![]() Maritime Education and Training
Maritime Education and Training![]()
12. Improving MET Quality: Relationship Between Motives of Choosing Maritime Professions and Students’ Approaches to Learning
G. Kalvaitiene, I. Bartusevičienė & V. Sencila
Lithuanian Maritime Academy, Klaipeda, Lithuania
ABSTRACT: Question of improvement quality of studies is a continual hot issue in every educational environment. In maritime education and training, this question is especially important because of international regulations of maritime professions. Quality of studies is a multidimensional and complex phenomenon. It is influenced by wide range of factors: from labour market and current educational policy to individual students’ efforts and characteristics. Motives of choosing maritime profession and approaches to learning are characteristics of an individual person. Quality of studies is influenced by students’ approaches to learning: deep approach to learning is related with higher quality of studies, surface approach – to lower quality. On the other hand approaches to learning could be influenced by motives of choosing profession, which affect entire professional career planning. Both phenomena are important for the improvement of quality of studies. The relation between motives of choosing maritime professions and students’ approaches to learning in the context of quality of studies are under investigation in this paper.
1 INTRODUCTION
Increasing the quality of maritime studies is a relevant problem, which may be studied in different aspects, and one of them is the study of the students’ approach to learning as the individual students’ characteristics. Quality of studies is a multidimensional and complex phenomenon (Heywood, 2000; Bartuseviciene, Rupsiene, 2010). The impact of the students’ approach to learning on the results of studies was investigated in the works of F. Marton and R. Säljö, (1976), P. Ramsden (2003), N. Petty (2004), G. Pask (1976), N. Entwistle, P. Ramsden (1983). The authors who had investigated the process of studies determined that there were two different students’ approaches to learning that were named by the scientists as deep and surface ones. According to those authors different approaches to learning determine different results of learning, therefore, investigating the students’ approaches to learning and determining the prerequisites of deep approach to learning that leads to better results of studies, it is possible to find an answer to the question about the increasing of the quality of studies.
J. Biggs (1987a) expanded F. Marton ir R. Säljö (1976) theoretical model by stating that the approach to learning consists of two components: motive of learning and strategy of learning which is understood as a whole of the ways and the habits of learning (Table 1). The construct of students’ theoretical approach to learning is based on the idea that the learning motives of students determine the strategies of learning and depend not only on personal characteristics of students but also on learning context and content of learning tasks (Biggs, 1987a). J. Biggs (1987b) created SPQ (Study Process Questionnaire) to determine the approach of students to learning, learning motives and strategies, and later on it was revised to a shorter one with 20 questions, R-2F-SPQ (The revised two-factor study process questionnaire) (Biggs, Kember, Leung, 2001).
Table 1. Motives and strategies as complex components of the approach to learning (Biggs, 1987b).
Approach | Motive | Strategy |
Surface (SA) | Surface motive (SM) is to meet requirements minimally, a balancing act between failing and working more than is necessary | Surface strategy (SS) is to limit target to bare Essentials and reproduce them through learning |
Deep (DA) | Deep motive (DM) is intrinsic interest in what is being learned; to develop competence in particular academic subject | Deep strategy (DS) is to discover meaning by reading widely, inter-relating with pervious relevant knowledge, etc. |
Analysing the possibilities how to improve MET efficiency of studies it is urgent to investigate the motivation concept of profession choosing and its relation with the approaches to learning that is the prerequisite of high efficiency of studies.
The initiator of the theory of modern choice of professions is considered by F. Parson, who founded the first professional consulting bureau in 1908 in the USA. He formulated the main principles of successful profession choosing (Parson, 1909):
– good self-cognition;
– good knowledge of peculiarities of the chosen profession;
– ability to correctly combine this knowledge and take the right profession solution.
R. Hoppock (1950) explains choosing profession via the satisfaction of need. The essence of his theory is revealed by ten postulates which speak about the fact that a man chooses his profession to satisfy his needs. According to R.Hoppock, choosing profession is being improved when a man starts to imply that the future profession will better satisfy his needs.
