Analysis
About this book
Each new chapter of the Second Edition covers an aspect of the fixed income market that has become relevant to investors but is not covered at an advanced level in existing textbooks. This is material that is pertinent to the investment decisions but is not freely available to those not originating the products. Professor Choudhry's method is to place ideas into contexts in order to keep them from becoming too theoretical. While the level of mathematical sophistication is both high and specialized, he includes a brief introduction to the key mathematical concepts. This is a book on the financial markets, not mathematics, and he provides few derivations and fewer proofs. He draws on both his personal experience as well as his own research to bring together subjects of practical importance to bond market investors and analysts.- Presents practitioner-level theories and applications, never available in textbooks- Focuses on financial markets, not mathematics- Covers relative value investing, returns analysis, and risk estimation
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Asset-Swap Spreads and Relative Value Analysis
Abstract
1.1 Asset-Swap Spread
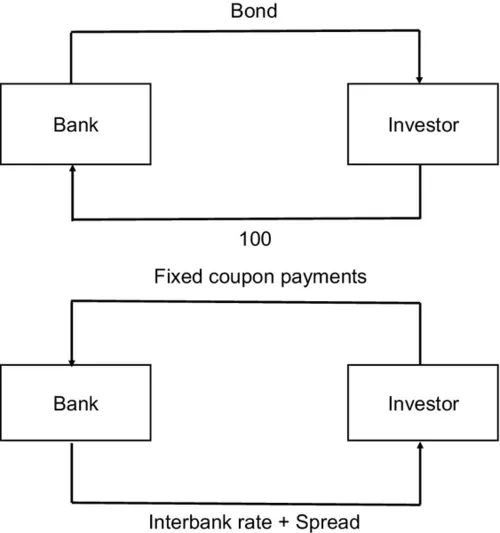
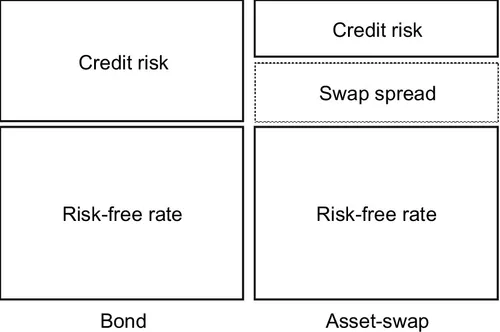
1.2 Swap Spread for Richness and Cheapness Analysis
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Dedication
- About the Authors
- Preface
- Preface to the First Edition (published 2004)
- Chapter 1: Asset-Swap Spreads and Relative Value Analysis
- Chapter 2: The Dynamics of Asset Prices
- Chapter 3: Interest-Rate Models I
- Chapter 4: Interest-Rate Models II
- Chapter 5: Fitting the Term Structure
- Chapter 6: Advanced Analytics for Index-Linked Bonds
- Chapter 7: Analysing the Long-Bond Yield
- Chapter 8: The Default Risk of Corporate Bonds
- Chapter 9: Convertible Securities: Analysis and Valuation
- Chapter 10: Floating-Rate Notes
- Chapter 11: Bonds with Embedded Options
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app