
eBook - ePub
Blast Furnace Ironmaking
Analysis, Control, and Optimization
- 828 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Blast Furnace Ironmaking
Analysis, Control, and Optimization
About this book
Blast Furnace Ironmaking: Analysis, Control, and Optimization uses a fundamental first principles approach to prepare a blast furnace mass and energy balance in Excel™. Robust descriptions of the main equipment and systems, process technologies, and best practices used in a modern blast furnace plant are detailed. Optimization tools are provided to help the reader find the best blast furnace fuel mix and related costs, maximize output, or evaluate other operational strategies using the Excel™ model that the reader will develop.
The first principles blast furnace Excel™ model allows for more comprehensive process assessments than the 'rules of thumb' currently used by the industry. This book is suitable for undergraduate and postgraduate science and engineering students in the fields of chemical, mechanical, metallurgical and materials engineering. Additionally, steel company engineers, process technologists, and management will find this book useful with its fundamental approach, best practices description, and perspective on the future.
- Provides sample problems, answers and assignments for each chapter
- Explores how to optimize the blast furnace operation while maintaining required temperatures and gas flowrates
- Describes all major blast furnace equipment and best practices
- Features blast furnace operating data from five continents
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
The Iron Blast Furnace Process
Abstract
The blast furnace is the most prolific of the metallurgical furnaces operating in the world. In 2016, over 1 billion tonnes of molten iron were produced from 700 to 900 blast furnaces operating on every continent, except Antarctica. Using iron ore-based sinter and pellets and fuels that include metallurgical coke and injected hydrocarbons, the blast furnace produces a carbon-saturated iron alloy known as hot metal—an important raw material for producing steel. The countercurrent flow of gas and solids makes the blast furnace extremely efficient from both a chemical and thermal point of view. The objectives of this chapter are to:
- 1. introduce readers to modern blast furnace ironmaking;
- 2. describe ironmaking’s raw materials, processes, and products;
- 3. mention ironmaking’s peripheral processes, for example, cokemaking, sintering, and blast heating; and
- 4. estimate blast furnace investment and operating costs.
Keywords
Blast furnace; metallurgical coke; sinter; pellets; operating costs; capital costs
1.1 Introduction to the Blast Furnace Process
The iron blast furnace is a tall vertical shaft furnace, Fig. 1.1. Its principle objective is to produce molten iron from iron ores for subsequent and immediate production of molten/liquid steel. A photograph of a blast furnace plant is shown in Fig. 1.2.
