
Omni-Channel Retail and the Supply Chain
Working Together for a Competitive Advantage
- 266 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About This Book
Omni-Channel Retail and the Supply Chain
The days of going to the local department store to buy a television, view the options available, and make a purchase now seem "quaint." The emergence of the internet, smartphones, social media, and other technologies has opened a world of new options for consumers (and businesses) to review, research, and buy online with an ever-increasing array of delivery options.
The emergence of e-commerce has resulted in what is commonly known today as "omni-channel" marketing, in which customers engage with companies in a variety of ways, including in a physical store or online via websites and mobile apps. This process puts the supply chain "front and center, " as consumers are increasingly demanding and browsing, buying, and returning goods through various channels, not just the traditional "brick and mortar" way. To accomplish this with high levels of service while remaining profitable requires real-time visibility of inventory across the supply chain and a single view of consumers as they continuously move from one channel to another.
While this is a boon to consumers, it has made the already complex global supply chain even more challenging to manage. On top of that, the 2020 Covid19 pandemic has accelerated this omni-channel retail trend, as consumers need even more ways to order and additional options for last-mile delivery, such as curbside pickup. Covid19 has exposed a lack of flexibility and readiness, resulting in shortages of everything from toilet paper and meats to personal protective equipment (PPE) and ventilators. It has been a real-life example of the "bullwhip effect, " where variability at the consumer end of the supply chain results in increased variability as one goes upstream towards distributors, manufacturers, and suppliers. This results in shortages, misallocations, and increased costs.
No longer can a manufacturer, distributor, or retailer of consumer products just "fill the pipeline" and wait for orders to come in. Now, they must anticipate various purchases and delivery items, while at the same time minimizing costs. To do this is no easy task, requiring a Lean, agile, and responsive supply chain.
Until now, there was no existing "playbook" for organizations to navigate their way through this new world. This book describes the impact of omni-channel marketing on the supply chain and logistics functions, and is intended to help management meet the needs of not only today's ever-changing world but to anticipate what may be required in the future to achieve superior customer service, profitability, and a competitive advantage.
Frequently asked questions
Information
Part I
Omni-Channel Retail and the Supply Chain
Working Together for a Competitive Advantage Introduction
1
Introduction: Where We Are Today

Omni-channel.
How Supply Chain Strategies Impact E-Commerce Success
- Individual product characteristics
- Demand volatility
- Product variety
- Product life cycle length and position
- Criteria for orders, profit margins, and dominant costs – for example, physical vs. marketing
- Quality of information available
- Type of forecast used – qualitative vs. quantitative
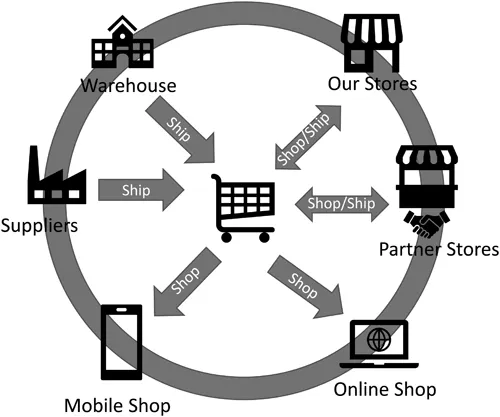
Omni-channel retail supply chain.
- The Internet and mobile devices – The platform where sales happen is moving from personal computers to mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones (also referred to as m-commerce).
- Omni-channel retailing – This process integrates brick-and-mortar, TV, catalog, social media, e-commerce, and m-commerce channels both for purchases and for returns.
- Changing supply chains – In retail, inventory must become more transparent to create efficiencies in new supply chains with direct-to-consumer shipments from online orders, sometimes with returns to stores. Adding to the complexity are ship-to-store and ship-from-store customer orders.
- Distribution and fulfillment centers – In the world of e-commerce, companies design and build fulfillment centers to satisfy online orders, which, in many cases, are for a single item. E-commerce orders typically are smaller than those for traditional brick-and-mortar distribution centers, and often require one-day fulfillment.
- Automated inventory systems – Beyond the increased current use of radio-frequency identification (RFID), barcode readers, handheld mobile computers, and automated carousels, e-commerce requires companies to plan for the design and implementation of robotic systems in their fulfillment centers and supply chains. These systems can range from the use of automated guide vehicles and robots to the potential future use of air and land drones for delivery.
Omni-Channel Retail and the Supply Chain: Challenges ahead
Omni-Channel Multiplies the Challenges for Distribution-Centric Supply Chains
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- PART I Omni-Channel Retail and the Supply ChainWorking Together for a Competitive Advantage Introduction
- PART II Traditional vs. Omni-Channel Marketing
- PART III Traditional vs. Omni-Channel Distribution
- PART IV Transformational Omni-Channel Supply Chain Strategies to Achieve a Competitive Advantage
- PART V The Shape of Things to Come
- References
- Index