
Notes on the Binomial Transform
Theory and Table with Appendix on Stirling Transform
- 208 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Notes on the Binomial Transform
Theory and Table with Appendix on Stirling Transform
About this book
-->
The binomial transform is a discrete transformation of one sequence into another with many interesting applications in combinatorics and analysis. This volume is helpful to researchers interested in enumerative combinatorics, special numbers, and classical analysis. A valuable reference, it can also be used as lecture notes for a course in binomial identities, binomial transforms and Euler series transformations. The binomial transform leads to various combinatorial and analytical identities involving binomial coefficients. In particular, we present here new binomial identities for Bernoulli, Fibonacci, and harmonic numbers. Many interesting identities can be written as binomial transforms and vice versa.
The volume consists of two parts. In the first part, we present the theory of the binomial transform for sequences with a sufficient prerequisite of classical numbers and polynomials. The first part provides theorems and tools which help to compute binomial transforms of different sequences and also to generate new binomial identities from the old. These theoretical tools (formulas and theorems) can also be used for summation of series and various numerical computations.
In the second part, we have compiled a list of binomial transform formulas for easy reference. In the Appendix, we present the definition of the Stirling sequence transform and a short table of transformation formulas.
--> Contents:
- Theory of the Binomial Transform:
- Introduction
- Prerequisite: Special Numbers and Polynomials
- Euler's Transformation for Series
- Melzak's Formula and Related Formulas
- Special Properties. Creating New Identities
- Binomial Transforms of Products
- Special Formulas and Power Series with Binomial Sums
- Table of Binomial Transforms:
- Assorted Binomial Formulas
- Identities Involving Harmonic Numbers
- Transforms of Binomial Coefficients
- Transforms of Special Numbers and Polynomials
- Transforms of Trigonometric and Hyperbolic Functions and Applications to Some Trigonometric Integrals
- Transforms of Some Special Functions
- Appendix:
- The Stirling Transform of Sequences
-->
--> Readership: Graduate and researchers in the areas of number theory, discrete mathematics, combinatorics, statistics working with applications using the binomial transform. -->
Keywords:Binomial Coefficients;Binomial Identities;Binomial Sums;Binomial Transform;Euler's Series Transformation;Discrete Mathematics;Finite Differences;Stirling Numbers of the First Kind;Stirling Numbers of the Second Kind;Stirling Transform;Special Numbers and Polynomials;Harmonic Numbers;Bernoulli Numbers;Fibonacci Numbers;Melzak's Formula;Exponential Polynomials;Geometric Polynomials;Laguerre Polynomials;Trigonometric IntegralsReview: Key Features:
- This is the first, long-overdue book on the subject. (At present, there are no competing books)
- The book provides interesting new material for researchers in discrete mathematics and will serve as a valuable reference for binomial identities, binomial transform formulas, and Euler series transformations
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
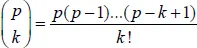
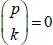

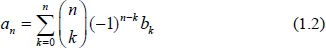
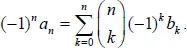
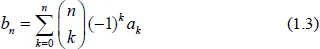
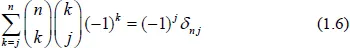
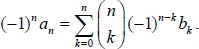
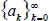
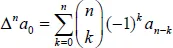
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Title
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Preface
- Contents
- Part 1. Theory of the Binomial Transform
- Part 2. Table of Binomial Transforms
- Appendix A The Stirling Transform of Sequences
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app