
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Introduction to Modern Virology
About this book
Praised forits clarity of presentation and accessibility, Introduction to Modern Virology has been a successful student text for over 30 years. It provides a broad introduction to virology, which includes the nature of viruses, the interaction of viruses with their hosts and the consequences of those interactions that lead to the diseases we see. This new edition contains a number of important changes and innovations including:
- The consideration of immunology now covers two chapters, one on innate immunity and the other on adaptive immunity, reflecting the explosion in knowledge of viral interactions with these systems.
- The coverage of vaccines and antivirals has been expanded and separated into two new chapters to reflect the importance of these approaches to prevention and treatment.
- Virus infections in humans are considered in more detail with new chapters on viral hepatitis, influenza, vector-borne diseases, and exotic and emerging viral infections, complementing an updated chapter on HIV.
- The final section includes three new chapters on the broader aspects of the influence of viruses on our lives, focussing on the economic impact of virus infections, the ways we can use viruses in clinical and other spheres, and the impact that viruses have on the planet and almost every aspect of our lives.
A good basic understanding of viruses is important for generalists and specialists alike. The aim of this book is to make such understanding as accessible as possible, allowing students across the biosciences spectrum to improve their knowledge of these fascinating entities.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
The Nature of Viruses
- 1 | Towards a definition of a virus
- 2 | The structure of virus particles
- 3 | Classification of viruses
- 4 | The evolution of viruses
- 5 | Techniques for studying viruses
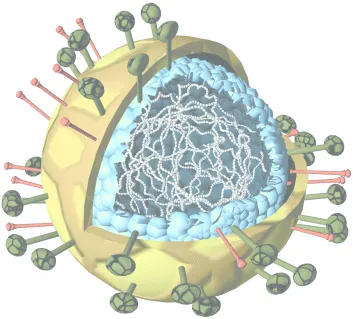
Chapter 1
Towards a Definition of a Virus
Chapter 1 Outline
- 1.1 Discovery of viruses
- 1.2 Multiplication of viruses
- 1.3 The virus multiplication cycle
- 1.4 Viruses can be defined in chemical terms
- 1.5 Multiplication of bacterial and animal viruses is fundamentally similar
- 1.6 Viruses can be manipulated genetically
- 1.7 Properties of viruses
- 1.8 Origin of viruses
1.1 Discovery of Viruses
Box 1.1 Properties Common to All Viruses
- Viruses have a nucleic acid genome of either DNA or RNA.
- Compared with a cell genome, viral genomes are small, but genomes of different viruses range in size by over 100-fold (ca 3000 nt to 1,200,000 bp)
- Small genomes make small particles – again with a 100-fold size range.
- Viral genomes are associated with protein that at its simplest forms the virus particle, but in some viruses this nucleoprotein is surrounded by further protein or a lipid bilayer.
- The outermost proteins of the virus particle allow the virus to recognise the correct host cell and gain entry.
- Viruses can only reproduce in living cells: they are obligate parasites.
1.2 Multipl...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- About the Companion Website
- Part I: The Nature of Viruses
- Part II: Virus Growth in Cells
- Part III: Virus Interactions with the Whole Organism
- Part IV: Viruses and Human Disease
- Part V: Virology – the Wider Context
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app