
Building Service-oriented Government: Lessons, Challenges And Prospects
Lessons, Challenges and Prospects
- 188 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Building Service-oriented Government: Lessons, Challenges And Prospects
Lessons, Challenges and Prospects
About This Book
Providing quality public service is one of the essential functions of a government. In the turbulent time, however, governments worldwide are experiencing a variety of unprecedented challenges to meet citizens' increasing demands and expectations. In China, building a service-oriented government and a harmonious society is central to the 12th Five-Year Plan and challenges the governance philosophies, capacities and competencies of Chinese government at every level. Researchers of Nanyang Centre for Public Administration (NCPA) at Nanyang Technological University systematically examined the concept of service-oriented government in the context of China and developed an assessment scheme to evaluate the performance of building service-oriented government in Chinese cities. Under the auspices of the Lien Foundation in Singapore, based on the assessment scheme, they conducted large-scale telephone surveys of citizens and businesses in 32 major Chinese cities in 2011. This book presents their findings and empirical studies on public service performance, citizen satisfaction, political trust and government transparency based on the data collected from the 2011 Lien project. Moreover, it also includes selected papers presented at the 2012 Lien International Conference on Public Administration in Singapore. Contributed by scholars from Mainland China, the US, Hong Kong and Singapore, these papers discuss various important issues related with building a service-oriented government including public ethical values, the roles of NGO, social accountability, urban integration, performance measurement and emotional labor in public service.
Contents:
- Evaluating Public Service Performance in Urban China: Findings From the 2011 Lien Chinese Cities Service-Oriented Government Project (WU Wei, YU Wenxuan, LIN Tingjin, WANG Jun and TAM Waikeung)
- Public Ethical Values and Service-Oriented Government (Kuotsai Tom LIOU)
- The Role of Emotional Labor in Public Service (Meredith A NEWMAN)
- Irrationality, Bricolage, Quality and Performance Measurement: Unpacking the Conundrum in a Comparative East–West Context (Paul HIGGINS)
- Social Accountability for Public Service in Higher Education: A Text Analysis of Chinese Research Universities' Undergraduate Teaching-Learning Quality Annual Reports (TIAN Linghui and XIONG Qingnian)
- Integrated Development of Metropolitan Governance and Public Service: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Region (YE Lin)
- The Role of NGOs in Maintaining Social Stability in China — Based on the Perspective of Public Security Service Delivery (HAN Lin)
- Political Trust, Public Service Performance and Government Transparency in China (YU Wenxuan)
- Explaining Citizens' Satisfaction With Public Service Quality in Chinese Cities 2010: Citizen-Level Predictors vs. City-Level Predictors (LIN Tingjin)
- Public Satisfaction Survey and Its Analysis on Chinese Cities Public Education Service — An Empirical Study Based on 2010 Lien Chinese Cities Public Service Quality Evaluation Survey Data (WANG Jun and WU Wei)
Readership: Students and researchers in the fields of policy studies and China studies.
Frequently asked questions
Information
Chapter 1
Evaluating Public Service Performance in Urban China: Findings From the 2011 Lien Chinese Cities Service-Oriented Government Project
1.1. Public Service, Service-Oriented Government and Evaluation

1.2. 2011 Lien Chinese Cities Service-Oriented Government Index
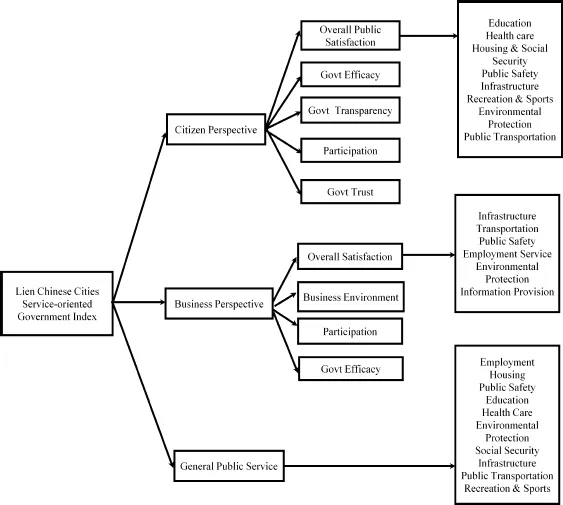
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Contents
- Chapter 1. Evaluating Public Service Performance in Urban China: Findings From the 2011 Lien Chinese Cities Service-Oriented Government Project
- Chapter 2. Public Ethical Values and Service-Oriented Government
- Chapter 3. The Role of Emotional Labor in Public Service
- Chapter 4. Irrationality, Bricolage, Quality and Performance Measurement: Unpacking the Conundrum in a Comparative East–West Context
- Chapter 5. Social Accountability for Public Service in Higher Education: A Text Analysis of Chinese Research Universities’ Undergraduate Teaching-Learning Quality Annual Reports
- Chapter 6. Integrated Development of Metropolitan Governance and Public Service: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Region
- Chapter 7. The Role of NGOs in Maintaining Social Stability in China — Based on the Perspective of Public Security Service Delivery
- Chapter 8. Political Trust, Public Service Performance and Government Transparency in China
- Chapter 9. Explaining Citizens’ Satisfaction With Public Service Quality in Chinese Cities 2010: Citizen-Level Predictors vs. City-Level Predictors
- Chapter 10. Public Satisfaction Survey and Its Analysis on Chinese Cities Public Education Service — An Empirical Study Based on 2010 Lien Chinese Cities Public Service Quality Evaluation Survey Data
- Index