
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Bio-Based Solvents
About this book
A multidisciplinary overview of bio-derived solvent applications, life cycle analysis, and strategies required for industrial commercialization
This book provides the first and only comprehensive review of the state-of-the-science in bio-derived solvents. Drawing on their own pioneering work in the field, as well as an exhaustive survey of the world literature on the subject, the authors cover all the bases—from bio-derived solvent applications to life cycle analysis to strategies for industrial commercialization—for researchers and professional chemists working across a range of industries.
In the increasingly critical area of sustainable chemistry, the search for new and better green solvents has become a top priority. Thanks to their renewability, biodegradability and low toxicity, as well as their potential to promote advantageous organic reactions, green solvents offer the promise of significantly reducing the pernicious effects of chemical processes on human health and the environment.
Following an overview of the current solvents markets and the challenges and opportunities presented by bio-derived solvents, a series of dedicated chapters cover all significant classes of solvent arranged by origin and/or chemical structure. Throughout, real-world examples are used to help demonstrate the various advantages, drawbacks, and limitations of each class of solvent.
Topics covered include:
- The commercial potential of various renewably sourced solvents, such as glycerol
- The various advantages and disadvantages of bio-derived versus petroleum-based solvents
- Renewably-sourced and waste-derived solvents in the design of eco-efficient processes
- Life cycle assessment and predictive methods for bio-based solvents
- Industrial and commercial viability of bio-based solvents now and in the years ahead
- Potential and limitations of methodologies involving bio-derived solvents
- New developments and emerging trends in the field and the shape of things to come
Considering the vast potential for new and better products suggested by recent developments in this exciting field, Bio-Based Solvents will be a welcome resource among students and researchers in catalysis, organic synthesis, electrochemistry, and pharmaceuticals, as well as industrial chemists involved in manufacturing processes and formulation, and policy makers.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
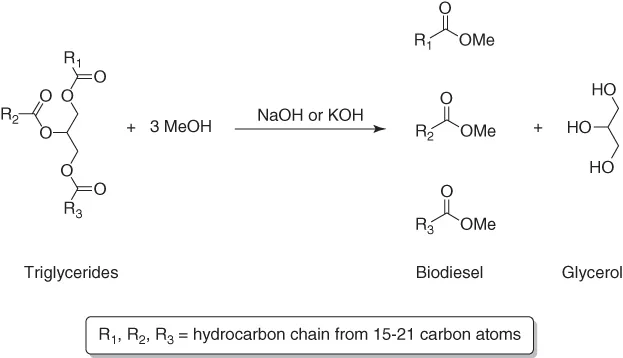
Glycerol as Eco-Efficient Solvent for Organic Transformations
1.1 Introduction
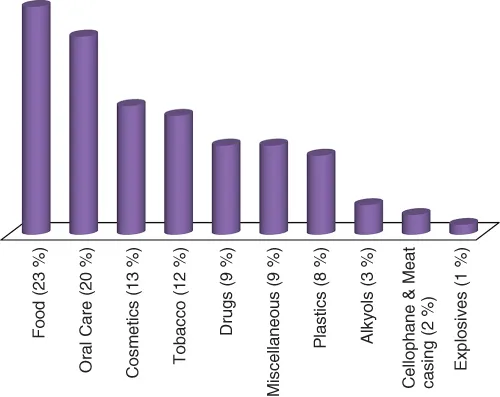
| Melting point | 17.8°C |
| Boiling point | 290°C |
| Viscosity (20°C) | 1200 cP |
| Vapour pressure (20°C) | <1 mm Hg |
| Density (20°C) | 1.26 g cm−3 |
| Flash point | 160°C (closed cup) |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 400°C |
| Critical temperature | 492.2°C |
| Critical pressure | 42.5 atm |
| Dielectric constant (25°C) | 44.38 |
| Dipole moment (30–50°C) | 2.68 D |
| LD50 (oral, rat) | 12600 mg kg−1 |
| LD50 (dermal, rabbit) | >10 000 mg kg−1 |
| LD50 (rat, 1 h) | 570 mg m−3 |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Table of Contents
- List of Contributors
- Series Preface
- Foreword
- Chapter 1: Glycerol as Eco-Efficient Solvent for Organic Transformations
- Chapter 2: Aromatic Bio-Based Solvents
- Chapter 3: Solvents from Waste
- Chapter 4: Deep Eutectic and Low-Melting Mixtures
- Chapter 5: Organic Carbonates: Promising Reactive Solvents for Biorefineries and Biotechnology
- Chapter 6: Life Cycle Assessment for Green Solvents
- Chapter 7: Alkylphenols as Bio-Based Solvents: Properties, Manufacture and Applications
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app