
Macrocyclic Polyamines
Synthesis and Applications
Xiaoqi Yu,Ji Zhang
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Macrocyclic Polyamines
Synthesis and Applications
Xiaoqi Yu,Ji Zhang
À propos de ce livre
The first comprehensive book focusing on synthesis and applications of macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives Macrocyclic polyamines are a class of widely used important compounds. This is the first book that systematically summarizes the synthesis and applications of macrocyclic polyamines and their analogues, including the properties and synthetic methods of macrocyclic polyamines, chemical nucleases based on macrocyclic polyamines, the derivatives of macrocyclic polyamines as nano-vector materials, macrocyclic polyamines derivatives for bio-imaging, chemical sensors based on macrocyclic polyamines, and other applications of macrocyclic polyamines. Macrocyclic Polyamines: Synthesis and Applications includes most of the studies involving macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives, and may be used as a reference for the researchers in related fields. It offers in-depth coverage of cyclization modes; special procedures for tetraza macrocyclic compounds; diacids-diamines condensation; oxidative DNA cleaving by macrocyclic polyamines; lipids with cationic MPA headgroups; the derivatives of DOTA, DO3A, and PCTA; receptors for anions; sensors for bioactive molecules; macrocyclic polyamines for solvent extraction and membrane transport of amino acids and their derivatives, electrophoretic separation, and open-tubular CEC; and much more.?The first book that systematically summarizes the chemistry of macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives in terms of synthetic methods for their preparation, functionalization, and application in the main fields of chemical sensors, chemical nucleases, drug-delivery, bio-imaging and vector materials
?Provides a comprehensive reference for the researchers working on macrocyclic polyamines
?Offers train of thought in related research fields such as organic chemistry, coordination chemistry, analytical chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, biomaterials, etc. Macrocyclic Polyamines: Synthesis and Applications will not only provide a reference for the researchers working on macrocyclic polyamines, but also offer opportunities for researchers in related research fields to understand the benefits of these key compounds.
Foire aux questions
Informations
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 Classification of Macrocyclic Polyamines
1.1.1 Aliphatic Macrocyclic Polyamines
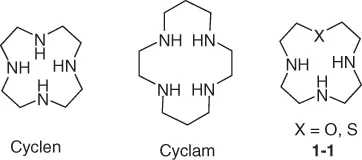
1.1.2 Aromatic-Containing Macrocyclic Polyamines
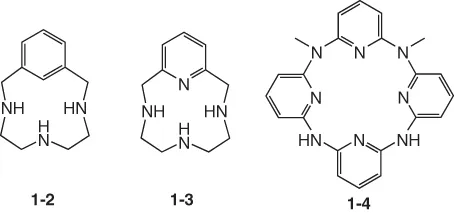
1.1.3 Macrocyclic Polyimines
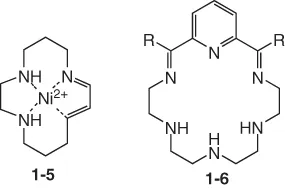
1.1.4 Macrocyclic Polyamides
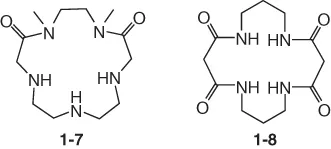
1.1.5 Cryptands
1.2 Properties of Macrocyclic Polyamines
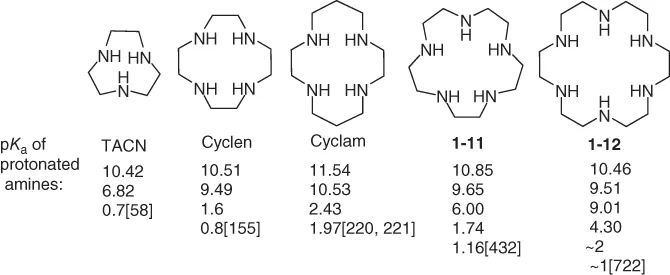
1.2.1 Acid–Base Properties
1.2.2 Coordination Property
Table des matières
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Synthetic Methods for Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Chapter 3: Chemical Nucleases Based on Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Chapter 4: Derivatives of Macrocyclic Polyamines as Nanovector Materials
- Chapter 5: Macrocyclic Polyamine Derivatives for Bio-Imaging
- Chapter 6: Chemical Sensors Based on Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Chapter 7: Other Applications of Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Index
- End User License Agreement