
- 408 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Machine Learning in Biotechnology and Life Sciences
About this book
Explore all the tools and templates needed for data scientists to drive success in their biotechnology careers with this comprehensive guideKey Features• Learn the applications of machine learning in biotechnology and life science sectors• Discover exciting real-world applications of deep learning and natural language processing• Understand the general process of deploying models to cloud platforms such as AWS and GCPBook DescriptionThe booming fields of biotechnology and life sciences have seen drastic changes over the last few years. With competition growing in every corner, companies around the globe are looking to data-driven methods such as machine learning to optimize processes and reduce costs. This book helps lab scientists, engineers, and managers to develop a data scientist's mindset by taking a hands-on approach to learning about the applications of machine learning to increase productivity and efficiency in no time.You'll start with a crash course in Python, SQL, and data science to develop and tune sophisticated models from scratch to automate processes and make predictions in the biotechnology and life sciences domain. As you advance, the book covers a number of advanced techniques in machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing using real-world data.By the end of this machine learning book, you'll be able to build and deploy your own machine learning models to automate processes and make predictions using AWS and GCP.What you will learn• Get started with Python programming and Structured Query Language (SQL)• Develop a machine learning predictive model from scratch using Python• Fine-tune deep learning models to optimize their performance for various tasks• Find out how to deploy, evaluate, and monitor a model in the cloud• Understand how to apply advanced techniques to real-world data• Discover how to use key deep learning methods such as LSTMs and transformersWho this book is forThis book is for data scientists and scientific professionals looking to transcend to the biotechnology domain. Scientific professionals who are already established within the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors will find this book useful. A basic understanding of Python programming and beginner-level background in data science conjunction is needed to get the most out of this book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Section 1: Getting Started with Data
- Chapter 1, Introducing Machine Learning for Biotechnology
- Chapter 2, Introducing Python and the Command Line
- Chapter 3, Getting Started with SQL and Relational Databases
- Chapter 4, Visualizing Data with Python
Chapter 1: Introducing Machine Learning for Biotechnology
- Understanding the biotechnology field
- Combining biotechnology and machine learning
- Exploring machine learning software
Understanding the biotechnology field
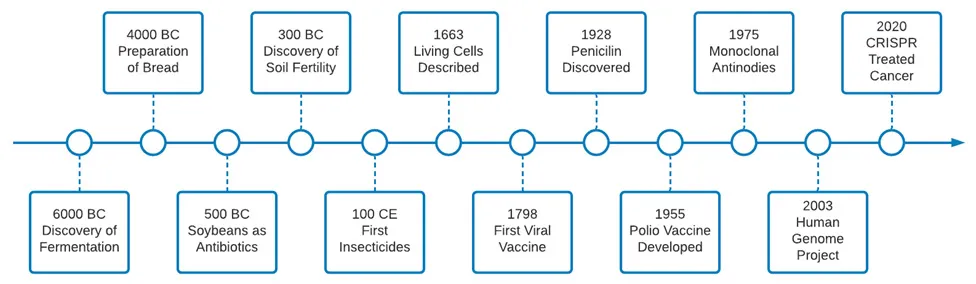

Combining biotechnology and machine learning
- Science and Innovation: All things related to the research and development of products.
- Business and Operations: All things related to processes that bring products to market.
- Patients and Human Health: All things related to patient health and consumers.
Table of contents
- Machine Learning in Biotechnology and Life Sciences
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1: Getting Started with Data
- Chapter 1: Introducing Machine Learning for Biotechnology
- Chapter 2: Introducing Python and the Command Line
- Chapter 3: Getting Started with SQL and Relational Databases
- Chapter 4: Visualizing Data with Python
- Section 2: Developing and Training Models
- Chapter 5: Understanding Machine Learning
- Chapter 6: Unsupervised Machine Learning
- Chapter 7: Supervised Machine Learning
- Chapter 8: Understanding Deep Learning
- Chapter 9: Natural Language Processing
- Chapter 10: Exploring Time Series Analysis
- Section 3: Deploying Models to Users
- Chapter 11: Deploying Models with Flask Applications
- Chapter 12: Deploying Applications to the Cloud
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app