
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About This Book
Medical students encounter many challenges on their path to success, from managing their time, applying theory to practice, and passing exams. The Medical Student Survival Skills series helps medical students navigate core subjects of the curriculum, providing accessible, short reference guides for OSCE preparation and hospital placements. These guides are the perfect tool for achieving clinical success.
Medical Student Survival Skills: ECG is an indispensable resource for students new to ECG interpretation and cardiac arrhythmia recognition and treatment. Integrating essential clinical knowledge with practical OSCE advice, this portable guide provides concise and user-friendly coverage of all aspects of ECG monitoring, including atrial and ventricular fibrillation, myocardial infarction, and 12 lead ECG interpretation. Easy-to-find information, plentiful illustrations, OSCE checklists and expert discussions of actual ECG trace examples help medical students and junior doctors quickly get up to speed with ECG interpretation skills.
Frequently asked questions
Information
1
Introduction to ECG monitoring
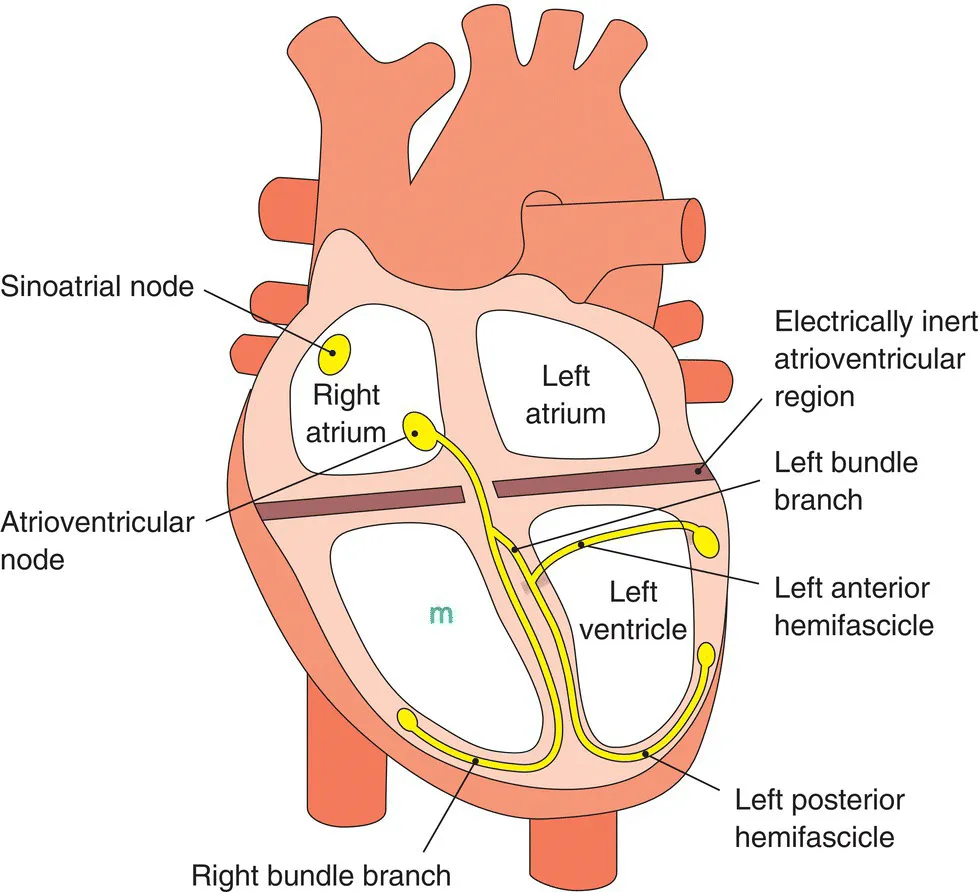
Conduction system of the heart (figure 1.1)
PQRST complex (figure 1.2)
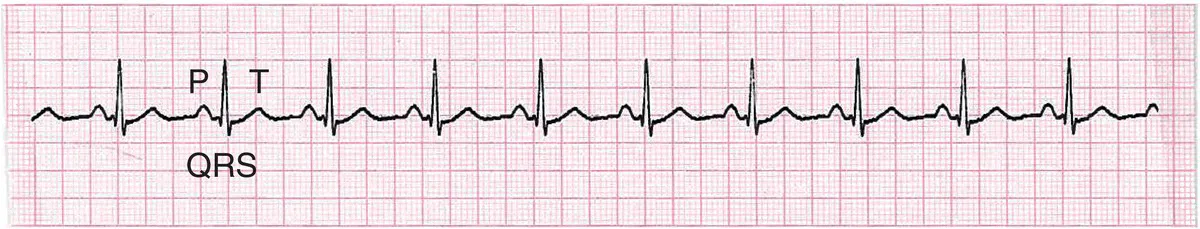
- P wave: atrial depolarisation
- PR interval: atrial depolarisation and the impulse delay in the atrioventricular (AV) node prior to ventricular depolarisation
- QRS complex: ventricular depolarisation
- T wave: ventricular repolarisation
Sinus rhythm (figure 1.3)
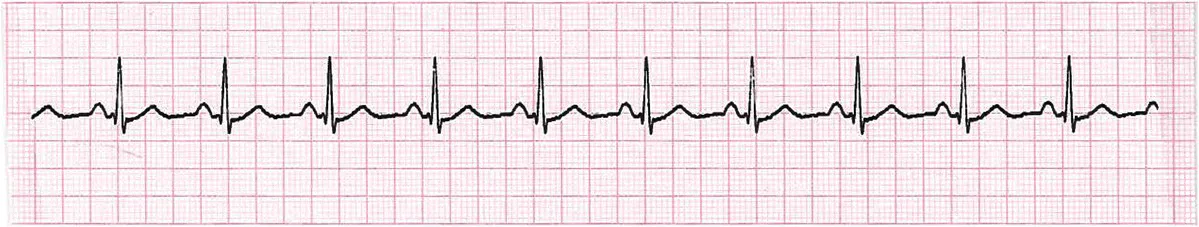
- Normal rhythm of the heart
- Impulse originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node (i.e. ‘sinus’), regular rate of 60–100 beats per minute (bpm)
- No abnormal conduction delays
