
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Clinical Atlas of Retreatment in Endodontics
About This Book
CLINICAL ATLAS OF RETREATMENT IN ENDODONTICS
Explore a comprehensive pictorial guide to the retreatment of root canals and failed endodontic cases with step-by-step advice on retreatment management
Clinical Atlas of Retreatment in Endodontics delivers an image-based reference to the management of failed root canal cases. It provides evidence-based strategies and detailed clinical explanations to manage and retreat previous endodontically failed cases. It contains concrete evidence-based and practical techniques accompanied by full-colour, self-explanatory clinical photographs taking the reader through a journey of successful management of the failed clinical cases.
Using a variety of clinical cases, the book demonstrates why and how endodontic failures occur, how to prevent them, and how to manage them in clinical practice. It also emphasises on evaluating the restorability and prognosis of the tooth in order to make a proper case selection for providing retreatment. This book also discusses the various factors that can help the clinician to make a case for nonsurgical or surgical retreatment. Readers will benefit from the inclusion of clinical cases thatprovide:
- A thorough introduction to perforation repair, with a clinical case that includes the repair of pulpal floor perforation caused due to excessive cutting of the floor of the pulp chamber
- An explanation of various factors for instrument separation, supported with a case that includes the removal of a fractured instrument
- Practical discussions of instrument retrieval, with a case that includes a fractured instrument at the apical third of mandibular molar
- A step wise pictorial description for guided root canal therapy
- Selective root canal treatment as a treatment option for retreatment of failed endodontic cases
- A detailed clinical description for how to explore and modify the endodontic access cavity for locating extra/missed canals
Perfect for endodontists, endodontic residents, and general dentists, Clinical Atlas of Retreatment in Endodontics is also useful for undergraduate dental students and private practitioners who wishto improve their understanding of endodontic retreatment and are looking for a one-stop reference on the subject.
Frequently asked questions
Information
1
Clinical Case 1 – Perforation repair: A case of repair of pulpal floor perforation caused by excessive cutting of the floor of the pulp chamber
1.1 Patient information
- Age: 30 years old.
- Gender: female.
- Medical history: non‐contributory.
1.2 Tooth
- Identification: mandibular left first molar (Tooth 36).
- Dental history: discomfort due to impingement of food inside her molar. Previous treatment done on this tooth 1 year ago.
- Clinical examination findings: deep decay, tooth was filled with food remnants, no mobility, no pain to percussion. After cleaning the tooth, big perforation was noted and bleeding also.
- Preoperative radiological assessment: deep decay and lesion at furcation area due to perforation (Figure 1.1).
- Diagnosis (pulpal and periapical): previously initiated root canal therapy with asymptomatic apical periodontitis.
1.3 Treatment plan
- First visit: local anaesthesia, rubber dam isolation, magnification (dental operative microscope), conventional access cavity, identification of orifices of the canals, placing cotton pellets inside them, stopping the bleeding physically with cotton pellet (Figure 1.2).
- Treatment plan for management of the endodontic mishap: applying MTA at the furcation area, then inserting a wet cotton pellet over MTA, temporary filling (Figure 1.3).
 Figure 1.1 Preoperative radiograph showing radiolucency in the furcation area.
