
- 360 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This book is an introduction to nonlinear programming. It deals with the theoretical foundations and solution methods, beginning with the classical procedures and reaching up to "modern" methods like trust region methods or procedures for nonlinear and global optimization. A comprehensive bibliography including diverse web sites with information about nonlinear programming, in particular software, is presented. Without sacrificing the necessary mathematical rigor, excessive formalisms are avoided. Several examples, exercises with detailed solutions, and applications are provided, making the text adequate for individual studies.
The book is written for students from the fields of applied mathematics, engineering, economy, and computation.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Introduction
1.1 The model
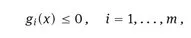

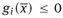
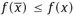
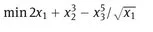
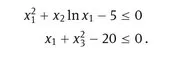
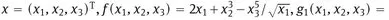
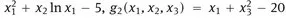
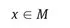
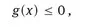
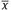
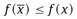
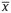
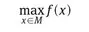
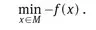
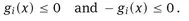
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Table of Contents
- Notations
- 1 Introduction
- Part I: Theoretical foundations
- Part II: Solution methods
- Appendix: Solutions of exercises
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app