![]()
THEME 1
CAPACITY BUILDING AND PROGRAM LEADERSHIP
![]()
CHAPTER 1
ENHANCING THE BENEFITS OF ACCOUNTING DOCTORAL CONSORTIA
Anne L. Christensen and Shelley C. Rhoades-Catanach
ABSTRACT
Each year, hundreds of accounting doctoral students attend doctoral consortia (DC) sponsored by universities and academic organizations. This chapter reports results of a survey of consortium attendees and analysis of related consortium programs. The authors seek a better understanding of the benefits attendees perceive from these consortia, the content attendees found most valuable, and whether these consortia appear to achieve the goals of the sponsoring organizations.
Survey results show that participants perceive significant benefits from consortium activities related to research, networking, and career management. Respondents did not find their consortium experience helpful on teaching-related dimensions; however, their comments suggest a desire for additional teaching coverage. The authors make recommendations to planners of accounting DC and leadership of the American Accounting Association (AAA), a major consortium sponsor, intended first to address respondents’ desire for additional teaching coverage. Second, the authors highlight opportunities to link doctoral education to AAA’s strategic initiatives and its vision to provide global thought leadership in accounting.
Keywords: Doctoral consortia; new scholars; accounting research; doctoral student publications; networking; career management
Accounting doctoral consortia (DC) provide opportunities for PhD students from diverse backgrounds and universities to gather in pursuit of scholarship, mentoring, and career development. In recent decades, the number of consortia has grown from a handful to several dozen. While each consortium has its own approach, all involve a significant investment of time and resources. This chapter seeks a better understanding of the benefits participants perceive from consortium attendance, the content attendees found most valuable, and whether consortia are achieving the stated goals of their sponsoring organizations. Our objective is to identify opportunities to make accounting DC more effective, ensuring significant benefits to participants and the broader academic community.
Evaluating consortium effectiveness is warranted given the substantial investment in these programs. In addition, DC are one of the first opportunities for the accounting academic community to mentor its newest members so that they have rewarding careers benefitting academia, accounting practice, future students, and themselves. DC are often the first chance for PhD students to see the wider academic world, in which views may coincide with, enhance, or contradict those at their home school. Prospective attendees at DC will benefit from a better understanding of what to expect from attendance. Organizers and sponsors of DC will benefit from an understanding of consortium participants, their expectations, and their reactions to the experience.
While various academic organizations and universities offer DC, our study focuses on 10 DC sponsored by the AAA and its segments. Table 1 lists the 10 consortia examined in this study. We review consortium programs for academic years 2010–2011 through 2014–2015 for these consortia. We then survey attendees to better understand their consortium experience, the content they found most valuable, and gather their suggestions for improving future consortia.
Our review of consortium programs reveals considerable diversity in structure, timing, and content. However, we note an overwhelming focus on academic research in formal sessions. While this focus is perhaps not surprising, it seems inconsistent with the AAA’s overall mission, and recommendations made by the Pathways Commission in its 2012 report, “Charting a National Strategy for the Next Generation of Accountants” (The Pathways Commission, 2012). The AAA’s strategic vision and the Pathways report stress the need for integrating accounting research, education, and practice. Yet, accounting DC largely ignore both teaching and practice in their formal programs. Our chapter identifies opportunities to improve DC programs and integrate research, education, and practice to address this need.
Our results demonstrate that participants perceive significant benefits from consortium activities related to research, networking, and career management. They value opportunities to network with future colleagues and senior researchers, meet potential co-authors, identify research topics, and understand the expectations, challenges, and benefits of their chosen career. Our respondents did not find their consortium experience helpful on teaching-related dimensions, yet their comments suggest a desire for increased teaching coverage at DC. Finally, respondents offer numerous suggestions for improving future accounting DC.
The remainder of this chapter is organized into five additional sections. The next section discusses prior literature relevant to our study. Background of AAA DC Section describes the objectives of AAA-sponsored DC and provides detail regarding program content for the consortia examined by this study. Survey and Data Section describes our survey and data collection procedures. Results Section presents survey results This is followed by the Summary and Conclusions Section. Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research Section present the limitations of our study. The last Recommendation Section details recommendations to consortium planners and sponsors.