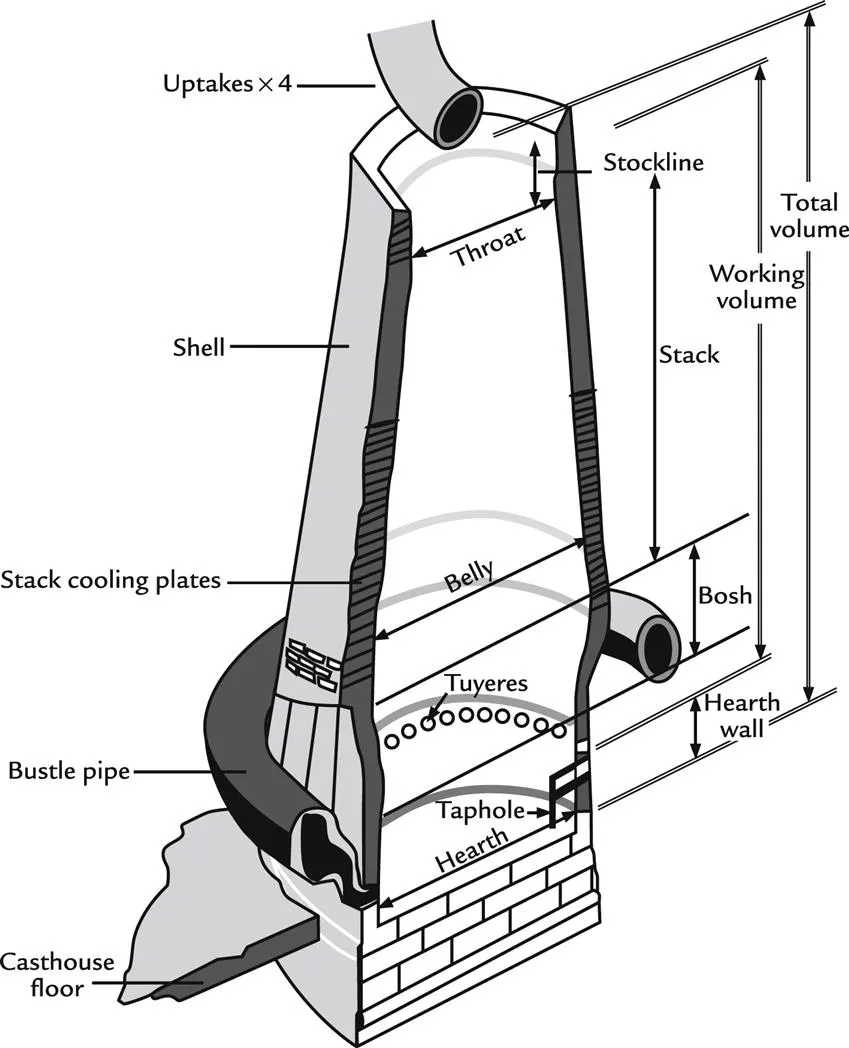

Solid Fe oxide ore (hematite, Fe2O3), coke (87–91% carbon), and fluxes are charged to the top of the blast furnace. A molten iron alloy, 1500°C, 94.5% Fe, 4.5% C, and 1% [Si + Mn], is cast from the hearth along with molten and impurity-rich oxide slag. Hot, high pressure air is blown into the blast furnace through the tuyeres, burning coke, and injected fuel to create the heat needed to smelt the iron ores and fluxes. The resulting gas rises quickly up through the furnace charge materials also known as burden. The burden is heated, Fe oxides are reduced to Fe, and solid materi...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Author Biography
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Chapter 1. The Iron Blast Furnace Process
- Chapter 2. Inside the Blast Furnace
- Chapter 3. Making Steel From Molten Blast Furnace Iron
- Chapter 4. Introduction to the Blast Furnace Mass Balance
- Chapter 5. Introduction to the Blast Furnace Enthalpy Balance
- Chapter 6. Combining Mass and Enthalpy Balance Equations
- Chapter 7. Conceptual Division of the Blast Furnace - Bottom Segment Calculations
- Chapter 8. Bottom Segment with Pulverized Carbon Injection
- Chapter 9. Bottom Segment With Oxygen Enrichment of Blast Air
- Chapter 10. Bottom Segment With Low Purity Oxygen Enrichment
- Chapter 11. Bottom Segment with CH4(g) Injection
- Chapter 12. Bottom Segment With Moisture in Blast Air
- Chapter 13. Bottom Segment With Pulverized Hydrocarbon Injection
- Chapter 14. Raceway Flame Temperature
- Chapter 15. Automating Matrix Calculations
- Chapter 16. Raceway Flame Temperature With Pulverized Carbon Injection
- Chapter 17. Raceway Flame Temperature With Oxygen Enrichment
- Chapter 18. Raceway Flame Temperature With CH4(g) Injection
- Chapter 19. Raceway Flame Temperature With Moisture in Blast Air
- Chapter 20. Top Segment Mass Balance
- Chapter 21. Top-Segment Enthalpy Balance
- Chapter 22. Top Gas Temperature Calculation
- Chapter 23. Top Segment Calculations With Pulverized Carbon Injection
- Chapter 24. Top Segment Calculations With Oxygen Enrichment
- Chapter 25. Top Segment Mass Balance With CH4(g) Injection
- Chapter 26. Top Segment Enthalpy Balance with CH4(g) Injection
- Chapter 27. Top Gas Temperature with CH4(g) Injection
- Chapter 28. Top-Segment Calculations With Moisture in Blast Air
- Chapter 29. Bottom Segment Calculations With Natural Gas Injection
- Chapter 30. Raceway Flame Temperature With Natural Gas Injection
- Chapter 31. Top-Segment Calculations With Natural Gas Injection
- Chapter 32. Bottom-Segment Slag Calculations - Ore, Fluxes, and Slag
- Chapter 33. Bottom-Segment Slag Calculations-With Excess Al2O3 in Ore
- Chapter 34. Bottom-Segment Slag Calculations
- Chapter 35. Bottom-Segment Calculations - Reduction of SiO2
- Chapter 36. Bottom-Segment Calculations - Reduction of MnO
