
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About This Book
This book presents a synthesis of Electronics through keynotes which are substantiated in three volumes. The first one comprises four chapters devoted to elementary devices, i.e. diodes, bipolar transistors and related devices, field effect transistors and amplifiers. In each of one, device physics, non linear and linearized models, and applications are studied. The second volume is devoted to systems in the continuous time regime and contains two chapters: one describes different approaches to the transfer function concept and applications, and the following deals with the quadripole properties, filtering and filter synthesis. The third volume presents the various aspects of sampling systems and quantized level systems in the two last chapters.
Frequently asked questions
Information
1
Continuous-time Systems: General Properties, Feedback, Stability, Oscillators
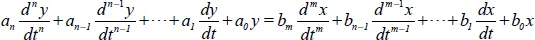

1.1. Representation of continuous time signals
1.1.1. Sinusoidal signals
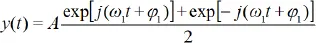
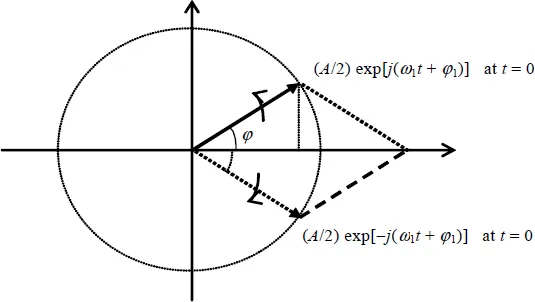
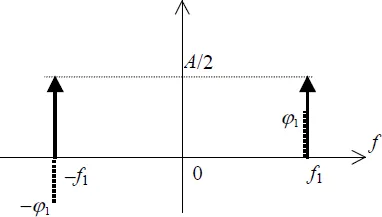
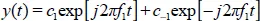
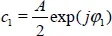
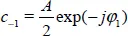
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Introduction
- 1 Continuous-time Systems: General Properties, Feedback, Stability, Oscillators
- 2 Continuous-time Linear Systems: Quadripoles, Filtering and Filter Synthesis
- Appendix: Notions of Distribution and Operating Properties
- Bibliography
- Index
- End User License Agreement