
This is a test
- 440 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
Dilemma Management is a harsh work for the harsh and changing times in the UK. This book has been written to challenge the reader, maybe even to disconcert him or her.
Tony Morden makes absolutely no apology for questioning outdated professional wisdoms or established paradigms, arguing that a large upward step change is urgently needed in professional mindset and competence in this country, and especially in a post-Coronavirus era.
Tony defines and describes the process of dilemma management and illustrates this process with a variety of case studies from business, politics, healthcare, procurement, security, sport, and more generally from the taxpayer-funded public sector.
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Dilemma Management by Tony Morden in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Commerce & Assurance. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Part One
What are Dilemmas, and Why Manage Them
Figure 2
Chapter One
Management Dilemmas Defined
The Oxford English Dictionary (OED) defines a Dilemma as ‘a form of argument involving an adversary in a choice between two (or … more) alternatives, both equally unfavourable to him; … a choice between two (or … several) alternatives which are equally unfavourable; also a position of doubt or perplexity’.
A MANAGEMENT DILEMMA DEFINED
A Management Dilemma is defined here as a set of circumstances in which a choice may have to be made, or instead must be made by a responsible person or persons between decision alternatives that are at the same time any or all of:




and in which:


DILEMMA CAUSES
There are likely to be two or more variables which must be taken as determinants of diagnosis, policy choice, decision or action; but at the same time:




and which will (i) act as drivers of the choice of options or objectives from which diagnoses, decision choices or modes of implementation may have to be made; but (ii) to which the relevant stakeholders may be more or less attached in their scale of priorities; and (iii) whose necessary identification or solution may be associated with varying perceptions of:





The causes of Management Dilemmas are analysed in more detail in Parts Two and Three of this Book.
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF MANAGEMENT DILEMMAS
Management Dilemmas will be significant where:




The significance of Management Dilemmas is analysed in more detail in Chapter 3 of this Book.
MAPPING A DILEMMA
A dilemma may be conceptualised and shown as a continuum between two polar extremes. The decision options that comprise the dilemma may then be mapped at various points between these extremes. For the specific purposes of this chapter the extent of the dilemma might be shown as more negative on the left and more positive on the right, as shown in Figure 3.
The more that the contents of the dilemma continuum can be described and the more that in this case:


the more likely it may be that effective decisions may be made and the dilemma resolved. This process is described in Part Four of this Book.
CASE EXAMPLE
Motorists take photos and videos at the wheel – an RAC survey showed an alarming increase in the number of UK motorists illegally using mobile phones whilst driving. One third of all drivers admitted to one form or other of this potentially lethal practice, which is now described by the RAC as the biggest safety concern amongst other road users. The causes of this increase included:



The immoral and anti-social practice of using a mobile phone whilst driving was described by the UK’s Department for Transport as a contributory factor in 492 accidents during 2014. Of these, 21 were fatal and 84 were classed as serious. One senior police officer commented of the dilemma revealed by the survey that people needed to start taking proper personal responsibility for their behaviour behind the wheel, and to exert strong social pressure on family, friends and colleagues who childishly and complacently put others at serious risk by persisting in the use of their mobile phones whilst driving.
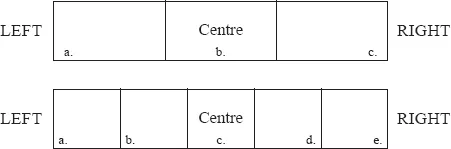
Figure 3
Mapping a Dilemma
Mapping a Dilemma
Chapter Two
Some Real-World Management Dilemmas
This chapter contains an illustrative selection of real-world Management Dilemmas, for instance as evident at the time of writing this Book.
THE PETER PRINCIPLE (I)
The Peter Principle, described by Laurence Peter, relies on a perception that any process that seems to work effectively now may be used in progressively more challenging applications until (eventually) it fails. People may use what has always worked for them before, until they discover (for instance as a result of professional complacency, inertia, laziness, an outdated knowledge/ competency base, or even bad luck / serendipity) that the approach is no longer appropriate or viable in the present circumstances. That is, the...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Contents
- Preface: What This Book is About
- Introduction: The Logic for This Book
- Part One – What Are Dilemmas and Why Manage Them?
- Part Two – Some Dilemma Sources (I): Big Pictures, People And Culture
- Part Three – Some Dilemma Sources (II): Time, Finance, Security, And Risk
- Part Four – A Dilemma Management Process
- Part Five – Endgame: Some Final Dilemma Management Issues
- And Finally
- Index
- Copyright