
eBook - ePub
Atlas of Retinal OCT E-Book
Optical Coherence Tomography
This is a test
- 400 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
- Features more than 1, 000 superb illustrations depicting the full spectrum of retinal diseases using OCT scans, supported by clinical photos and ancillary imaging technologies.
- Presents images as large as possible on the page with an abundance of arrows, pointers, and labels to guide you in pattern recognition and eliminate any uncertainty.
- Includes the latest high-resolution spectral domain OCT technology and new insights into OCT angiography technology to ensure you have the most up-to-date and highest quality examples available.
- Provides key feature points for each disorder giving you the need-to-know OCT essentials for quick comprehension and rapid reference.
- An excellent diagnostic companion to Handbook of Retinal OCT: Optical Coherence Tomography, by the same expert author team of Drs. Jay S. Duker, Nadia K. Waheed, and Darin R. Goldman.
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Atlas of Retinal OCT E-Book by Darin Goldman, Nadia K Waheed, Jay S. Duker in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Opthalmology & Optometry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Topic
MedicineSubtopic
Opthalmology & OptometryPart 1
Normal Optical Coherence Tomography
Section 1
Normal Optic Nerve
1.1
Normal Optic Nerve
Carlos A. Moreira Neto, Carl Rebhun
Spectral domain OCT (SD-OCT) devices have two scan patterns to analyze the optic nerve head (ONH): volume scans and line scans.
Volume Scans
Volume scans acquire a volumetric set of data, centered at the ONH. It delineates the optic disc margin and optic disc surface contour and is segmented to obtain the retinal nerve fiber boundaries. Each device has its own scanning protocol. The Cirrus HD-OCT identifies the center of the optic disc and creates a 3.46-mm circle on this location and calculates the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). The Heidelberg Spectralis creates a cylindrical volume with a diameter of 3.4 mm through and around the ONH (Duker, Waheed & Goldman 2014). The Optovue RTVue's protocol for the ONH consists of a grid pattern with circular and radial scans that acquires a 4- × 4-mm volume around the optic nerve. Because different machines use circles of different diameters around the center of the ONH, the measurement of RNFL between machines is not comparable (Duker et al. 2014).
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness (RNFL)
OCT devices calculate RNFL thickness as the distance between the internal limiting membrane and the outer aspect of the RNFL (Fig. 1).
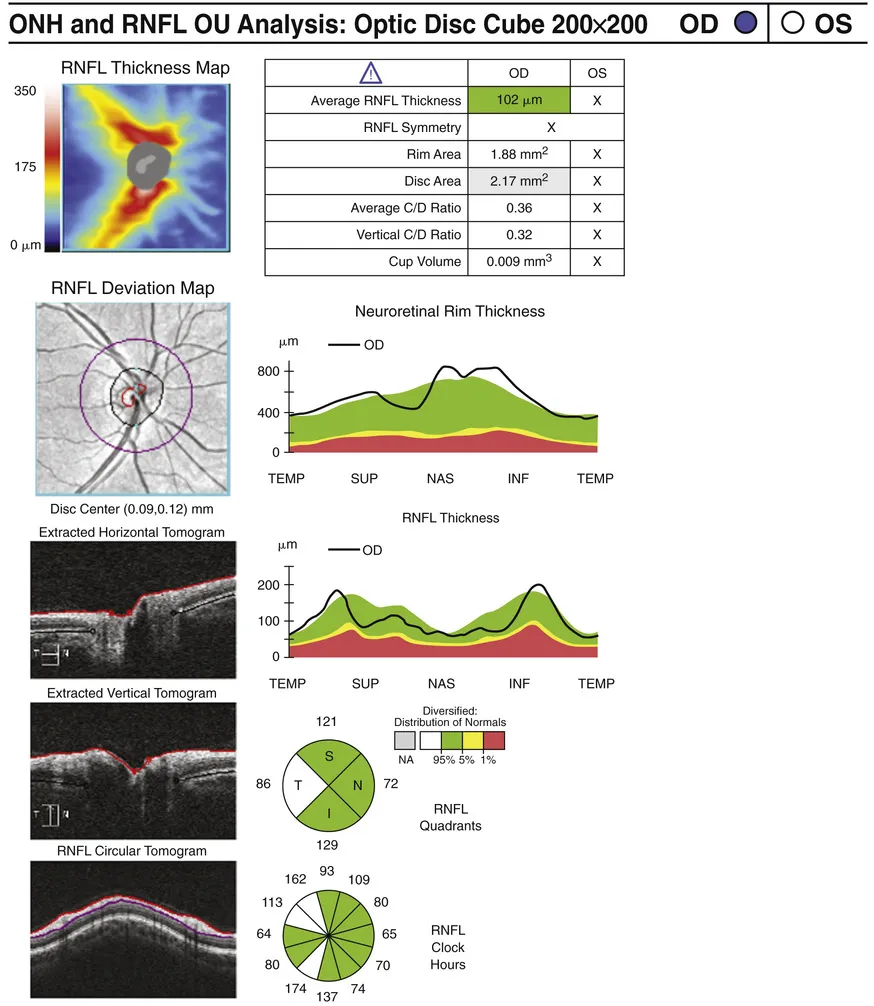
FIG. 1 Normal peripapillary RNFL, neuroretinal rim thickness, and disc area measurements using SD-OCT.
