
eBook - ePub
Evaluation of Solar Proposals
A Guide for Financial Institutions, Solar Developers and EPCs
This is a test
- 168 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Evaluation of Solar Proposals
A Guide for Financial Institutions, Solar Developers and EPCs
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
This handbook deals with the subject of how an individual can review and evaluate a detailed project report of a Solar PV power plant, which includes feasibility study of the site for installation, assessing of the techno - commercial feasibility, determining the financial viability of setting up a Solar PV Power Plant.
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Evaluation of Solar Proposals by Tanmay Bishnoi, Ronnie Khanna, Arvind Karandikar, Deepanker Bishnoi in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Education & Education General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1. Introduction to Rooftop Solar PV Sector in India
Unit 1.1 - Overview of Renewable Energy and Solar Sector in India
Unit 1.2 - Overview of Rooftop Solar Sector in India
Unit 1.3 - Overview of Rooftop Solar PV Technology
Unit 1.4 - Business Models for Rooftop Solar Deployment
UNIT 1.1: OVERVIEW OF RENEWABLE ENERGY AND SOLAR SECTOR IN INDIA
1.1.1 Renewable Energy Technologies
‘Renewable Energy’ means the grid quality electricity generated from renewable energy sources. ‘Renewable Energy Power Plants’ means the power plants other than the conventional power plants generating grid quality electricity from renewable energy sources. ‘Renewable Energy Sources’ means renewable sources such as solar, wind, small hydro, biomass, including its integration with combined cycle, biomass, bio fuel cogeneration, urban or municipal waste and other such sources as approved by the MNRE.
“Renewable Energy is derived from the natural processes that are replenished constantly. In its various forms, it derives directly from the sun, or from heat generated deep within the earth. Included in the definition is electricity and heat generated from solar, wind, ocean, hydropower, biomass, geothermal resources and biofuels and hydrogen derived from renewable resources.” (Source: International Energy Agency)

We can thus discuss about the following renewable energy sources that can provide us energy for sustaining our civilization:
Solar Energy
Solar Energy which is being received as heat and light can be converted into thermal energy and electricity. ‘Solar PV power’ means the Solar Photo Voltaic power project that uses sunlight for direct conversion into electricity through Photo Voltaic technology. ‘Solar Thermal power’ means the Solar Thermal power project that uses sunlight for direct conversion into electricity through Concentrated Solar Power technology based on either line focus.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is a term that includes all energy materials derived from biological sources, including wood wastes, agricultural residues, food industry wastes, sewage, municipal solid waste (MSW), and dedicated herbaceous or woody energy crops. ‘Biomass gasification’ means a process of incomplete combustion of biomass resulting in production of combustible gases consisting of a mixture of Carbon monoxide (CO), Hydrogen (H2) and traces of Methane (CH4), which is called producer gas.
Wind Energy
Energy harnessed from the velocity of wind is known as Wind Energy. Wind technologies convert the energy of moving air masses at the earth’s surface to rotating shaft power that can be directly used for mechanical energy needs (e.g., milling or water pumping) or converted to electric power in a generator. Two major types of turbines exist and are defined based on the axis of blade rotation: horizontal-axis (which currently dominate commercial markets) and vertical-axis turbines. Evaluating the quality of wind resource at a specific location is critical in determining the suitability of wind turbines.
Hydropower
Hydropower facilities exploit the kinetic energy in flowing or falling water to generate electricity. Conventional hydropower facilities use water from a river, stream, canal, or reservoir to continually produce electrical energy, and water releases from single-purpose reservoirs (i.e., dedicated to power production) can be quickly adjusted to match electricity loads.
Geothermal Energy
The energy harnessed from the stored thermal energy below the earth’s surface is known as geothermal energy. We can also use geothermal energy to make electricity. A geothermal power plant works by harnessing steam or hot water reservoirs underground; the heat is used to drive a generator to produce electricity.
Wave Energy
Wave energy is produced when electricity generators are placed on the surface of the ocean. The energy provided is most often used in desalination plants, power plants and water pumps. Energy output is determined by wave height, wave speed, wavelength, and water density.
With depleting fossil fuels in the background and their adverse impact on our environment, a number of technologies have been developed as alternative energy technologies that supplement our energy needs through renewable and environmentally friendly energy sources.
1.1.2 Solar Energy Technologies
As discussed above, the solar energy technologies can be classified into solar thermal energy technologies and solar photovoltaic energy technologies.
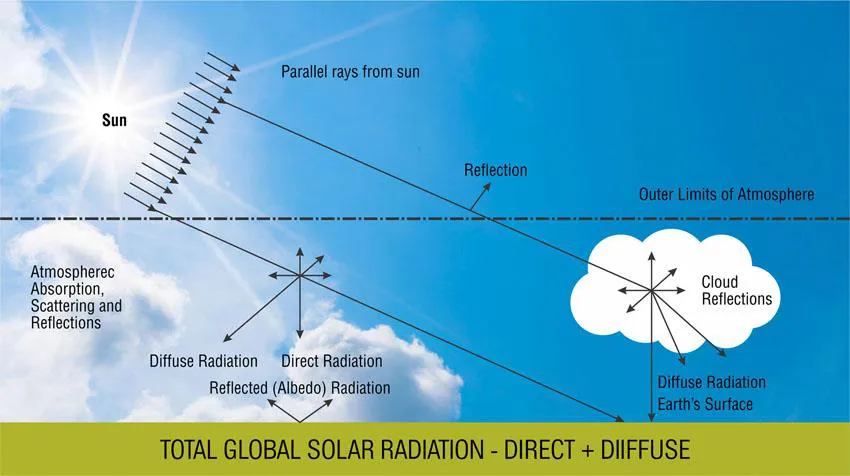
Solar Radiation
The main energy source of these technologies is solar radiation. The energy produced by the sun is emitted to the PV system primarily as radiation. The radiation that falls directly on the earth’s surface is termed as direct radiation. The fraction of solar radiation that is reflected back into space is known as the albedo of the atmosphere. And the radiation that passes through clouds and gases in the atmosphere is known as diffused radiation.
Movement of Sun Across the Sky
Solar radiation available at a particular location keeps changing both on a daily basis as well as annually. Hence the amount of solar radiation keeps fluctuating at any given time interval depending on the position of the sun and the location of the site. The three main cases of solar radiation depending on the position of the sun can be categorized with the help of the Solstices. The Southern Solstice occurs on 22nd December. The Equinox is when the sun is directly over the equator and occurs between 21st March and 23rd September and the Northern Solstice occurs on 22nd June.
Working of Solar Thermal System
The basic principle of solar thermal heating is to utilize the sun’s energy and convert it into heat. Solar thermal heating systems harvest solar energy through a collector which absorbs energy from the sun to heat a fluid. Direct systems circulate water through solar collectors where it is heated by the sun. The heated water is then stored in a tank, or used directly. These systems are preferred in climates where it rarely freezes. For low-temperature applicati...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Disclaimer
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Rooftop Solar PV Sector in India
- 2. Check the Site Feasibility of Solar PV Power Plant
- 3. Assess the Technology Feasibility if Solar PV Power Plant
- 4. Determine the Financial Viability of Solar PV Power Plant
- Annexure I: Sample Solar Project Simulation report