
- 168 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Macroscopic Electrodynamics Instructor's Solutions Guide
About this book
This instructor's solutions guide accompanies our introductory graduate electrodynamics textbook, "Macroscopic Electrodynamics". We emphasize that this is a guide and not a step-by-step exposition for the 391 problems furnished in the text. Helpful indications of starting points and methods are given, as well as enough intermediate steps (and occasional final results) that a knowledgeable instructor can readily fill in the gaps. This approach is designed to provide the instructor with a powerful and time-saving teaching aid for introducing students to this beautiful and wide-ranging subject.
Request Inspection Copy
This instructor's solutions guide accompanies our introductory graduate electrodynamics textbook, "Macroscopic Electrodynamics". We emphasize that this is a guide and not a step-by-step exposition for the 391 problems furnished in the text. Helpful indications of starting points and methods are given, as well as enough intermediate steps (and occasional final results) that a knowledgeable instructor can readily fill in the gaps. This approach is designed to provide the instructor with a powerful and time-saving teaching aid for introducing students to this beautiful and wide-ranging subject.
Request Inspection Copy
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction and Perspectives
Guide to Exercise 1.1.1
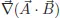
Guide to Exercise 1.1.2
Guide to Exercise 1.1.3

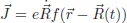
Guide to Exercise 1.4.1
Guide to Exercise 1.4.2
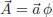

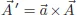

Guide to Exercise 1.4.3
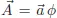

Guide to Exercise 1.5.1
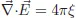
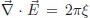
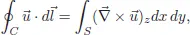
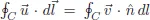
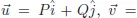
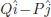
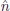
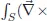
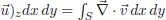
Chapter 2
Introduction to Electrostatics
Guide to Exercise 2.1.1
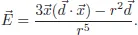
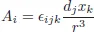
Table of contents
- Cover page
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Preface
- Contents
- 1. Introduction and Perspectives
- 2. Introduction to Electrostatics
- 3. Boundary Value Problems in Electrostatics
- 4. Electrostatics in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates
- 5. Multipoles, Electrostatics of Macroscopic Media, Dielectrics
- 6. Magnetostatics
- 7. Time Varying Fields I
- 8. Time Varying Fields II
- 9. Plane Electromagnetic Waves and Propagation in Matter
- 10. Waveguides and Resonant Cavities
- 11. Radiation of Systems and Point Paricles
- 12. Scattering and Diffraction
- 13. Relativistic Formulations of Electrodynamics
- 14. Special Topics
- 15. Appendix
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app