
eBook - ePub
Biosensors
Fundamentals and Applications
Chandra Mouli Pandey, Bansi Dhar Malhotra
This is a test
- 164 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Biosensors
Fundamentals and Applications
Chandra Mouli Pandey, Bansi Dhar Malhotra
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
This book focuses on the state-of-the-art of biosensor research and development for specialists and non-specialists. It introduces the fundamentals of the subject with relevant characteristics of transducer elements, as well as biochemical recognition molecules. This book is ideal for researchers of nanotechnology, materials science and biophysics.
Frequently asked questions
How do I cancel my subscription?
Can/how do I download books?
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
What is the difference between the pricing plans?
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
What is Perlego?
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Do you support text-to-speech?
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Is Biosensors an online PDF/ePUB?
Yes, you can access Biosensors by Chandra Mouli Pandey, Bansi Dhar Malhotra in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Nanoscience. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 Fundamentals of Biosensors
1.1 Introduction
The role of biological and biochemical processes is paramount in clinical diagnostics, medical applications, bioreactors, food quality control, agriculture, control of industrial waste water, mining, and the military defense industry [1, 2]. However, the conversion of biological data to measurable electrical signals is currently a tedious and time-consuming process [3]. In this context, biosensors have been explored widely because they can be used to convert a biochemical process into a measurable signal [4, 5]. The basic difference between the biosensor and physical/chemical sensor is that its recognition element is biological [6]. With advances in device technology, the use of biosensors has increased and they can be used to detect what many others traditional sensing systems cannot. Nowadays, many biosensors are being produced industrially and utilised to develop large scale multi-valued sensing systems [7]. Much research is being conducted in the field of biosensors, with an estimated 60% annual growth rate, with the major contribution coming from the healthcare industry [8].
The history of biosensors began through the development of an enzyme electrode by Clark [9]. Thereafter, researchers from various fields (physics, chemistry, and material science) have come together to develop more sophisticated, reliable, and mature biosensing devices [10]. Biosensors can be used in the fields of medicine, agriculture, biotechnology, defence as well as the war against bioterrorism [11]. Depending on the area of application, various definitions and terminologies are being used to define a biosensor. The most common cited definitions are those by Higson (a chemical sensing device in which a biologically derived recognition entity is coupled to a transducer, to allow the quantitative development of some complex biochemical parameter) and Frazerare [an analytical device incorporating a deliberate and intimate combination of a specific biological element (that creates a recognition event) and a physical element (that transduces the recognition event)] [9]. In general, a biosensor is an analytical device that incorporates a biological sensing element integrated with a physico-chemical transducer that measures the sensitivity and specificity of a biochemical reaction to deliver complex bioanalytical measurements with a simple, easy-to-use format. A biosensor consists of two main components: a bio-element and a sensor element (Figure 1.1). For the fabrication of a biosensor for non-specialist markets, the following conditions are required [3, 5]:
- – The desired analyte should be specific and stable under a normal storage condition.
- – The sensor should be accurate, precise and show high sensitivity in a reproducible way, and linearity must be obtained with different concentrations.
- – Physical parameters such as pH, temperature should be optimised, which will lead to sample analysis with minimal pre-treatment.
- – The biosensor should be small and biocompatible so that it can be used for invasive monitoring in clinical diagnostics.
- – The fabricated biosensor should be portable, cost-effective, small, and capable of being used by semi-skilled operators.
- – The biosensor should provide real-time analysis so that it can be employed for rapid measurements of analytes from human samples.
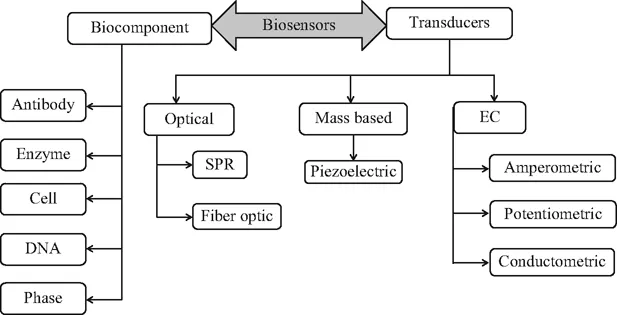
Biosensors are composed mainly of two elements: bioreceptors and transducers.
