
eBook - ePub
Group Reporting with SAP S/4HANA
This is a test
- 375 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Group Reporting with SAP S/4HANA
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Group Reporting with SAP S/4HANA by Eric Ryan, Thiagu Bala, Satyendra Raghav, Azharuddin Mohammed in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Computer Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 Introduction to Consolidation
We’ll start our journey through SAP S/4HANA Finance for group reporting with consolidation basics and detail how consolidation functionality has evolved over the years with SAP.
One of the most critical steps for any company is closing its financial books. As part of this financial process, companies with many business units will combine financial data from several business units within one single entity to report all business units together. This process is commonly referred to as financial consolidation. We’ll explore further details regarding financial consolidations, regulations associated with consolidation, and the history of consolidation with SAP in this chapter.
1.1 Financial Consolidation Basics
In financial accounting, consolidated financial statements provide a comprehensive view of the financial position of both the parent company and its subsidiaries, rather than one company’s standalone position. In consolidated accounting, the information from a parent company and its subsidiaries is treated as though it comes from a single entity. Figure 1.1 is an example consolidation entity structure with a parent and each of its children. The example used is a fictional soda company with Natural Soda Parent Company as the parent and its subsidiaries in North America and the United Kingdom. Further, you’ll see Natural Soda Bottling is only 80% owned by Natural Soda NA, while Natural Soda UK is a minority owner in Natural Soda Iceland at only 40%. The consolidation entity structure is also commonly referred to as the ownership structure.
There are primarily two types of consolidation:
- Legal consolidation
Performed due to the legal requirement of submitting financial statements to legal and statutory authorities. This consolidation is typically performed following Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). - Management consolidation
Performed due to management requrements to understand the management view of the profit and loss (P&L) statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
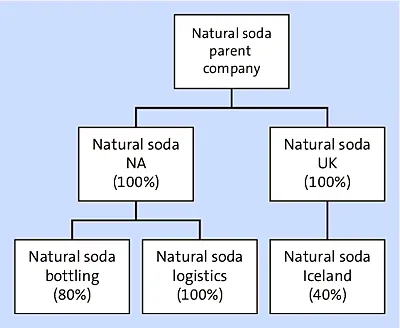
Figure 1.1 Example Consolidation Entity Structure
In both types of consolidation, activities fall into four main buckets:
- Data preparation
- Preconsolidation activities, including balance carryforward, manual journal entries, and so on
- Postconsolidation activities, including currency translation, intercompany elimations, and consolidation of investments
- Reporting and analysis
In the following sections, we’ll unpack the main process steps that fall within these four buckets, before exploring key consolidation concepts.
1.1.1 Consolidation Steps
Figure 1.2 walks through the standard consolidation process steps, starting with data collection:
- Data collection
Data is collected from multiple sources, including but not limited to other general ledgers, flat file uploads, or a central repository. - Balance carryforward
The ending balance from the prior fiscal year is carried forward to the beginning balance of the current fiscal year for all balance sheet accounts. - Currency translation
Local currency is converted to one or more group currencies in accordance with accounting principles. - Retained earnings reclass
All activities that impact the income statement are completed so net income can be calculated for the corporate group. This activity closes out the income statement by transferring the balance of the income summary, net income, to the retained earnings account. - Intercompany elimination
All intercompany transactions should be eliminated at a parent level company to avoid double counting of transactions. - Journal entries
Post-elimination journal entries are made in the form of topside adjustments usually at the request of finance during the month-end close. - Reporting
Finance and accounting will want to run the P&L report, balance sheet report, trial balance report, and cash flow statement each month. Other specific operational reports may also be requested, for example, a specific segment P&L statement. - Lock period
After the revenue accounts, expense accounts, income summary, and dividend accounts are closed out, the period can be locked, which doesn’t allow any further financial transactions to occur for the period. For instance, if you’ve just closed the month of June, period 6, after it’s locked, no further entries are allo...
Table of contents
- Dear Reader
- Notes on Usage
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 Introduction to Consolidation
- 2 Group Reporting Architecture and Components
- 3 Master Data
- 4 Transaction Data
- 5 Currency Translation
- 6 Intercompany Elimination
- 7 Consolidation of Investments
- 8 Consolidation Entries
- 9 Matrix Consolidation
- 10 Financial Close
- 11 Consolidation Reporting
- 12 Conclusion
- The Authors
- Index
- Service Pages
- Legal Notes