
Carbohydrate Chemistry
Proven Synthetic Methods, Volume 5
- 292 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About This Book
Volumes in the Proven Synthetic Methods Series address the concerns many chemists have regarding irreproducibility of synthetic protocols, lack of identification and characterization data for new compounds, and inflated yields reported in chemical communications—trends that have recently become a serious problem.
Exploring carbohydrate chemistry from both the academic and industrial points of view, this unique resource brings together useful information into one convenient reference. The series is unique among other synthetic literature in the carbohydrate field in that, to ensure reproducibility, an independent checker has verified the experimental parts involved by repeating the protocols or using the methods.
Featuring contributions from world-renowned experts and overseen by a highly respected series editor, this latest volume compiles reliable protocols for the preparation of intermediates for carbohydrate synthesis or other uses in the glycosciences.
Key Features:
- Explains reliable and tested protocols for the preparation of intermediates for carbohydrate synthesis
- Offers a unique resource in glycosciences, compiling useful information in one reference
- Presents protocols that are of wide use to a broad range of readers in the carbohydrate field and the life sciences, including undergraduates taking carbohydrate workshops
- Explores synthetic carbohydrate chemistry from both the academic and industrial points of view
- Guarantees the reader a good, clean, reproducible experiment
Frequently asked questions
Information
Part I
Synthetic Methods
1
Synthesis of Glycosyl Thiols via 1,4-Dithiothreitol-Mediated Selective Anomeric S-Deacetylation
- Experimental
- General Methods
- General Procedure for Anomeric S-Deacetylation
- 2,3,4-Tri-O-Acetyl-6-Deoxy-1-Thio-β-D-Galactopyranose (2A )
- 2,3,4-Tri-O-Acetyl-6-Deoxy-1-Thio-β-D-Glucopyranose (2B )
- Acknowledgments
- References
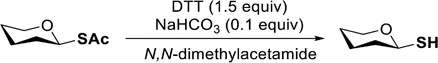
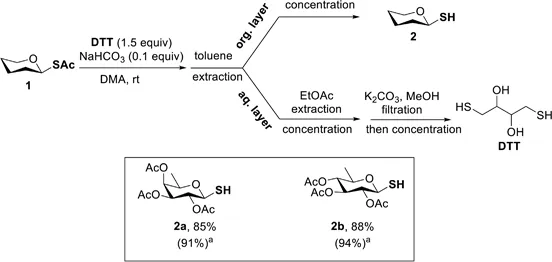
EXPERIMENTAL
GENERAL METHODS
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Carbohydrate Chemistry: Proven Synthetic Methods
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Foreword
- Introduction
- About the Series Editor
- About the Editors
- Contributors
- PART I SYNTHETIC METHODS
- PART II SYNTHETIC INTERMEDIATES