Figure 1.1 Preoperative radiograph showing radiolucency in the furcation area. Figure 1.2 Clinical picture showing the pulpal floor perforation.
Figure 1.2 Clinical picture showing the pulpal floor perforation.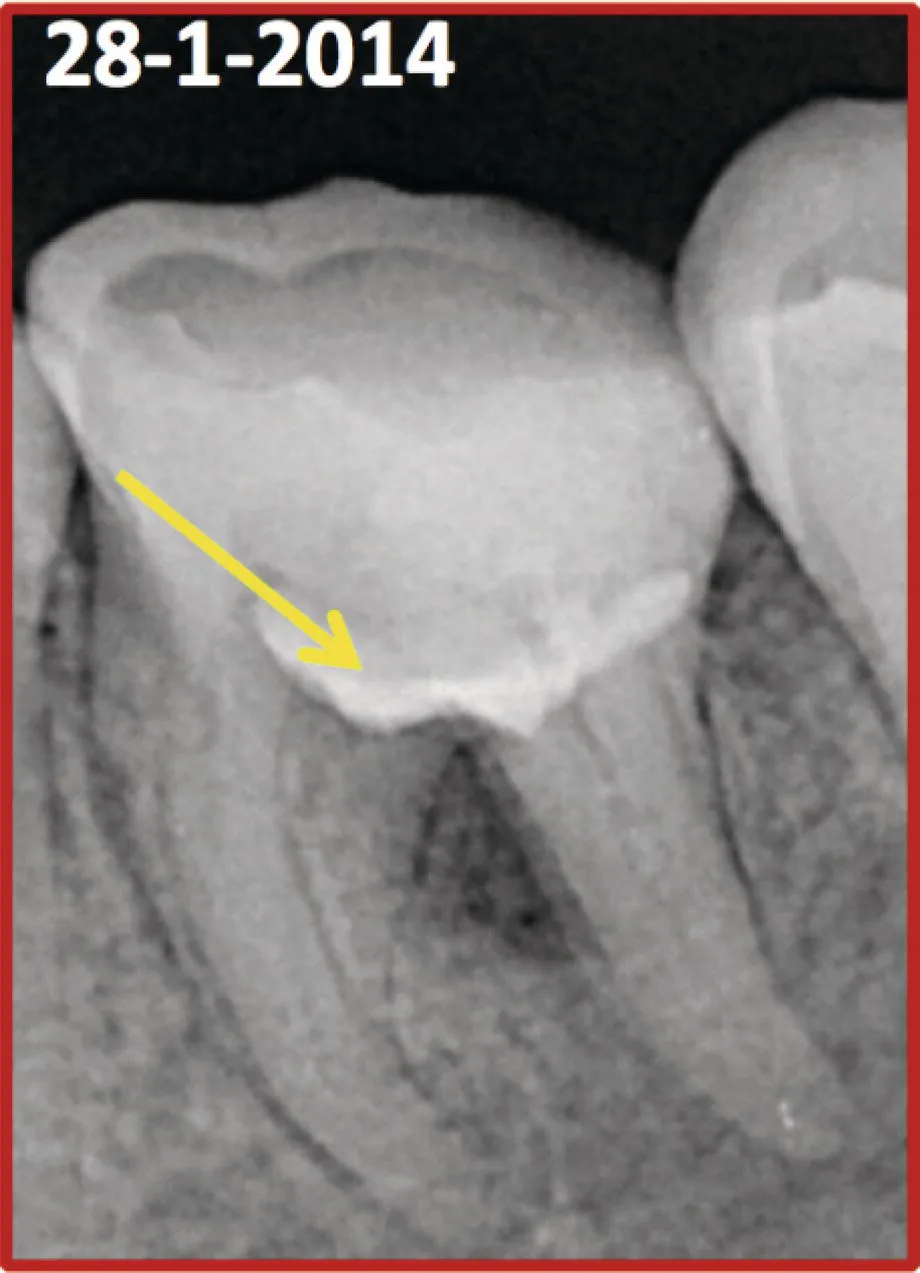 Figure 1.3 Radiograph showing MTA placed on the pulpal floor.
Figure 1.3 Radiograph showing MTA placed on the pulpal floor. - Second visit: removing temporary filling and cotton pellets, Check the condition of MTA (hardness), canal preparation with rotary files.
- Irrigation protocol (solution and technique): 5.25% NaOCl; passive sonic irrigation.
- Final irrigation protocol: 17% EDTA (syringe irrigation) for 1 minute.
- Obturation (materials and technique): zinc oxide‐based sealer (SealiteTM Ultra) and gutta‐percha; warm vertical compaction.
- Permanent filling (Figures 1.4 and 1.5).
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Foreword
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- List of Contributors
- List of Abbreviations
- About the Companion Website
- Introduction to endodontic retreatment
- 1 Clinical Case 1 – Perforation repair
- 2 Clinical Case 2 – Instrument separation
- 3 Clinical Case 3 – A case of retreatment of Tooth 16
- 4 Clinical Case 4 – Instrument retrieval
- 5 Clinical Case 5 – Perforation repair with instrument retrieval
- 6 Clinical Case 6 – Management of strip perforation and fractured instrument
- 7 Clinical Case 7 – Management of root canal treatment failure case with missed lateral canal anatomy and inadequate obturation
- 8 Clinical Case 8 – Management of a case with faulty cast post and asymptomatic lateral periodontitis
- 9 Clinical Case 9 – Management of a case with endo‐perio lesion following a previous root canal treatment
- 10 Clinical Case 10 – Management of a failed root canal treatment with silver cone obturation and fractured instrument
- 11 Clinical Case 11 – Management of a failed root canal treated maxillary molar with selective root treatment
- 12 Clinical Case 12 – Guided endodontics and its application for non‐surgical retreatments
- 13 Clinical Case 13 – Management of pulpal floor perforation with periapical lesion in the mesial root
- 14 Clinical Case 14 – Management of root canal treatment failure with missed canal anatomy and inadequate obturation
- 15 Clinical Case 15 – Management of root canal treatment failure with inadequate obturation, hidden fractured instrument and ledge formation in a severely curved mandibular molar
- 16 Clinical Case 16 – Management of root canal treatment with an instrument fracture in a mandibular molar
- 17 Clinical Case 17 – Management of a mandibular molar with fractured instrument extending in the periapical area
- 18 Clinical Case 18 – Management of root canal treatment failure with inadequate obturation and apically calcified canals
- 19 Clinical Case 19 – Management of root canal treatment failure with inadequate obturation and missed canals
- 20 Clinical Case 20 – Management of root canal treatment failure with inadequate obturation, unusual distal root anatomy and suspected ledge formation in a mandibular molar
- 21 Clinical Case 21 – Management of root canal treatment failure with inadequate obturation and faulty post placement
- 22 Clinical Case 22 – Management of root canal treatment failure with inadequate obturation, multiple perforations, fractured instrument and ledge formation in maxillary right first molar
- 23 Clinical Case 23 – Management of root canal treatment failure with inadequate obturation, fractured instrument and periapical lesion in mandibular left first molar
- 24 Clinical Case 24 – Retreatment of Tooth 21
- 25 Nonsurgical versus surgical retreatment
- Index
- End User License Agreement