
This is a test
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
An in-depth look at how banks and financial institutions manage assets and liabilities
Created for banking and finance professionals with a desire to expand their management skillset, this book focuses on how banks manage assets and liabilities, set up governance structures to minimize risks, and approach such critical areas as regulatory disclosures, interest rates, and risk hedging. It was written by the experts at the world-renowned Hong Kong Institute of Bankers, an organization dedicated to providing the international banking community with education and training.
- Explains bank regulations and the relationship with monetary authorities, statements, and disclosures
- Considers the governance structure of banks and how it can be used to manage assets and liabilities
- Offers strategies for managing assets and liabilities in such areas as loan and investment portfolios, deposits, and funds
- Explores capital and liquidity, including current standards under Basel II and Basel III, funding needs, and stress testing
- Presents guidance on managing interest rate risk, hedging, and securitization
Frequently asked questions
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes, you can access Bank Asset and Liability Management by in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Economía & Bancos y banca. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
PART 1
ASSET AND LIABILITY MANAGEMENT
CHAPTER 1
Managing Bank Profitability
Learning outcomes
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
- Identify the process of asset and liability management (ALM) in the context of a bank's structure, regulations, financial statements and profits.
- Describe how financial information on a balance sheet and a profit-and-loss statement can be used to analyse a bank.
- Identify and explain the key sources of a bank's income, including net interest income and non-interest income.
- Explain the general outlines of ALM as coordinated balance sheet management.
Introduction
Risk, return and capital provisions permeate all banking activity. Indeed, return on capital is a core objective of banking, and the degree of risk in an activity often determines a specified return on the capital used. How effectively a bank uses its capital often determines its success. That is why asset and liability management (ALM), which is overseen by the Asset and Liability Management Committee (ALCO), is so critical to all banking activities.
In this chapter, we put ALM in context by looking at bank structures and the regulations that proscribe them in different jurisdictions, bank financial statements, and evaluation of bank profits. Subsequent chapters will explore in greater detail the specifics of managing bank assets and liabilities, and of managing capital, including capital adequacy and planning. Later, we will also examine liquidity risk management and management of interest-rate risk, which are two areas that have a great impact on ALM.
Banks undertake all their activities on a foundation of capital, so understanding how capital is managed is of paramount importance to any prospective banking professionals. The differences between the banking book and the trading book and the various regulations that impact the movements of both for authorised institutions (AIs) in Hong Kong are examined in this chapter. Also considered are the basis of those regulations, often international agreements and accords.
The ultimate goal of ALM is to manage the risks associated with mismatches between assets and liabilities, risks that can be caused by, for example, issues with the liquidity that banks require to meet their liabilities or changes in interest rates, particularly given that banks tend to borrow short-term funds but lend long term. This chapter considers various ways to ensure profitability including return on equity, return on assets, net interest margin and net interest spread. At the same time, we consider how banks manage their balance sheets and distinguish between accounting and economic profit.
Structure and Regulation
Let us begin by examining bank structures and regulation in Hong Kong. Larger banks usually undertake a complex array of activities. These can be broadly grouped under two headings: commercial banking, which covers the more traditional deposits and loans business; and investment banking, which covers trading activity and fee-based income such as stock-exchange listing and mergers and acquisitions.
Banking Activities
As Figure 1.1 shows, the scope of banking is varied, ranging from everyday lending to such complex transactions as securitisation and trading of hybrid products. We will not discuss the nature of these transactions in detail in this chapter, but a general knowledge of the basic products is useful as background. Most of them have been discussed in previous books in this series.
