
Fundamentals of Medical-Surgical Nursing
A Systems Approach
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Fundamentals of Medical-Surgical Nursing
A Systems Approach
About This Book
Fundamentals of Medical-Surgical Nursing
Fundamentals of Medical-Surgical Nursing
A Systems Approach
Fundamentals of Medical-Surgical Nursing is a comprehensive yet easy-to-read overview of medical and surgical nursing, designed specifically to support all nursing students learning to care for the adult patient. Highly illustrated and with an easy-to-follow systems-based structure, it provides a thorough foundation in anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, medical management, and nursing care for the full spectrum of adult health conditions.
KEY FEATURES:
- Extensive coverage of principles of nursing assessment, medication administration, infection prevention and control, and nutritional care
- Key need-to-know-information and definitions for the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of a range of illnesses and conditions
- Detailed overviews of nursing care, including patient education, treatment, and complications
- An online resource centre with a range of extras for both lecturers and students, including case studies, reflective activities, interactive multiple choice questions, and further reading lists
Fundamentals of Medical-Surgical Nursing is the ideal textbook to help students succeed on their adult nursing course.
with online self-test
www.wileyfundamentalseries.com/medicalnursing
- Interactive multiple-choice questions
- Reflective questions for downloading
- Case studies
- Links to online resources
When you purchase the book you also receive access to the Wiley E-Text: Powered by VitalSource. This is an interactive digital version of the book, featuring downloadable text and images, highlighting and notetaking facilities, bookmarking, cross-referencing, in-text searching, and linking to references and abbreviations. Fundamentals of Medical-Surgical Nursing is also available on CourseSmart, offering extra functionality as well as an immediate way to access the book. For more details, see www.coursesmart.co.uk/9780470658239.
Frequently asked questions
Information
- Why – to explain the purpose of nursing assessment and why it is vital to quality patient care
- What – to consider what patient information is collected and the rationale for using an assessment framework
- How – to identify a range of methods available to assess patients and collect information that support clinical decision-making and individualised patient care plans.
Introduction
The purpose of nursing assessment
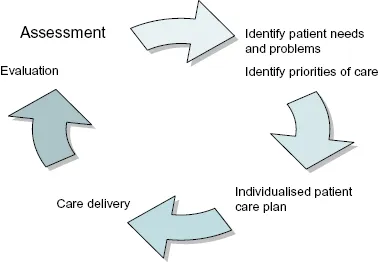
- Obtain baseline data and track changes. On admission to hospital or on a first visit to the clinic, it is important to carry out a comprehensive assessment of the patient to establish a set of baseline data against which subsequent assessments can be compared and any changes indicating a deterioration or improvement in the patient's condition tracked.
- Early recognition of the critically ill or deteriorating patient. Identifying patients who are ‘at risk’ is key to initiating a rapid response from the medical emergency or rapid response team. ‘Track and Trigger’ (e.g. Alert® and other early warning systems) incorporate objective physiological and subjective criteria that can be used to support the nurse's decision about when to call the medical team for help and avert more serious patient emergencies (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence [NICE], 2007). If a Track and Trigger system has not been set up in the hospital, a nurse who is concerned about a patient should take urgent action and notify the medical team.
- Risk assessment. Assessment is the first step in preventing complications, the aim being to identify patients who are ‘at risk’ of developing complications associated with their healthcare problem, hospitalisation and reduced mobility. Key areas for risk assessment include pressure ulcers, infection, falls and constipation. Local hospital policy may include risk assessment tools as part of the admission procedure, for example the Braden, Waterlow and Norton scores to identify patients at risk of pressure ulcers and to activate an action plan and interventions to prevent pressure ulcers developing.
- Screening for health problems. Nursing assessment provides an ideal opportunity for health promotion and for screening patients for risk factors associated with obesity, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus and other major Irish and UK health problems. It also provides the opportunity to screen for specific problems such as emotional distress or organisms important in infection control (e.g. methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [MRSA] and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus [VRE]).
- Identify actual and potential problems and prioritise care. The patient's current problems (actual problems) and problems that could develop in the future (potential problems) need to be identified so that the care plan can be tailored to individual patient needs. Importantly, once the range of patient problems has been identified, care can be prioritised so that major problems are dealt with first.
- Care planning, tailored to individual patient needs. The purpose of assessment is not only to determine and document the patient's current condition, but also to provide evidence for the planning and provision of nursing care. Although standardised care plans are available in some units or hospitals, the nursing actions that are required to meet a patient's needs and problems should be tailored to take account of individual patient needs.
- Discharge planning. Patient assessment also includes the early identification of patients' needs for forward planning and organising the supports and community services necessary to facilitate a timely discharge from hospital. Recent trends indicate that patients' stay in hospital is shortening, the use of day surgery is increasing, and policies on early discharge and discharge planning are setting the standards for healthcare practice (Capelastegui et al. 2008; Saczynski et al. 2010; Shepperd et al. 2010). Although the reasons for a delay in discharging the patient home from hospital are multifactorial, patient assessment that includes information about the patient's home and social circumstances, family and community supports will help prevent problems arising from a poor knowledge of a patient's home situation or the support available, and will avert delays related to non-medical reasons.
Assessment frameworks
Table of contents
- Cover
- Titles of related interest
- Title page
- Copyright page
- About the series
- Preface
- About the editors
- Contributors
- How to get the best out of your textbook
- About the companion website
- Part 1: Common Principles Underlying Medical and Surgical Nursing Practice
- Part 2: Adult Medical and Surgical Nursing
- Index