
eBook - ePub
Saliva: Secretion and Functions
- 166 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Saliva: Secretion and Functions
About this book
Health professionals are more and more aware of the importance of saliva for oral health and well-being. As saliva secretion is steadily compromised with advancing age, it becomes a factor of concern in societies with an aging population, especially with a growing number of people who keep their own teeth. The numerous functions of saliva, like antimicrobial activity, lubrication, wound healing and its role in taste experience are only truly recognized when saliva secretion is hampered. In medical diagnostics, saliva shows its value as a safe and economical alternative to blood. This publication provides a comprehensive overview of the latest developments in salivary research by some of the world's leading experts in the field. Chapters deal with various aspects: anatomy and physiology, e.g. regeneration of salivary glands, saliva functions, e.g. its protective and rheological properties, and diagnostics and disorders, e.g. xerostomia and hypersalivation. This book is not only recommended to basic scientists working in the field of oral biology, but also to dental students, dentists and health professionals who want to know more about one of the most underestimated bodily fluids.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Diagnostics and Disorders
Ligtenberg AJM, Veerman ECI (eds): Saliva: Secretion and Functions.
Monogr Oral Sci. Basel, Karger, 2014, vol 24, pp 88-98 (DOI: 10.1159/000358791)
Monogr Oral Sci. Basel, Karger, 2014, vol 24, pp 88-98 (DOI: 10.1159/000358791)
______________________
Saliva Diagnostics: Utilizing Oral Fluids to Determine Health Status
Christopher A. Schafera · Jason J. Schaferb· Maha Yakoba · Patricia Limaa · Paulo Camargoa · David T.W. Wonga
aUCLA Center for Oral/Head and Neck Oncology Research, School of Dentistry, UCLA, Los Angeles, Calif., and bDepartment of Pharmacy Practice, Jefferson School of Pharmacy, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pa., USA
______________________
Abstract
Imagine a time where your health status could be available to you without the pain, discomfort and inconvenience of a physical examination. Distant vision of an inconceivable future or impending reality with potentially immeasurable impact? Recent advancements in the field of molecular diagnostics indicate this is not only possible, but closer than we think. Novel discoveries and substantial advancements have revealed that saliva may contain real-time information describing our overall physiological condition. Researchers are now reporting that, like blood and tissue biopsies, oral fluids could be a source of biochemical data capable of detecting certain diseases. What is even more intriguing is that this phenomenon not only applies to local disorders like oral cancer and Sjögren's syndrome, but distant pathologies like autoimmune, cardiovascular and metabolic diseases as well as viral/bacterial infections and even some cancers. These revelations have provided a foundation for the burgeoning field of salivary diagnostics and hence spurred the onset of investigations poised at deciphering the salivary milieu. This paper overviews salivary diagnostics from biomarker development to the multitude of techniques utilized in identifying saliva-based molecular indicators of disease. In doing so, we present oral fluids as an easily accessible noninvasive alternative to traditional diagnostic avenues and not just an essential component of the digestive process. Determining saliva as a credible means of evaluating health status represents a considerable leap forward in health care, one that could lead to enormous translational advantages and significant clinical opportunities.
© 2014 S. Karger AG, Basel
Molecular diagnostics is defined as the application of molecular biology techniques for the purpose of evaluating tissues and biofluids to diagnose, monitor and prognosticate disease. These techniques precisely target molecular and/or microbial entities (also called biomarkers) commonly considered as signs of specific pathologies. Identifying biomarkers at early stages of disease can expedite therapeutic interventions leading to increased survival rates, decreased suffering and low likelihood of recurrence. Current diagnostic assessments require the procurement of testing materials obtained by blood draws, biopsies or other painfully invasive procedures resulting in substantial patient discomfort and augmented health care costs. Furthermore, many disorders do not warrant diagnostic evaluations as a great deal are asymptomatic and typically remain undiagnosed until they have reached an advanced stage when damage is irreversible and treatment futile. Altogether, these statements point to the necessity for noninvasive modalities capable of distinguishing biomarkers indicative of early stage pathogenesis.
To that end, one common ambition among clinicians and basic scientists is to create a credible manner of painless predictive diagnostics. One approach is the exploration of biofluids containing analytes sensitive to our overall health status.