- Chapter 37. Bottom-Segment Calculations With Pulverized Coal Injection
- Chapter 38. Bottom-Segment Calculations With Multiple Injectants
- Chapter 39. Raceway Flame Temperature With Multiple Injectants
- Chapter 40. Top-Segment Calculations With Multiple Injectants
- Chapter 41. Top-Segment Calculations with Raw Material Moisture
- Chapter 42. Top Segment With Carbonate Fluxes
- Chapter 43. Top-Charged Scrap Steel
- Chapter 44. Top Charged Direct Reduced Iron
- Chapter 45. Bottom-Segment Calculations With H2(g) Injection
- Chapter 46. Top-Segment Calculations With H2(g) Injection
- Chapter 47. CO(g) Injection Into Bottom and Top Segments
- Chapter 48. Introduction to Blast Furnace Optimization
- Chapter 49. Blast Furnace Optimization Case Studies
- Chapter 50. Blast Furnace Rules of Thumb
- Chapter 51. The Blast Furnace Plant
- Chapter 52. Blast Furnace Proper
- Chapter 53. Blast Furnace Refractory Inspection Technologies
- Chapter 54. Blast Furnace Ferrous Burden Preparation
- Chapter 55. Metallurgical Coke - A Key to Blast Furnace Operations
- Chapter 56. Blast Furnace Fuel Injection
- Chapter 57. Casting the Blast Furnace
- Chapter 58. Blast Furnace Slag
- Chapter 59. Burden Distribution
- Appendix A. Compound Molecular Masses and Compositions
- Appendix B. Air Composition and Nitrogen/Oxygen Ratio Assumption
- Appendix C. Effect of Argon on Blast Furnace Calculations
- Appendix D. CO Raceway Exit Gas Proof
- Appendix E. CO2(g)+C(s)→2CO(g) Equilibrium Constant
- Appendix F. Oxygen Concentration in Blast Furnace Tuyere Raceway With CO(g) Production
- Appendix G. H2(g) Raceway Exit Gas Proof
- Appendix H. H2O(g)+C(s)→H2(g)+CO(g) Equilibrium Constant
- Appendix I. Using Excel to Solve Matrices
- Appendix J. How to Compute Element and Compound Enthalpies
- Appendix K. CO(g)+Fe0.947O→CO2(g)+0.947Fe Equilibrium Constants
- Appendix L. Equilibrium CO2(g)/CO(g) Mass Ratio
- Appendix M. Calculation of H2(g)+Fe0.947O(s)→H2O(g)+0.947Fe(s) Equilibrium Constants
- Appendix N. Equilibrium H2O(g)/H2(g) Mass Ratio
- Appendix O. Conversion of Grams H2O(g)/Nm3 of Dry Blast Air to kg H2O(g)/kg of Dry Blast Air
- Appendix P. Top Gas Mass%, Volume% Calculator
- Appendix Q. Calculation of Natural Gas Composition in Mass%
- Appendix R. Natural Gas Enthalpy
- Appendix S. Enthalpy of Si in Molten Iron
- Appendix T. C/Fe, Si/Fe, Mn/Fe in Molten Iron Mass Ratio Calculator
- Appendix U. Enthalpy of Mn in Molten Iron
- Appendix V. Coal Elemental Composition
- Appendix W. CO(g)+3Fe2O3(s)→CO2(s)+2Fe3O4(s) Equilibrium Constant
- Appendix X. Slag Liquidus Temperature Lookup Tables
- Appendix Y. Answers to Exercises
- Epilogue
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Blast Furnace Ironmaking by Ian Cameron,Mitren Sukhram,Kyle Lefebvre,William Davenport in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Chemical & Biochemical Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.