
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Metals in Medicine
About this book
Working from basic chemical principles, Metals in Medicine, 2nd Edition describes a wide range of metal-based agents for treating and diagnosing disease. Thoroughly revised and restructured to reflect significant research activity and advances, this new edition contains extensive updates and new pedagogical features while retaining the popular feature boxes and end-of-chapter problems of the first edition.
Topics include:
- Metallo-Drugs and their action
- Platinum drugs for treating cancer
- Anticancer agents beyond cisplatin including ruthenium, gold, titanium and gallium
- Responsive Metal Complexes
- Treating arthritis and diabetes with metal complexes
- Metal complexes for killing bacteria, parasites and viruses
- Metal ion imbalance and its links to diseases including Alzheimer's, Wilson's and Menkes disease
- Metal complexes for detecting disease
- Nanotechnology in medicine
Now in full colour, Metals in Medicine, 2nd Edition employs real-life applications and chapter-end summaries alongside feature boxes and problems. It provides a complete and methodical examination of the use of metal complexes in medicine for advanced undergraduate and postgraduate students in medicinal inorganic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry, biochemistry, pharmacology, biophysics, biology and bioengineering. It is also an invaluable resource for academic researchers and industrial scientists in inorganic chemistry, medicinal chemistry and drug development.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Inorganic Chemistry Basics
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Crystal Field Theory
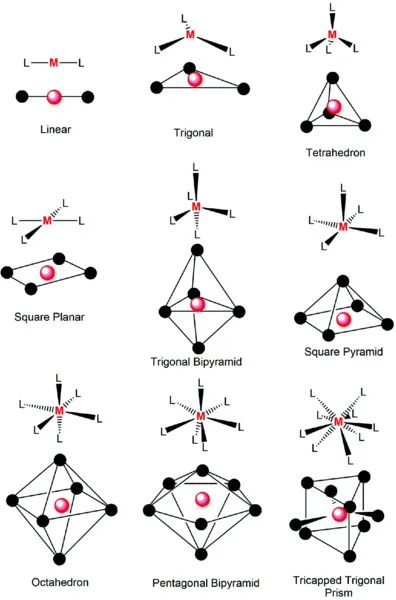
1.2.1 Octahedral Crystal Field
Table of contents
- Cover
- TitlePage
- Copyright
- Feature Boxes
- Preface to the Second Edition
- Preface to the First Edition
- Acknowledgments
- About the Companion Website
- 1 Inorganic Chemistry Basics
- 2 Metallo-Drugs and Their Action
- 3 Platinum Drugs for Treating Cancer
- 4 Anticancer Agents Beyond Cisplatin
- 5 Responsive Metal Complexes
- 6 Metal Complexes for Treating Arthritis and Diabetes
- 7 Metal Complexes for Killing Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses
- 8 Metal Ion Imbalance in the Body
- 9 Metal Complexes for Detecting Disease
- 10 Nanomedicine
- Eula
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app