Ganglion Cell Complex
The ganglion cell complex (GCC) consists of the thickness of three inner retinal layers: the NFL, the ganglion cell layer, and the inner plexiform layer. The scan is centered at the fovea, and the software presents the results as a color-coded map, comparing to a normative database (Fig. 2).
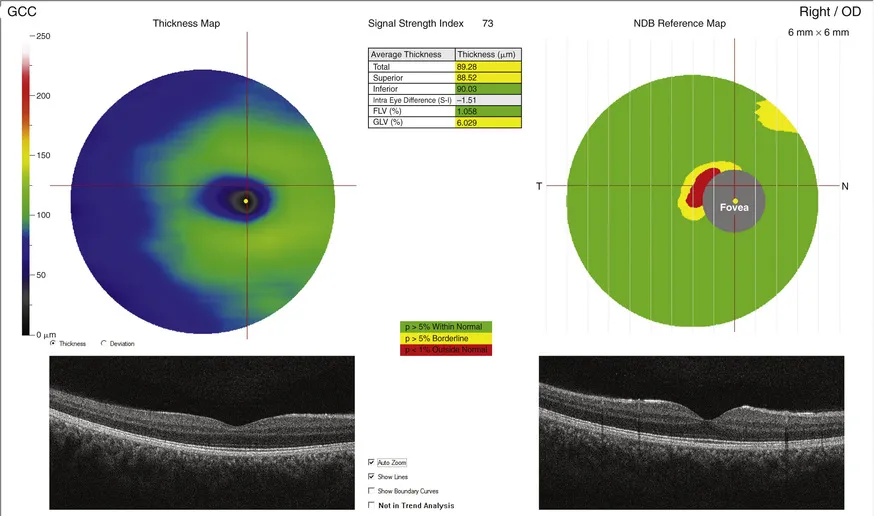
FIG. 2 Normal color-coded ganglion cell complex (GCC) thickness using SD-OCT.
Optic Nerve Morphology
SD-OCT devices also calculate optic nerve diameter, area, cup, and rim measurements (see Fig. 1). Each measurement varies according to age (Cavallotti et al. 2002) and ethnicity (Girkin 2008). According to Budenz et al. (2007), the mean RNFL thickness in a normal population is 100.1 µm. Thinner RNFL measurements were associated with older age. Caucasians had slightly thinner RNFL thickness than Hispanics or Asians. Persons with smaller optic disc areas also have thinner RNFL thickness.
Line Scans
Aiming to obtain a higher resolution visualization of structure and anatomic anomalies at the ONH, line scans provide a single or a series of high-resolution B-scans similar to the scans obtained in the macula (Fig. 3).
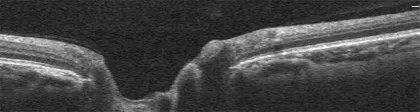
FIG. 3 Line scan of the ONH.
OC...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contributors
- Acknowledgments
- Dedications
- Part 1 Normal Optical Coherence Tomography
- Part 2 Isolated Macular Disorders
- Part 3 Vasoocclusive Disorders
- Part 4 Uveitis and Inflammatory Disorders
- Part 5 Retinal and Choroidal Tumors
- Part 6 Trauma
- Part 7 Inherited Retinal Degenerations
- Part 8 Vitreous Disorders
- Part 9 Miscellaneous Retinal Disorders
- Index