
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Progress in Adhesion and Adhesives, Volume 4
About this book
A solid collection of interdisciplinary review articles on the latest developments in adhesion science and adhesives technology
With the ever-increasing amount of research being published, it is a Herculean task to be fully conversant with the latest research developments in any field, and the arena of adhesion and adhesives is no exception. Thus, topical review articles provide an alternate and very efficient way to stay abreast of the state-of-the-art in many subjects representing the field of adhesion science and adhesives.
Based on the success of the preceding volumes in this series "Progress in Adhesion and Adhesives"), the present volume comprises 9 review articles published in Volume 6 (2018) of Reviews of Adhesion and Adhesives.
The subject of these reviews fall into the following general areas:
1. Adhesion to wood and wood bonds
2. Adhesive joints
3. Adhesion in microelectronic packaging
4. Surface modification
5. Contact angle, wettability and surface free energy.
The topics covered include: Adhesion phenomena in microelectronic packaging; adhesives for wood and lignocellulosic materials; adhesion to wood and lignocellulosic materials; adhesively bonded lap joints having bi-adhesive and modulus-graded bondlines; adhesion between compounded elastomers; applications of contact angle measurements in pharmaceuticals and foods; oxygen or ammonia plasma treatment of polyolefin surfaces; surface free energy determination of powders and particles; wood bonds; and dispersion adhesion forces between macroscopic objects.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Adhesion Phenomena Pertaining to Thermal Interface Materials and Solder Interconnects in Microelectronic Packaging: A Critical Review
Abstract
1.1 Introduction
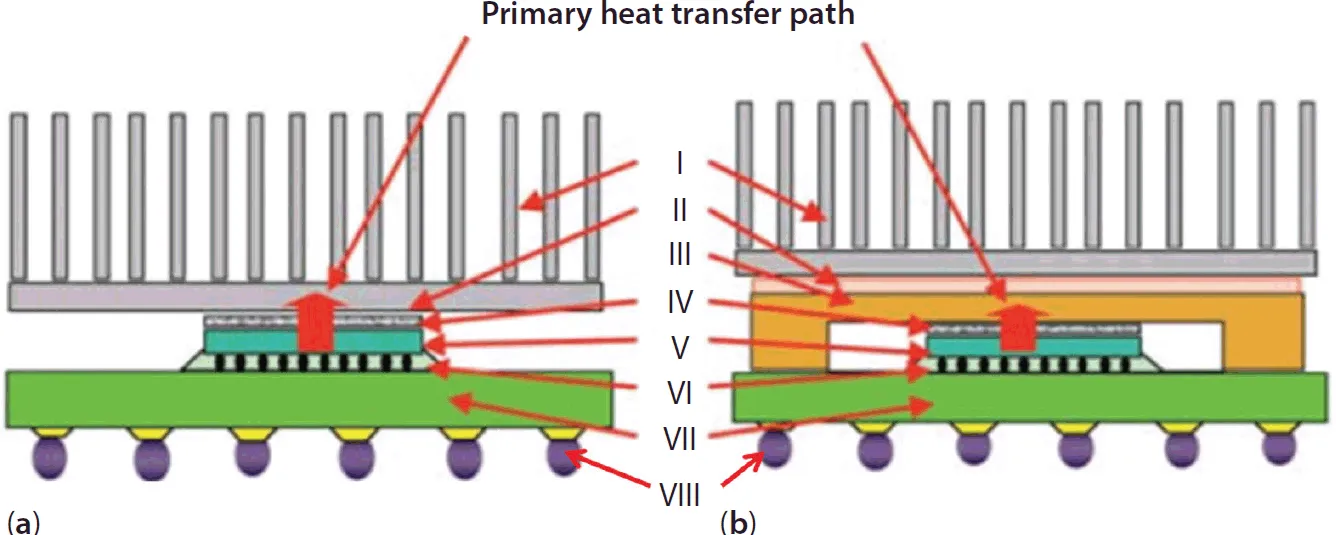
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Adhesion Phenomena Pertaining to Thermal Interface Materials and Solder Interconnects in Microelectronic Packaging: A Critical Review
- Chapter 2: Influence of Silicon-Containing Compounds on Adhesives for and Adhesion to Wood and Lignocellulosic Materials: A Critical Review
- Chapter 3: Recent Advances in Adhesively Bonded Lap Joints Having Bi-Adhesive and Modulus-Graded Bondlines: A Critical Review
- Chapter 4: Adhesion between Compounded Elastomers: A Critical Review
- Chapter 5: Contact Angle Measurements and Applications in Pharmaceuticals and Foods: A Critical Review
- Chapter 6: The Formation Processes of Functional Groups at Polyolefin Surfaces on Exposure to Oxygen or Ammonia Plasma: A Critical Review
- Chapter 7: Surface Free Energy Determination of Powders and Particles with Pharmaceutical Applications: A Critical Review
- Chapter 8: Understanding Wood Bonds–Going Beyond What Meets the Eye: A Critical Review
- Chapter 9: Dispersion Adhesion Forces between Macroscopic Objects–Basic Concepts and Modelling Techniques: A Critical Review
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app