![]() PART 1: SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
PART 1: SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT![]()
APPROACHES TO MANAGING SUSTAINABILITY AMONG
ENTERPRISES
GIL LAFUENTE, ANNA MARÍA
Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Barcelona, Av. Diagonal 690
Barcelona, Catalonia 08034, Spain
BARCELLOS PAULA, LUCIANO
IS Consulting, Lúcio Bittencourt Street, nº 109/509, Vila Santa Cecília, Volta Redonda,
Rio de Janeiro 27260-110, Brazil
The stakeholder theory posits that a firm’s ability to generate sustainable wealth over time, and thus its long-term value, is determined by its relations with its stakeholders. The challenge for the companies is to decide what actions and initiatives to continuing and the best way of handling them. Because of the complexity to managing sustainability is essential to address the analysis with an approach based on complex systems and models that help entrepreneurs in making decisions, especially in an uncertain environment. For these reasons, it is justified to analyze the sustainability using fuzzy logic algorithms. To complete the study, we present the contributions and conclusions of our investigation.
1. Introduction
In recent decades various changes have occurred in the context of business, such as technological innovations and regulatory policy changes, social trends and market development. These changes have altered the nature of relationships between companies and its stakeholders. The companies have turned from traditional business interactions with employees, customers, suppliers, investors and regulators to interact with larger groups, with local communities, workers in the purchasing chain, relatives of employees, civil society organizations, medium environment, among others. Another change relates to the topics discussed with interest groups, legal and contractual issues, such as marketing, industrial relations, choice of locations for plants, business planning and shopping, to emerging issues and new responsibilities, such as corruption, social exclusion, human rights, health risks, economic development, working conditions in the purchasing chain, environmental impact. Ultimately the way to make communication with stakeholders has also changed such as market research, corporate communications, advertising and broadcast media, to dialogue and cooperation, consultations, advisory panels, feedback online, call networks, forums and partnerships of multiple stakeholders. As changes have occurred in the business environment and nature in the relations with stakeholders, therefore the relationship of companies with interest groups have evolved. Initial experiences of relationships with interest groups responded to external pressures, limited to certain issues that generated conflict with stakeholders. Subsequently, the companies have demonstrated their potential to increase mutual understanding, manage risks and resolve conflicts more effectively. Currently, the relations with stakeholders enable companies to align their social, environmental and economic with its main strategy. This new context in the business underscores the complexity of acquiring the management of stakeholders in the companies with the expansion of emerging groups and emerging issues and new responsibilities. Together the company’s relationships with stakeholders get greater importance through dialogue and collaboration. Certainly this new reality allows us to consider how it can be the management of interest groups so as to enable a comprehensive strategic relationship for achieving sustainable competitiveness.
In this paper, we will focus our research on sustainability management among enterprises. Because of this complexity, it is essential to address the analysis with an approach based on complex systems and models that help entrepreneurs in making decisions, especially in an uncertain environment. For these reasons, it is justified to analyze the sustainability using fuzzy logic algorithms.
The fuzzy sets theory [27] is a mathematical theory in the field of multivalent logics. Its origin is in the work done by Professor Lotfi A. Zadeh and is the starting point for a mathematical theory currently expanding in all scientific disciplines and built with the entire rigor that enables the treatment of subjectivity and/or uncertainty [9]. At first, the fuzzy sets theory has been applied in the field of formal science, but in the last 45 years, researchers around the world have published many papers and studies with applications in various fields. It should be noted, the pioneering and important contribution to science of the teachers Kaufmann and Gil Aluja who published the first book in the world dedicated exclusively to the processing of financial and management problems with the mathematics of uncertainty [2]. It included very diverse studies (investments, renewal of equipment, inventory management and product distribution). Currently, the use of fuzzy logic takes place in practically every field of science studies. It is in the business management, engineering, biology, medicine, geology, sociology, phonetics, and even in music, among others. Every problem is located in the area of uncertainty is likely to be treated by the theory of fuzzy subsets and that as time passes it is becoming increasingly feasible to introduce in formal schemes, mechanisms of thinking, such as sensations and numeric views.
To complete the study, we present the contributions and conclusions of our investigation. We believe that our contribution will serve to support future research on the application of algorithms to business sustainability, a field that has been only scarcely investigated.
2. The challenges in relations with stakeholders
According to Freeman [32], the stakeholders of a company are by definition any group or individual who can affect or is affected by the achievement of the objectives of the revision l. Since Freeman’s research, other authors have revision the concept of stakeholders [8, 7, 16, 30, 18, 10, 12, 39, 33, 17, 29, 35, and 37] with the publication of several books and articles on the subject.
There is a generic list of stakeholders from business, even for a single company, because they change over time [33]. The groups and individuals affected and affecting businesses rely on the industry, business, geographic location and subject matter. The new business strategies and contextual changes often determine a new set of stakeholders. For Elkington [14] through the constructive engagement of stakeholders, companies can increase external confidence in its intentions and activities, helping to improve corporate reputation and catalyze the diffusion of more sustainable practices in the enterprise system in general.
