
- 312 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Ordinary Differential Equations with Applications
About this book
During the past three decades, the development of nonlinear analysis, dynamical systems and their applications to science and engineering has stimulated renewed enthusiasm for the theory of Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE).
This useful book, which is based on the lecture notes of a well-received graduate course, emphasizes both theory and applications, taking numerous examples from physics and biology to illustrate the application of ODE theory and techniques.
Written in a straightforward and easily accessible style, this volume presents dynamical systems in the spirit of nonlinear analysis to readers at a graduate level and serves both as a textbook and as a valuable resource for researchers.
This new edition contains corrections and suggestions from the various readers and users. A new chapter on Monotone Dynamical Systems is added to take into account the new developments in ordinary differential equations and dynamical systems.
Contents:
- Introduction
- Fundamental Theory
- Linear Systems
- Stability of Nonlinear Systems
- Method of Lyapunov Functions
- Two-Dimensional Systems
- Second Order Linear Equations
- The Index Theory and Brouwer Degree
- Perturbation Methods
- Introduction to Monotone Dynamical Systems
Readership: Graduate students in mathematics, applied mathematics, and engineering.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
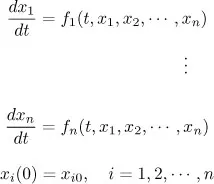

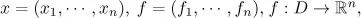
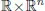
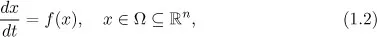
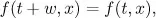

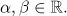


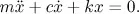
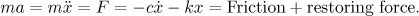
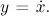
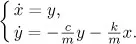
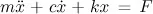
Table of contents
- Front Cover
- Half Title
- Series Title
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface to the First Edition
- Preface to the Second Edition
- Contents
- 1. INTRODUCTION
- 2. FUNDAMENTAL THEORY
- 3. LINEAR SYSTEMS
- 4. STABILITY OF NONLINEAR SYSTEMS
- 5. METHOD OF LYAPUNOV FUNCTIONS
- 6. TWO-DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS
- 7. SECOND ORDER LINEAR EQUATIONS
- 8. THE INDEX THEORY AND BROUWER DEGREE
- 9. PERTURBATION METHODS
- 10. INTRODUCTION TO MONOTONE DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app