J. Holland’s theory (1959) is popular among the theoretical and practical people very much, which states that personalities can be divided to six types that were named as realistic, researcher’s, artistic, sociable, initiative and normative. In J. Holland’s opinion people tend to look for such labour activity environment, where they might express themselves. He states that similar people choose similar professions, but satisfaction from work, success and stability depend on how the personality matches to the environment (Holland, 1966).
The most striking representative of the development model of choosing profession is Donald Super (Super, 1957). The scientist states that by choosing profession a man essentially chooses one of the main means how to express his personal “ego”. Professional behavior of a person is a way to implement his professional self-image.
The background of D. Krumboltz theory is learning (1979). According to his statement, there are 4 groups of factors important for the professional self-determination: genes – inherited properties, limiting learning possibilities and choosing profession; environment – social, cultural, political, economical, natural conditions; knowledge of learning – priority development of professions, distribution of certain works, as each individual person has got unique learning knowledge it makes impact on profession choosing; task fulfillment skills – there come out task fulfillment standards and values, labour habits, cognition processes and emotional reactions.
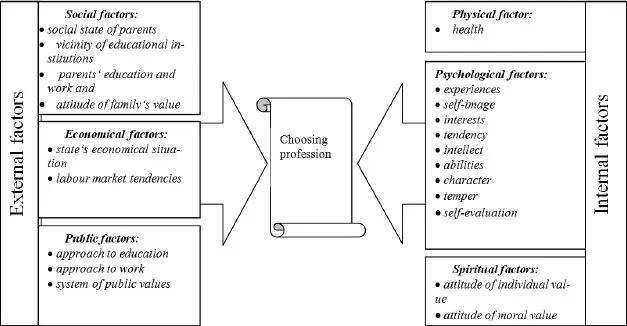
According to prof. L. Jovaiša (1999) there are the following motivation factors of profession choosing: social (social state of parents, vicinity of educational institutions), economical (payment for work), psychological (interests, turns, values, intellect and character), health.
The discussed theories should help to understand the factors that determine the solution of profession choosing process. Summarizing scheme of factors, influencing choosing of profession is shown on figure 1.
Tasks of presented investigation are:
– Investigate the motives determining the choice of seafarer’s profession.
– Diagnose the individual characteristics of students, their approach to learning that determines the efficiency of studies.
Determine the relations between the motives and approaches to learning.
Figure 1. Factors, influencing choosing of profession.
2 THE RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
2.1 The sample size
Sample of research was made of full-time students of maritime specialties’ studying at Lithuanian Maritime Academy. Making the samples of research the voluntary principle was followed – all the students that were present on query days at school and who expressed their wish were included. Such way of sampling is considered reliable.
In December 2010 – January 2011 233 students from all courses were interrogated (95 % of all maritime specialties’ students): first year students – 39,1 percent, second year students – 33,0 percent, third year students – 19,3 percent and fourth year students – 8,6 percent. The sample consisted of 145 students from Marine Navigation study program (62,2 percent) and 88 – Marine Engineering study program students (37,8 percent).
2.2 The research instrument
The questionnaire survey was used to collect data in order to examine and verify theoretical and exploratory insights about relationship between motives of choosing maritime professions and students’ approaches to learning. The originally developed questionnaire consisted out of 117 questions. The Revised-Two Factor-Study Process Questionnaire (Biggs, Kember, Leung, 2001) translated into the Lithuanian language, adapted, and validated was used as a part of the originally developed questionnaire.
The validity of the R-2F-SPQ questionnaire was checked by confirmatory factor analysis, using VARIMAX method of co-ordinate turning. High KMO ratio (0, 838) and the meaning of Bartlett test (p=0,000) confirmed the suitability of data for factor analysis. During factor analysis four factors were pointed out corresponding subscales of Biggs questionnaire, where the factor weights (L) of components are rather high: from 0,543 to 0,817. Four pointed out factors explained 52,23 percent of variance – such percentage is satisfactory in social sciences (Pett, Lackey, Sullivan, 2003).
2.3 The data analysis
The data acquired during the research were analysed using statistical analysis methods (using SPSS for Windows program, 13th versi...