
Ioannis Tsiouras - The risk management according to the standard ISO 31000
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Ioannis Tsiouras - The risk management according to the standard ISO 31000
About This Book
The organizations, of any type and size, conducting their activities are faced to uncertainties, due, mainly, to the factors and influences that reside in the external as well as in the internal context. The uncertainties, therefore, are sources of risks, which have an effect on the achievement of the objectives and the impact could be significant to the business.
The organizations to deal with this situation try in any case to manage the risks by implementing approaches more or less known, sometimes in effective manner and sometimes not and often they rely on the technological solutions.
To address risks in systematic, effective and efficient manner, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has issued a set of standards for the risk. Among them, the main standard for the risk management is the ISO 31000.
The ISO 31000 Risk Management - Principles and guidelines is applicable to all types of organizations and to any size and type of goods. The ISO 31000 as a guideline provides a framework for risk management giving quick instructions without examining in detail the concepts and without providing operational support for the effective implementation of methodology proposed.
With a wide and significant lived experience in this field, the author proposes to managers, security managers and all those who want or are forced to make decisions in the presence of uncertainty, a practical method for risk management, also through practical case study. The author does not limit to generic interpretations, but develops approaches in detail through matrices and calculations of real risks and refers to case studies bringing examples in order to guide those involved in managing any form of risk in a systematic, transparent and credible and in any scope and context.
The book provides an introduction to risk management, to risk governance and to the risk management process; provides an introduction on the concept of risk, risk factors, the level of risk and correlation between the elements involved in risk analysis. It illustrates also the importance of risk management in decision-making, the awareness to the risk management and the benefits that may obtained from risk management.
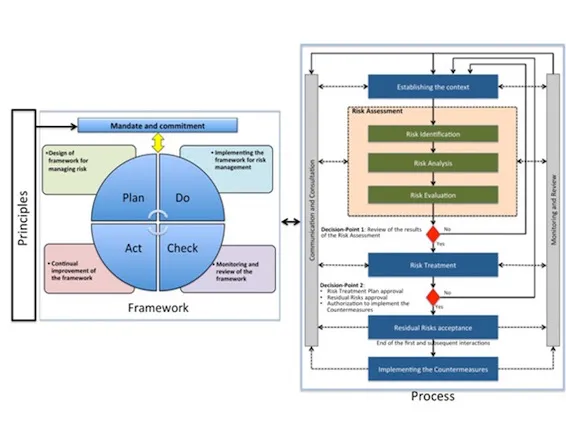
The author has paid special attention to the process of developing risk management flow and detailing all activities: establishing the context and the scope, risk assessment (identification, analysis and risk assessment), treatment plan with countermeasures to implement in order to reduce the risks, calculation of the residual risks, acceptance of the residual risks proposed, implementation of the countermeasures and monitoring and review.
The risk management process here developed is supported by a practical case study example useful to learn and to apply the methodology in all the contexts of the life of the organizations, but also in the activities of life.
Frequently asked questions
Information
- increase the likelihood of achieving objectives;
- encourage proactive management;
- be aware of the need to identify and treat risk throughout the organization;
- improve the identification of threats;
- comply with relevant legal and regulatory requirements and international as well as the requirements of the management systems standards (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22301, ISO/IEC 27001 and others);
- improve mandatory and voluntary reporting;
- improve governance;
- improve stakeholders confidence and trust;
- improve organizational resilience;
- an introduction to the risk management;
- the principles that should guide risk management;
- the framework for an effective risk management;
- the risk management process.
- establish the principles for the risk management,
- create and manage the necessary framework for deploying the principles through the processes of the organization, and
- make applicable and manage effectively the process of risk management.
- have different aspects, such as economic/financial, health, safety, environmental protection, information security, etc.;
- be applied at different levels: strategic, organization-wide, project, product and process);
- be expressed as the desired results, as a goal or as a criterion; They can be express...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title and rights
- The author
- Dedication
- Foreword
- Index
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Risk governance
- 3. Risk
- 4. Risk management and decision-making
- 5. Risk management principles
- 6. Risk management framework
- 7. Risk management process
- 8. Risk management process - Case Study
- 9. Bibliography
- 10. Appendix A - Tools and techniques for risk management