
- 378 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Pile Design and Construction Rules of Thumb
About This Book
Pile Design and Construction Rules of Thumb presents Geotechnical and Civil Engineers a comprehensive coverage of Pile Foundation related theory and practice. Based on the author's experience as a PE, the book brings concise theory and extensive calculations, examples and case studies that can be easily applied by professional in their day-to-day challenges.
In its first part, the book covers the fundamentals of Pile Selection: Soil investigation, condition, pile types and how to choose them. In the second part it addresses the Design of Pile Foundations, including different types of soils, pile groups, pile settlement and pile design in rock. Next, the most extensive part covers Design Strategies and contains chapters on loading analysis, load distribution, negative skin friction, design for expansive soils, wave equation analysis, batter piles, seismic analysis and the use of softwares for design aid. The fourth part covers Construction Methods including hammers, Inspection, cost estimation, load tests, offshore piling, beams and caps.
In this new and updated edition the author has incorporated new pile designs such as helical, composite, wind turbine monopiles, and spiral coil energy piles. All calculations have been updated to most current materials characteristics and designs available in the market. Also, new chapters on negative skin friction, pile driving, and pile load testing have been added.
Practicing Geotechnical, and Civil Engineers will find in this book an excellent handbook for frequent consult, benefiting from the clear and direct calculations, examples, and cases. Civil Engineering preparing for PE exams may benefit from the extensive coverage of the subject.
- Convenient for day-to-day consults
- Numerous design examples for sandy soils, clay soils, and seismic loadings
- Now including helical, composite, wind turbine monopiles, and spiral coil energy piles
- Methodologies and case studies for different pile types
- Serves as PE exam preparation material
Frequently asked questions
Information
Site investigation and soil conditions
Abstract
Keywords
1.1. Origin of rocks and soils

1.1.1. Earth cools down
1.1.2. Rock weathering
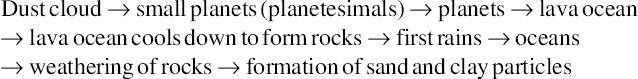
1.1.3. Brief overview of rocks
1.1.3.1. Igneous rocks
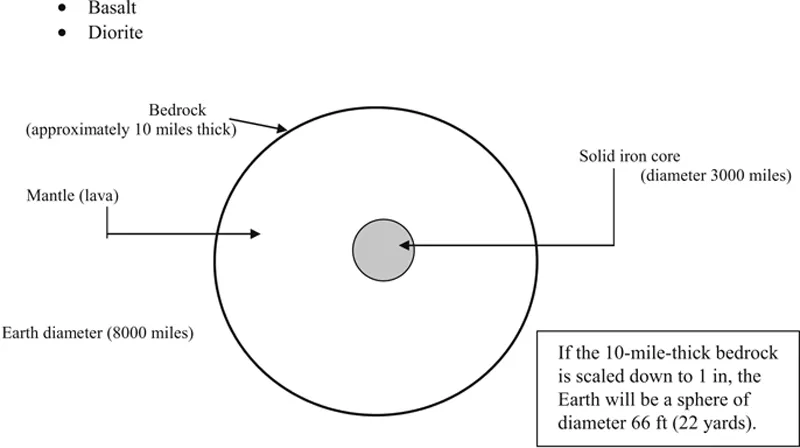
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- 1: Site investigation and soil conditions
- 2: Geophysical methods
- 3: Groundwater
- 4: Foundation types
- 5: Pile types
- 6: Selection of piles
- 7: Static and dynamic analysis
- 8: Design of driven piles
- 9: Design of bored piles
- 10: Caisson design
- 11: Piles in rock
- 12: Underpinning
- 13: Pile settlement
- 14: Wave equation basics
- 15: Negative skin friction (downdrag)
- 16: Bitumen-coated pile design
- 17: Laterally loaded piles
- 18: Short course on seismology
- 19: Seismic analysis of piles
- 20: Batter pile design
- 21: Pile design software
- 22: Pile driving methods
- 23: Water jetting
- 24: Pile load testing
- 25: Pile construction verification
- 26: Pile identification plan
- 27: As built plans
- 28: Code issues (Eurocode and other building codes)
- 29: Economic considerations and costing
- Subject Index