
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Discover how to manage diabetes for a healthier and happier life!
Written for anyone diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (and for anyone who loves someone with diabetes), Managin g Type 2 Diabetes For Dummies is an essential guide to understanding the effects of diabetes and knowing what steps to take to successfully manage this chronic illness. Diabetes can lead to serious complications but people with diabetes can control the condition and lower the risk of its many complications. This is your easy-to-understand guide that shows you how. Under the direction of The American Diabetes Association, Managin g Type 2 Diabetes For Dummies gives hope to the one in 11 people in the United States who are affected by the disease.
Written in simple-to-understand terms, Managin g Type 2 Diabetes For Dummies is filled with a wealth of expert advice and includes the most current information on recent medical advances for treatment. Improperly managed diabetes and consistently high blood glucose levels can lead to serious diseases affecting the heart and blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and teeth. With the authorities at the American Diabetes Association on your side, you will have a practical handbook for preventing complications and managing diabetes with confidence!
- Prevent and manage the complications of the disease
- Combat diabetes-related anxiety and depression
- Lead a healthy life with type 2 diabetes
Tap into the better living "rules of the road" with Managin g Type 2 Diabetes For Dummies. By modifying your diet, consulting with your doctors, staying active, and understanding what medications are right for you, you will be on the path to a happier and healthier lifestyle.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Getting Started with Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes: The Basics





What Exactly Is Diabetes?
Getting the lowdown on blood glucose
The mighty hormone insulin
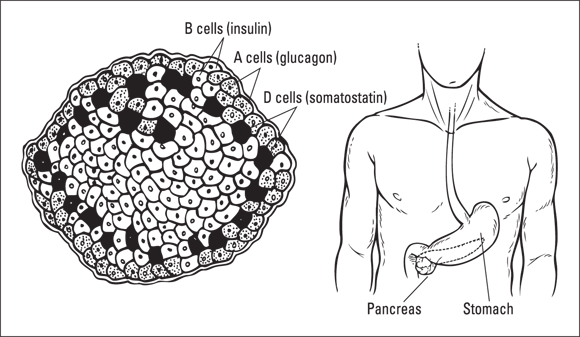
- The beta cells don’t work well. They don’t make as much insulin as they’re supposed to.
- There may be fewer beta cells than usual.
- The beta cells that are making all the insulin get burned out (super tired) and eventually make less insulin. It’s a cycle in which insulin production can get worse over time.
Don’t forget glucagon
High blood glucose is not good
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part 1: Getting Started with Diabetes
- Part 2: Your Healthcare Team and Medications
- Part 3: Checking Blood Glucose and Reducing Complications
- Part 4: Eating Healthy and Staying Active
- Part 5: Finding Support
- Part 6: Standing Up for Yourself
- Part 7: The Part of Tens
- Glossary
- About the Author
- Advertisement Page
- Connect with Dummies
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app


