
- 350 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Synthetic Glycomes
About this book
Glycans play essential roles in diverse biological and etiological processes and their structural complexity endow various functions. The glycome is the entire set of glycans produced by an individual organism. As the glycan microarray emerged, a good amount of knowledge has been obtained in understanding the functions of glycans. However, limited accessibility of glycans is a major obstacle to the functional glycomics study. Although isolation from biology samples provided some structures, the low abundance of glycans obtained and the difficulty in complete structural assignment restricted the subsequent assay. To circumvent this limitation, many synthetic strategies, including chemical, enzymatic and chemo-enzymatic ones have been developed to make libraries of structurally defined complex glycans available. The glycans provided by these techniques combined with high-throughput glycoarray techniques have broadened and deepened our understanding about functional glycomics. The aim of this book is to provide a comprehensive review of the current state of the synthetic glycome and a brief introduction of the application of the synthetic glycome in glycoarray assay. Accordingly, synthetic strategies toward generating glycans with comprehensive structures as well as the glycoarrays to unveil the glycan functions are described in this book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
*E-mail:[email protected]
Carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and proteins comprise the three major macromolecules found in mammalian systems. As genomics and proteomics represent the studies of nucleic acids and proteins, respectively, the term “glycomics” describes the systematic study of the complete repertoire of glycans. Unlike genomics and proteomics, which both have methods for sequencing, automatic synthesis, and amplification, glycomics is comparatively underdeveloped. In this chapter, the challenge, opportunities, and achievement of glycomics and the development of the “glyco-toolbox” will be discussed.
1.1 Introduction




| Blood type | Type O | Type A | Type B | Type AB |
| Antigen | H antigen | A antigen | B antigen | A antigen and B antigen |
 | 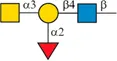 | 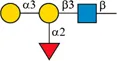 | ||
| Antibodies in plasma | Anti-A and Anti-B | Anti-B | Anti-A | None |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Title
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Introduction: Glycome and the Glyco-toolbox 1
- Chapter 2 Methodologies in Chemical Syntheses of Carbohydrates 15
- Chapter 3 Synthetically Useful Glycosyltransferases for the Access of Mammalian Glycomes 46
- Chapter 4 Chemical Synthesis of N-Glycans 83
- Chapter 5 Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of N-Glycans 105
- Chapter 6 Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of α-Dystroglycan O-Mannose Glycans 125
- Chapter 7 Chemical Synthesis of Glycopeptides and Glycoproteins 151
- Chapter 8 Synthesis of Chondroitin Sulfate Oligosaccharides and Chondroitin Sulfate Glycopeptides 172
- Chapter 9 Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Heparan Sulfate and Heparin 207
- Chapter 10 Synthesis of Glycosphingolipids (GSLs) 226
- Chapter 11 Enzymatic and Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOS) 254
- Chapter 12 Synthesis of Marine Polysaccharides/Oligosaccharides and Their Derivatives 281
- Chapter 13 Glycan Production by Bacterial Fermentation 311
- Chapter 14 Solid-phase Glycan Synthesis 331
- Chapter 15 Reverse Synthesis of Natural Glycans 356
- Chapter 16 Novel Technologies for Quantitative O-Glycomics and Amplification/Preparation of Cellular O-Glycans 370
- Chapter 17 Current Stage of Commercially Available Glycans to Support Realization of Biologic Drugs 393
- Chapter 18 Glycan Microarrays with Semi-synthetic Neoglycoconjugate Probes in Understanding Glycobiology 421
- Chapter 19 Current Stage of Commercial Glycan Microarrays 447
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app