
Hands-On Data Analysis with NumPy and pandas
Implement Python packages from data manipulation to processing
- 168 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Hands-On Data Analysis with NumPy and pandas
Implement Python packages from data manipulation to processing
About this book
Get to grips with the most popular Python packages that make data analysis possible
Key Features
- Explore the tools you need to become a data analyst
- Discover practical examples to help you grasp data processing concepts
- Walk through hierarchical indexing and grouping for data analysis
Book Description
Python, a multi-paradigm programming language, has become the language of choice for data scientists for visualization, data analysis, and machine learning.
Hands-On Data Analysis with NumPy and Pandas starts by guiding you in setting up the right environment for data analysis with Python, along with helping you install the correct Python distribution. In addition to this, you will work with the Jupyter notebook and set up a database. Once you have covered Jupyter, you will dig deep into Python's NumPy package, a powerful extension with advanced mathematical functions. You will then move on to creating NumPy arrays and employing different array methods and functions. You will explore Python's pandas extension which will help you get to grips with data mining and learn to subset your data. Last but not the least you will grasp how to manage your datasets by sorting and ranking them.
By the end of this book, you will have learned to index and group your data for sophisticated data analysis and manipulation.
What you will learn
- Understand how to install and manage Anaconda
- Read, sort, and map data using NumPy and pandas
- Find out how to create and slice data arrays using NumPy
- Discover how to subset your DataFrames using pandas
- Handle missing data in a pandas DataFrame
- Explore hierarchical indexing and plotting with pandas
Who this book is for
Hands-On Data Analysis with NumPy and Pandas is for you if you are a Python developer and want to take your first steps into the world of data analysis. No previous experience of data analysis is required to enjoy this book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Operations on NumPy Arrays
Selecting elements explicitly

Slicing arrays with colons

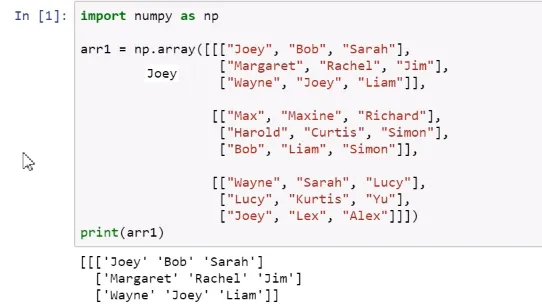

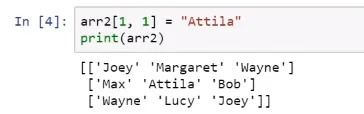

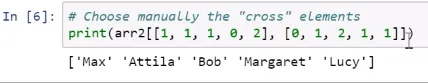
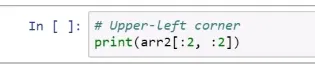
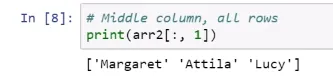

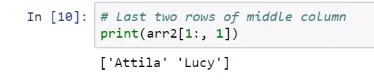
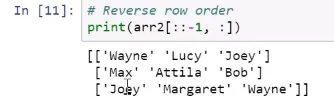
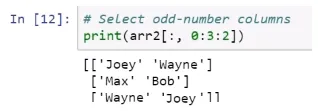
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Packt Upsell
- Contributors
- Preface
- Setting Up a Python Data Analysis Environment
- Diving into NumPY
- Operations on NumPy Arrays
- pandas are Fun! What is pandas?
- Arithmetic, Function Application, and Mapping with pandas
- Managing, Indexing, and Plotting
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app