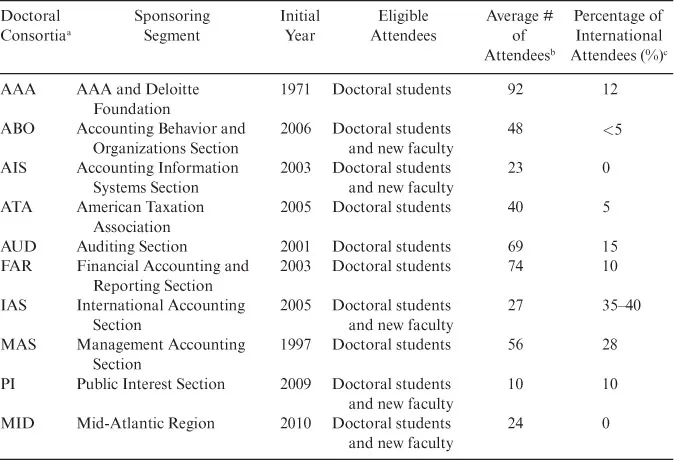
Table 1. Key Characteristics of AAA Doctoral Consortia.
aAAA, American Accounting Association/Deloitte Foundation/Michael Cook Doctoral Consortium; ABO, Accounting Behavior and Organizations Doctoral Consortium; AIS, Accounting Information Systems New Scholars Consortium; ATA, KPMG/American Taxation Association Doctoral Consortium; AUD, Auditing Section Doctoral Consortium; FAR, Financial Accounting and Reporting Section Doctoral Consortium; IAS, International Accounting Section Doctoral Student/New Faculty Consortium; MAS, Managerial Accounting Section Doctoral Consortium; PI, Public Interest Doctoral Student and New Scholar Consortium; MID, Mid-Atlantic Region Doctoral Student/Junior Faculty Consortium.
bAveraged across our sample period of 2011–2015. For consortia that permit new faculty attendance, these statistics reflect only doctoral student attendance.
cThese percentages are from 2013 to 2014 AAA Doctoral Consortia Taskforce Report; the AAA consortium international attendee percentage is based on attendance records provided by AAA headquarters.
RELATED LITERATURE
Scholarly organizations have hosted doctoral student gatherings to discuss effective research methods and build professional networks for years. However, few studies examine DC effectiveness. Two published papers recount personal experiences with accounting DC (see Abdel-khalik, 1986; Ikaheimo, 1992). Both studies are decades old, and likely dated in their relation to current consortia. Other studies focus on accounting doctoral programs, including Brink, Glasscock, and Wier (2012), Gribbin, Sobery, and Braswell (2002), Baldwin, Brown, and Trinkle (2010), Beyer, Herrmann, Meek, and Rapley (2010), and Panozzo (1997). Although these studies make recommendations for improving doctoral education and attracting students to doctoral programs, none specifically address the benefits of DC.
A 2013 American Taxation Association (ATA) taskforce analyzed data related to the initial offerings of the KPMG/ATA Tax Doctoral Consortium. The taskforce notes that one of the primary reasons for initiating the ATA DC was to attract doctoral students to tax research, tax education, and membership in the ATA. Based on their analysis, the ATA taskforce concludes that the consortium is achieving its goals. In particular they note that 85% of past consortium attendees became or expect to become ATA members.
Brink and Quick (2016) report survey results on characteristics of accounting doctoral programs. Their objective is to provide prospective PhD students with information on doctoral program characteristics to facilitate informed decisions on the type of program to attend. Although their study is focused primarily on prospective students versus current students, they mention DC as providing opportunities to broaden students’ understanding and appreciation of accounting research.
Close and Guidry (2007) and Close, Moulard, and Monroe (2011) report survey results on factors influencing salary and first-year faculty placement of marketing doctoral candidates. Both studies find that a significant factor influencing initial salary was attendance at the AMA-Sheth Foundation Doctoral Consortium, an invitation-only DC sponsored by the American Marketing Association (AMA, 2018). The authors speculate that consortium attendance is perceived as an extrinsic cue of candidate quality and prospects as a new faculty member.
BACKGROUND OF AAA DC
History of the Consortia
Table 1 presents characteristics for each AAA-sponsored DC, including initial years, eligible attendees, average number of attendees, and percentage of international attendees. While five of the listed consortia invite both doctoral students and new faculty to attend, the focus of this chapter is on doctoral student attendees at these 10 consortia during our sample period.
In 1971, the AAA launched its first DC, currently known as the American Accounting Association/Deloitte Foundation/J. Michael Cook Doctoral Consortium (AAA Consortium) (Flesher, 1991). The most recent consortium examined in this study is the Mid-Atlantic Region Doctoral/Junior Faculty Consortium (MID), launched in 2010. The consortia listed on Table 1 vary considerably in size. The AAA consortium is the largest, with 92 average annual attendees during our sample period. The Public Interest Section Doctoral Student and Early Scholar Consortium (PI) is the smallest with 10 average annual attendees during our sample period. Attendance by students from non-U.S. doctoral programs also varies, from a high of 35% to 40% for the International Accounting Section (IAS) Doctoral/New Faculty Consortium (NFC) to a low of zero for both the Accounting Information Systems (AIS) and MID consortia.
Consortia Goals and Objectives
We reviewed consortium programs on the AAA and segment websites to better understand DC-stated goals and objectives. While this information might not provide a full picture of consortia goals and objectives, it does provide some basic and relatively consistent information. For example, all consortia examined indicate a focus on stimulating student research. Not surprisingly, most of the section-sponso...