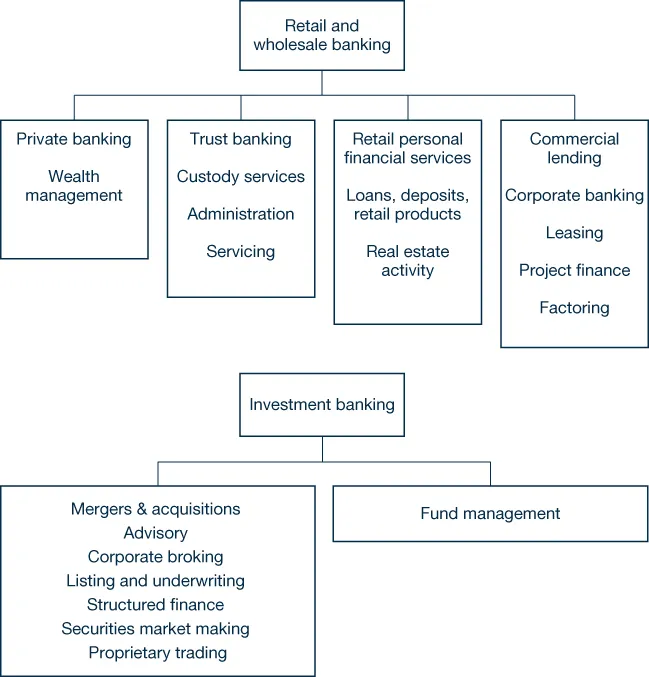
FIGURE 1.1 Scope of banking activities
Source: Choudhry, Moorad (2007) Bank Asset and Liability Management: Strategy, Trading, Analysis. Singapore: John Wiley & Sons, p. 4.
Because asset and liability management (ALM) is focused on the efficient management of banking capital, it has to concern itself with all banking operations—even if day-to-day contact between the ALM desk (which is responsible for the treasury and money-markets activities of the entire bank) and other parts of the bank is remote. In fact, we can draw a box with ALM in it around the whole of Figure 1.1.
This is not to say that the ALM function does all these activities, rather, that all the various activities represent assets and liabilities for the bank and one central function—ALM—is responsible for the coordinated management of these activities.
Capital is the equity of a bank. It enables a bank to continue operating and avoid insolvency in bad economic times and to give shareholders a good return on equity during normal and bull times.
The value of a bank's assets and liabilities tends to be far greater than the value of its capital. Even modest fluctuations (1% reduction) in the valuations of assets and liabilities can cause a significant (10% reduction) movement in capital. Capital management is thus a very important part of bank management. A bank organises its business into a banking book and a trading book.
The banking book records traditional banking activity such as deposits and loans. For accounting purposes, the banking book follows the accrual concept, which is accruing interest cash flows as they occur. There is generally no mark-to-market. The banking book holds assets for which corporate banking, retail banking as well as corporate centre are represented. The type of business activity dictates whether it is placed in the banking book, not the type of counterparty or the bank department involved.
Assets and liabilities in the banking book generate interest-rate and credit risks for the bank, and liquidity and term-mismatch (‘gap’) risk, which arises from either excess or shortage of cash. (Liquidity refers to the ease of transforming an asset into cash, or of raising funds in the market.)
The trading book records wholesale market activity, including market-making and proprietary trading. Assets on the trading book usually have a high turnover, and are marked-to-market daily. The counterparties to such activity can include other banks and financial institutions such as hedge funds, corporations and central banks.
Banking Regulation
Any discussion of ALM will not be complete without mentioning bank regulation. Banking is a highly regulated industry.
Hong Kong's banking regulator is the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA), which is responsible for maintaining monetary and banking stability. Its policy objectives are to maintain currency stability (the Hong Kong dollar is pegged to the US dollar); promote the safety and stability of the banking system; enhance the efficiency, integrity and development of the financial system; and promote Hong Kong's role as an international financial centre.
Bank regulators have the same objective in making sure banks do not take risks that are inappropriate for their size, capital, lines of business, ownership structure and other factors. The level of scrutiny and regulation has intensified in the wake of the 2008–2009 global financial crisis (GFC), when banks deemed too big to fail had to be bailed out i...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- PART 1: ASSET AND LIABILITY MANAGEMENT
- PART 2: MANAGING LIQUIDITY RISK AND INTEREST RATE RISK
- APPENDIX A: Principles for Sound Liquidity Risk Management and Supervision
- Index
- End User License Agreement