
Introduction to Mobile Network Engineering: GSM, 3G-WCDMA, LTE and the Road to 5G
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Introduction to Mobile Network Engineering: GSM, 3G-WCDMA, LTE and the Road to 5G
About This Book
Summarizes and surveys current LTE technical specifications and implementation options for engineers and newly qualified support staff
Concentrating on three mobile communication technologies, GSM, 3G-WCDMA, and LTE—while majorly focusing on Radio Access Network (RAN) technology—this book describes principles of mobile radio technologies that are used in mobile phones and service providers' infrastructure supporting their operation. It introduces some basic concepts of mobile network engineering used in design and rollout of the mobile network. It then follows up with principles, design constraints, and more advanced insights into radio interface protocol stack, operation, and dimensioning for three major mobile network technologies: Global System Mobile (GSM) and third (3G) and fourth generation (4G) mobile technologies. The concluding sections of the book are concerned with further developments toward next generation of mobile network (5G). Those include some of the major features of 5G such as a New Radio, NG-RAN distributed architecture, and network slicing. The last section describes some key concepts that may bring significant enhancements in future technology and services experienced by customers.
Introduction to Mobile Network Engineering: GSM, 3G-WCDMA, LTE and the Road to 5G covers the types of Mobile Network by Multiple Access Scheme; the cellular system; radio propagation; mobile radio channel; radio network planning; EGPRS - GPRS/EDGE; Third Generation Network (3G), UMTS; High Speed Packet data access (HSPA); 4G-Long Term Evolution (LTE) system; LTE-A; and Release 15 for 5G.
- Focuses on Radio Access Network technologies which empower communications in current and emerging mobile network systems
- Presents a mix of introductory and advanced reading, with a generalist view on current mobile network technologies
- Written at a level that enables readers to understand principles of radio network deployment and operation
- Based on the author's post-graduate lecture course on Wireless Engineering
- Fully illustrated with tables, figures, photographs, working examples with problems and solutions, and section summaries highlighting the key features of each technology described
Written as a modified and expanded set of lectures on wireless engineering taught by the author, Introduction to Mobile Network Engineering: GSM, 3G-WCDMA, LTE and the Road to 5G is an ideal text for post-graduate and graduate students studying wireless engineering, and industry professionals requiring an introduction or refresher to existing technologies.
Frequently asked questions
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
Chapter 2
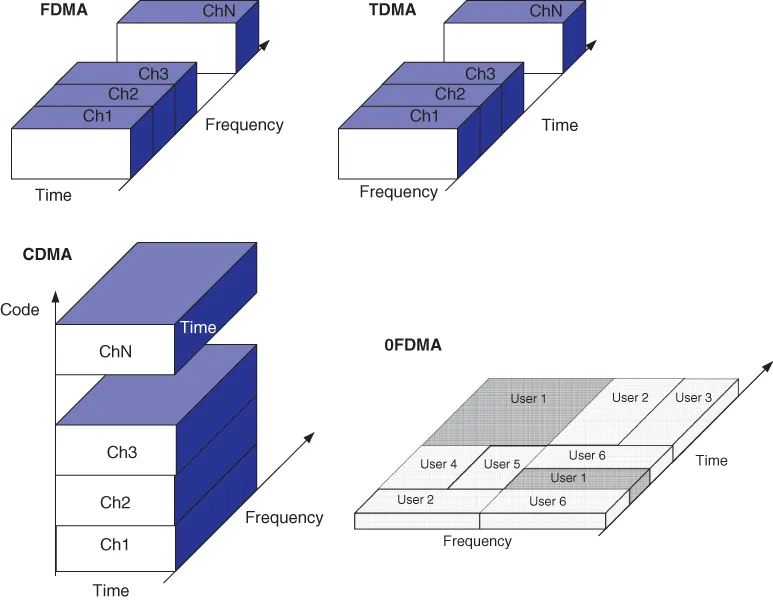
Types of Mobile Network by Multiple‐Access Scheme
- frequency division multiple access (FDMA)
- time‐division multiple access (TDMA)
- code division multiple access (CDMA)
- orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA)
Chapter 3
Cellular System
3.1 Historical Background
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Dedication
- Foreword
- Acknowledgements
- Abbreviations
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Types of Mobile Network by Multiple‐Access Scheme
- Chapter 3: Cellular System
- Chapter 4: Radio Propagation
- Chapter 5: Mobile Radio Channel
- Chapter 6: Radio Network Planning
- Chapter 7: Global System Mobile, GSM, 2G
- Chapter 8: EGPRS: GPRS/EDGE
- Chapter 9: Third Generation Network (3G), UMTS
- Chapter 10: High‐Speed Packet Data Access (HSPA)
- Chapter 11: 4G‐Long Term Evolution (LTE) System
- Chapter 12: LTE‐A
- Chapter 13: Further Development for the Fifth Generation
- Chapter 14: Annex: Base‐Station Site Solutions
- Index
- End User License Agreement