- Electrical activity: present
- QRS rate: 60–100 bpm
- QRS rhythm: regular
- QRS width: normal width and morphology
- P waves: present and of constant morphology
- Relationship between P waves and QRS complexes: P waves associated to QRS complexes; PR interval normal and constant

Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- About the companion website
- 1 Introduction to ECG monitoring
- 2 Principles of ECG monitoring
- 3 Six stage approach to ECG interpretation
- 4 Sinus tachycardia
- 5 Sinus bradycardia
- 6 Sinus arrhythmia
- 7 Atrial ectopic beats
- 8 Atrial tachycardia
- 9 Atrial flutter
- 10 Atrial fibrillation
- 11 AV junctional ectopics
- 12 AV junctional escape rhythm
- 13 Junctional tachycardia
- 14 Ventricular ectopics
- 15 Idioventricular rhythm
- 16 Ventricular tachycardia
- 17 Torsades de pointes
- 18 First degree AV block
- 19 Second degree AV block Mobitz type I (Wenckebach phenomenon)
- 20 Second degree AV block Mobitz type II
- 21 Third degree (complete) AV block
- 22 Ventricular fibrillation
- 23 Ventricular standstill
- 24 Asystole
- 25 Recording a 12 lead ECG
- 26 What the standard 12 lead ECG records
- 27 Interpretation of a 12 lead ECG
- 28 ECG changes associated with myocardial infarction
- 29 ECG changes associated with myocardial ischaemia
- 30 ECG changes associated with bundle branch block
- 31 Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
- Appendix A: Resuscitation council (UK) bradycardia algorithm
- Appendix B: Resuscitation council (UK) tachycardia algorithm
- Appendix C: Resuscitation council (UK) advanced life support (ALS) algorithm
- Appendix D: Vagal manoeuvres
- Appendix E: Synchronised electrical cardioversion
- Appendix F: External (transcutaneous) pacing
- Appendix G: Procedure for transcutaneous pacing
- Appendix H: Definitions
- References
- Index
- End User License Agreement