While primarily considered an indispensable element of early digestion, saliva is actually a heterogeneous biofluid comprised of numerous molecules along with a diverse range of microbes. Interestingly, in recent years it has become evident that these very salivary constituents become detectably altered in response to certain disease states. Even so, what is most impressive is that salivary biomarkers not only arise in correlation with oral disorders, but also those of distal tissues and organs. This suggests that oral fluids may represent a substantial reservoir of molecular and microbial information capable of communicating the onset or presence of disease throughout the body.
In consideration, a growing number of studies are focused on elucidating and developing saliva-based biomarkers indicative of both local and systemic diseases. Establishing these markers as credible could usher in a new era of patient evaluation by permitting individuals to avoid the anxiety of traditional diagnostic procedures. The potential impact of utilizing saliva as a means to ascertain the existence or likelihood of disease could markedly advance medicine, as we know it.
We begin our discussion by exploring bio-marker development and how disease-specific analytes are scrutinized prior to widespread acceptance and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval. Next, we delve into the vast arena of molecular and microbial analyses by describing a number of diagnostic foci. Termed ‘salivaomics’ these categories include: proteomics, epigenomics, metabolomics, immunomics, microbiome and transcriptomics. Highlighting each library as crucial to biomarker development, we review a selection of their respective biomarkers that lend credence to the continued pursuit of salivary diagnostics. Last we discuss evidence that details one possible mechanism responsible for the induction of systemic disease indicators in salivary secretions.
The discovery of discriminatory biomarkers in oral fluids epitomizes an almost incomparable breakthrough in clinical and translational science. Continuation in this area could credential saliva as an acceptable diagnostic medium, an end point with the potential to bring about a paradigm shift in the discipline of molecular diagnostics.
Biomarker Development
Challenges
In the past decade, the field of molecular diagnostics has made profound leaps forward in bio-marker discovery and the development of clinically applicable diagnostic techniques. However, definitive diagnoses can be difficult to achieve based solely on the detection of biomarkers and usually require affirmation by the employment of more traditional and often painful clinical procedures. These obstacles, among other limitations, challenge diagnosticians in their ongoing quest to establish reliable markers of disease. Table 1 lists a summary of the main issues confronting us along with the questions they pose.
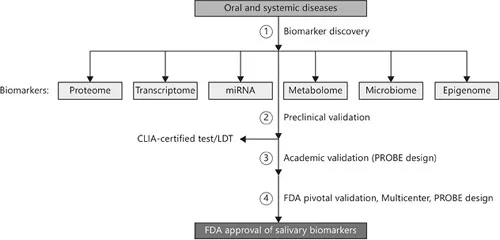
Fig. 1. Process of biomarker discovery through definitive validation and approval. Biomarkers of oral and systemic diseases are discovered using one or more of the ‘omics’ libraries. Verified biomarkers are subjected to increasing scrutiny and larger independent cohorts until they reach a pivotal multicenter validation. CLIA = Clinical laboratory improvement amendments; LDT = laboratory developed test.
Table 1. Main issues and questions
Challenges | Questions |
(1) Identifying molecular biomarkers of disease | Can we identify disease-specific molecules in biofluids? |
(2) Establishing noninvasive means of sample collection | Can we devise procedures to procure biofluids while minimizing patient discomfort? |
(3) Developing cost-effective platforms for disease detection | Can we create affordable, accurate and efficient modes of sample analysis? |
Process
The process of biomarker development is a difficult task with multiple levels of evaluation prior to definitive approval by the FDA (fig. 1). During the initial stages samples are analyzed using 1 or more of the 6 ‘omics’ libraries: proteome, transcriptome, immunome, metabolome, microbiome and epigenome. Each library contains a vast collection of information potentially useful in determining an individual's current state of health. Following discovery, verified biomarkers proceed through successive levels of validation using prospective randomized open blinded end point (PROBE) designed studies and independent cohorts [1]. FDA approval is achieved after substantial evaluations have been performed using ...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Front Matter
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Saliva Functions
- Diagnostics and Disorders
- Author Index
- Subject Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Saliva: Secretion and Functions by A. J. M. Ligtenberg,E. C. I. Veerman,A.J.M., Ligtenberg,E.C.I., Veerman, Adrian Lussi,Marilia A. R. Buzalaf,Adrian, Lussi,Marilia A.R., Buzalaf in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Dentistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.