- – Bioreceptors are biological recognition elements that consist of an immobilised biocomponent that can detect the specific target analyte (e.g., enzyme substrate, complementary DNA, antigen).
- – The second and the most important part of the biosensor is the transducer, which converts a biochemical signal into an electrical signal, resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the bioreceptor. The intensity of signal general as a result of the biochemical reaction is directly or inversely proportional to the analyte concentration.
1.2 Developments in Biosensors
For the development of biosensors, the selection of suitable transducers, immobilisation methods, and bioreceptors are crucial [6]. There is enough scope relating to the innovation in the fabrication of a biosensor for application of clinical diagnostics. Further, this multi-disciplinary field of science and technology is predicted to result in miniaturised, cheaper, and faster biosensors that not only provide accurate information but also feedback to the real world for necessary actions [12]. Further, on the basis of the transducing elements, biosensors can be classified into four types: electrochemical (EC), optical, piezoelectric, and thermal sensors (Figure 1.2).
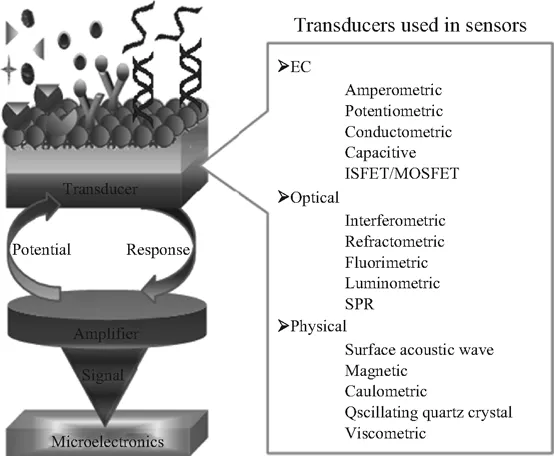
1.2.1 Electrochemical Biosensors
EC biosensors have been explored widely in the fabrication of biosensors because they allow analyses of biomolecules with high specificity, sensitivity, and selectivity, have low response time and are cost-effective [13]. An EC biosensor can be used for clinical analyses, in online control processes for industry or environment, or even in vivo studies. According to a recommendation from the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in 1999, ‘An electrochemical biosensor is a self-contained integrated device, that is capable of providing specific quantitative or semi-quantitative analytical information using a biologica...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- 1 Fundamentals of Biosensors
- 2 Biorecognition Elements in a Biosensor
- 3 Nanomaterial-based Biosensors
- 4 Conducting Polymer-based Biosensors
- 5 Applications of Biosensors
- 6 Challenges and Prospects
- Abbreviations
- Index
Citation styles for Biosensors
APA 6 Citation
Pandey, C. M., & Malhotra, B. D. (2019). Biosensors (1st ed.). De Gruyter. Retrieved from https://www.perlego.com/book/923269/biosensors-fundamentals-and-applications-pdf (Original work published 2019)
Chicago Citation
Pandey, Chandra Mouli, and Bansi Dhar Malhotra. (2019) 2019. Biosensors. 1st ed. De Gruyter. https://www.perlego.com/book/923269/biosensors-fundamentals-and-applications-pdf.
Harvard Citation
Pandey, C. M. and Malhotra, B. D. (2019) Biosensors. 1st edn. De Gruyter. Available at: https://www.perlego.com/book/923269/biosensors-fundamentals-and-applications-pdf (Accessed: 14 October 2022).
MLA 7 Citation
Pandey, Chandra Mouli, and Bansi Dhar Malhotra. Biosensors. 1st ed. De Gruyter, 2019. Web. 14 Oct. 2022.