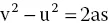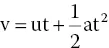- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Construction Science and Materials
About this book
Construction Science & Materials is designed to cover topics studied at levels 2 – 5 on Construction HND courses and is also suitable for first year undergraduates on construction courses as well as Building surveying, Architectural Technology and Quantity Surveying. It is an essential text for those who have done no science since their GCSEs.
Divided into 17 chapters, each with written explanations supplemented by solved examples and relevant diagrams to substantiate the text. Chapters end with numerical questions covering a range of problems and their answers are given at the end of the book and on the book's website.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Introduction to Physics
LEARNING OUTCOMES
- Define speed, velocity and acceleration.
- Explain mass, gravitation and weight.
- Explain Newton’s laws of motion and solve numerical problems based on these laws.
- Explain work, energy and power, and solve numerical problems.
1.1 Speed and Velocity
In the study of moving objects, one of the important things to know is the rate of motion. The rate of motion of a moving object is what we call speed. It may be defined as the distance covered in a given time:

If the distance covered is in metres (m) and the time taken in seconds (s), then speed is measured in metres per second (m/s). If the distance is in kilometres (km) and the time in hours (h), the unit of speed is kilometres per hour (km/h).
When the direction of movement is combined with the speed, we have the velocity of motion. Quantities that have both magnitude and direction are known as vector quantities. Velocity is a vector quantity; its magnitude and direction can be represented by an arrow. Speed, on the other hand, has magnitude but no direction; therefore it is called a scalar quantity.
1.2 Acceleration
An object is said to accelerate if its velocity increases. The rate of increase of velocity is called the acceleration.

If velocity is measured in metres and time in seconds, then acceleration is measured in metres per second per second (m/s/s) or metres per second squared (m/s2). If the velocity of a moving object decreases, it is said to decelerate, i.e. the acceleration is negative. The following relationships may be used to solve problems involving velocity and acceleration:
where, u = initial velocity
- v = final velocity
- a = acceleration
- t = time
- s = distance
1.3 Mass
The amount of matter contained in an object is known as its mass. The basic SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg).
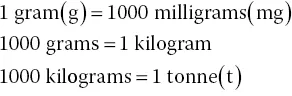
Th...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface to the Second Edition
- About the Companion Website
- 1 Introduction to Physics
- 2 Introduction to Chemistry
- 3 Effects of Chemicals and the Atmosphere on Materials
- 4 Electricity
- 5 Introduction to Construction Technology
- 6 Introduction to Building Services
- 7 Thermal Energy 1
- 8 Thermal Energy 2 (Including Humidity)
- 9 Forces and Structures 1
- 10 Forces and Structures 2
- 11 Forces and Structures 3
- 12 Fluid Mechanics
- 13 Sound
- 14 Light
- 15 Human Comfort
- 16 Construction Materials
- 17 Assignments
- Appendix 1: Formulae for Example 8.2
- Appendix 2: Solutions for Example 13.10
- Appendix 3: Answers to Exercises
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Construction Science and Materials by Surinder Singh Virdi in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Civil Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.