According to Post et al. [17], stakeholders of a firm are individuals and groups who contribute, voluntarily or involuntarily, to its capacity and wealth-creation activities, and therefore they are potential beneficiaries and/or risk bearers. Interest groups cover a wide variety of stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, customers, local communities, government, NGOs, suppliers. For Freeman and Evan [31], stakeholder theory predicts that sustainability should have a positive impact on financial results because companies benefit from ‘addressing and balancing the claims’of the many key stakeholders. Moreover, “the continuing failure to address the concerns and expectations of the groups, ultimately, reduces the confidence of investors in company shares, which affect their cost of funds (weighted average cost of capital) and therefore, opportunities for profit” [38].
To do sustainable business, companies must have good knowledge of all actors with influence in its sphere of activity. This identification of stakeholders is the first step. Once organisations have become aware of the various publics that interact with them, it is important to categorize in terms of expectations, problems, geographical areas, its impact on business activity and vice versa. The result of the identification and segmentation is called mapping stakeholders. To do a map involves identifying stakeholder expectations and influence of each. This helps establish priorities that meet, while allowing an overall view of other possible interactions between groups. Subsequently, companies must establish a hierarchy among them, in order to determine the relevance of their modes of interaction.
According to the stakeholder engagement manual [40], engaging with all stakeholders or on all issues is neither possible nor desirable. This would go beyond any available resources, and at the same time make it very difficult to adequately respond to stakeholders, leading to frustration. Therefore, the enterprise should try and prioritise its stakeholders and issues to ensure that time, resources and expectations are well managed. Another item relevant to the topic relates to compliance with the Guidelines for Sustainability Reporting [13]. According to the GRI in subsection 4.15, the revision l must submit the procedure for defining its stakeholder groups and for the determination of the groups involved and those not.
3. Approaches to managing sustainability among enterprises
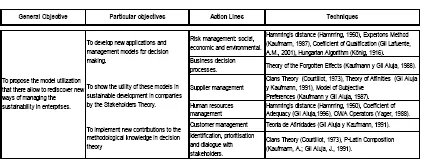
The main aim of sustainability is to reconcile economic growth with social care environment and environmental protection. However, in an uncertain environment, enterprises need tools that help both decision making and the definition of their strategies. Therefore, with this new reality is necessary to raise the use of models to rediscover new ways to manage not only businesses but also their objectives, strategies and policies to simultaneously support the prosperity of enterprise and promote a sustainable quality of life at the planetary level. To do this, we must rely on flexible models that enable the hybrid treatment of objective and subjective estimates and allow estimates of the future conduct of companies, institutions and social actors, thereby offering a redesign of economic relations that affect all entities involved. In figure 1, we propose an approach to managing sustainability among enterprises.
Figure 1. Approaches to managing sustainability among enterprises
The application of Hamming distance [36] to sustainability in business is an innovation to be used in the selection process for proposals and sustainable management of human resources and enables decision-making considering the subjective weighting priority on the criteria of sustainability in business [21]. In the case of Experton Method [6], this algorithm can facilitate decision making by obtaining qualitative data from the dialogue with different stakeholders. This is a useful tool to be used in the processes of aggregation and unification of views or differing expectations among its stakeholders [24]. The model also allows knowing the distribution function levels characteristic of belonging to the aggregate values. The Model of Subjective Preferences [5] can be applied in the ordering process by facilitating decision making in various contexts in companies, such as the revision l of stakeholders [26]. On the other hand, OWA operators [34] can facilitate decision making in the field of corporate sustainability in general and particular aspects of it such as environmental management, economic, social and human resources, among many other approaches [26].
Another contribution concerns Hungarian Algorithm [11] that can be used in decision-making processes in implementing eco-efficiency practices. It is also a model for the resolution, among others, the important problem of mapping tools that help the scope of eco-efficiency in business [19]. The Clans Theory [28] as a grouping algorithm can facilitate decision making by obtaining qualitative data from a dialogue with managers or specialists on a certain subject and used in the process of identifying stakeholders [20]. The results with the application of the Theory of the Forgotten Effects [3] provides a model that allows sequential nature of causality introduced to the study of sustainability in the company, be a useful tool for use in processes targeting [23]. In the case of P-Latin Composition [4], this technique can be applied in ordering processes and provides a useful model in making decisions, for example, the revision l of stakeholders considering criteria for sustainability in business.
On the other hand, the Theory of Affinities [1] can facilitate decision making by obtaining qualitative data from a dialogue with managers or specialists on a particular topic. The model can be used in the process of identifying stakeholders and serves to establish the level of relationship between different stakeholders and obtain affinities [22, 25]. Using the Adequacy Ratio [15] can facilitate decision making by obtaining qualitative data from the dialogue with different stakeholders and can be used in the selection process for proposals and sustainable management human resources in enterprises [26] and institutions, among others. And the Qualification Ratio [9] can be used in the stakeholders management and facilitate decision making in different areas of the company as human resources, finance and purchasing.
4. Conclusions
The study about the stakeholder shows that compared with the changes we are living is essential to find models that will help employers in making decisions, especially in an uncertain environment. Because of the importance and complexity that is the sustainability management for companies in our research we try to analyse these complex systems using fuzzy logic.
First we look at how changes in the business environment and nature in relations with stakeholders also have influen...