
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
The first comprehensive book focusing on synthesis and applications of macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives
Macrocyclic polyamines are a class of widely used important compounds. This is the first book that systematically summarizes the synthesis and applications of macrocyclic polyamines and their analogues, including the properties and synthetic methods of macrocyclic polyamines, chemical nucleases based on macrocyclic polyamines, the derivatives of macrocyclic polyamines as nano-vector materials, macrocyclic polyamines derivatives for bio-imaging, chemical sensors based on macrocyclic polyamines, and other applications of macrocyclic polyamines.
Macrocyclic Polyamines: Synthesis and Applications includes most of the studies involving macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives, and may be used as a reference for the researchers in related fields. It offers in-depth coverage of cyclization modes; special procedures for tetraza macrocyclic compounds; diacids-diamines condensation; oxidative DNA cleaving by macrocyclic polyamines; lipids with cationic MPA headgroups; the derivatives of DOTA, DO3A, and PCTA; receptors for anions; sensors for bioactive molecules; macrocyclic polyamines for solvent extraction and membrane transport of amino acids and their derivatives, electrophoretic separation, and open-tubular CEC; and much more.
?The first book that systematically summarizes the chemistry of macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives in terms of synthetic methods for their preparation, functionalization, and application in the main fields of chemical sensors, chemical nucleases, drug-delivery, bio-imaging and vector materials
?Provides a comprehensive reference for the researchers working on macrocyclic polyamines
?Offers train of thought in related research fields such as organic chemistry, coordination chemistry, analytical chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, biomaterials, etc.
Macrocyclic Polyamines: Synthesis and Applications will not only provide a reference for the researchers working on macrocyclic polyamines, but also offer opportunities for researchers in related research fields to understand the benefits of these key compounds.
Macrocyclic polyamines are a class of widely used important compounds. This is the first book that systematically summarizes the synthesis and applications of macrocyclic polyamines and their analogues, including the properties and synthetic methods of macrocyclic polyamines, chemical nucleases based on macrocyclic polyamines, the derivatives of macrocyclic polyamines as nano-vector materials, macrocyclic polyamines derivatives for bio-imaging, chemical sensors based on macrocyclic polyamines, and other applications of macrocyclic polyamines.
Macrocyclic Polyamines: Synthesis and Applications includes most of the studies involving macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives, and may be used as a reference for the researchers in related fields. It offers in-depth coverage of cyclization modes; special procedures for tetraza macrocyclic compounds; diacids-diamines condensation; oxidative DNA cleaving by macrocyclic polyamines; lipids with cationic MPA headgroups; the derivatives of DOTA, DO3A, and PCTA; receptors for anions; sensors for bioactive molecules; macrocyclic polyamines for solvent extraction and membrane transport of amino acids and their derivatives, electrophoretic separation, and open-tubular CEC; and much more.
?The first book that systematically summarizes the chemistry of macrocyclic polyamines and their derivatives in terms of synthetic methods for their preparation, functionalization, and application in the main fields of chemical sensors, chemical nucleases, drug-delivery, bio-imaging and vector materials
?Provides a comprehensive reference for the researchers working on macrocyclic polyamines
?Offers train of thought in related research fields such as organic chemistry, coordination chemistry, analytical chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, biomaterials, etc.
Macrocyclic Polyamines: Synthesis and Applications will not only provide a reference for the researchers working on macrocyclic polyamines, but also offer opportunities for researchers in related research fields to understand the benefits of these key compounds.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 Classification of Macrocyclic Polyamines
Macrocyclic polyamines (MPAs) are important complexing agents for cations, anions, and neutral molecules. In this book, MPAs are defined as having at least three nitrogen atoms and nine atoms in the ring. Although polyazamacrocycles containing amide and imine functional groups cannot be named amines strictly, these macrocycles are also included here. According to the functional groups in the ring, MPAs can be divided into aliphatic MPAs, aromatic-containing MPAs, macrocyclic polyimines, macrocyclic polyamides, and cryptands.
1.1.1 Aliphatic Macrocyclic Polyamines
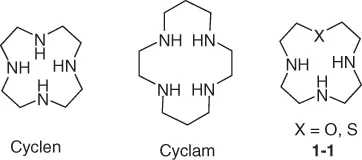
In an aliphatic macrocycle, all carbon and hetero atoms are sp3-hybridized. Cylen and cyclam are the most used aliphatic MPAs. One or more nitrogen atoms can be substituted with other heteroatoms, such as oxygen or sulfur, to afford heteroatom-substituted MPAs (compound 1-1).
1.1.2 Aromatic-Containing Macrocyclic Polyamines
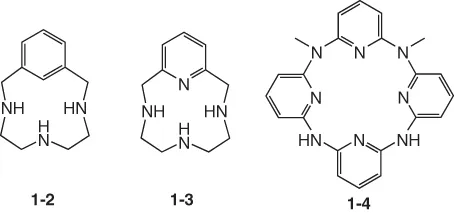
To adjust the rigidity of MPAs, aromatic motifs such as benzene and pyridine are introduced. Most aromatic-containing MPAs have a linker between the aromatic motif and the nitrogen atom (compounds 1-2 and 1-3). Modern transition metal catalysis enables the direct combination of the aromatic motif with the nitrogen atom through the formation of CAr−N bonds (compound 1-4).
1.1.3 Macrocyclic Polyimines
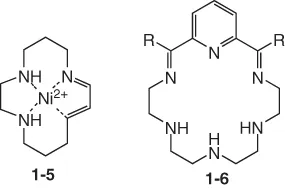
Macrocyclic polyimines have at least one imine bond in the ring. Because aliphatic macrocyclic Schiff bases have rather low hydrolytic stability, they often complex with a suitable metal template (compound 1-5). Aromatic-containing macrocyclic polyimines are hydrolytically stable to a certain extent in the absence of a template (compound 1-6).
1.1.4 Macrocyclic Polyamides
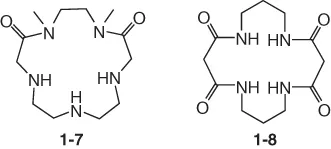
Macrocyclic polyamides have at least one amide bond in the ring (compounds 1-7 and 1-8). Macrocyclic polyamides possess the dual features of cyclic peptides and MPAs. Amide-containing macrocycles are usually prepared by cyclocondensation of acids with amines or coupling of the amide-containing precursors.
1.1.5 Cryptands
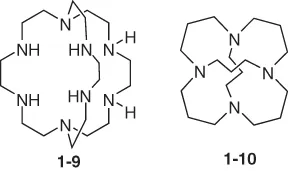
Cryptands (compound 1-9) are three-dimensional analogs of crown ethers but offer much better selectivity and strength of binding. Spherical cryptands (compound 1-10) can be described as twice-bridged azamacrocycles.
1.2 Properties of Macrocyclic Polyamines
1.2.1 Acid–Base Properties
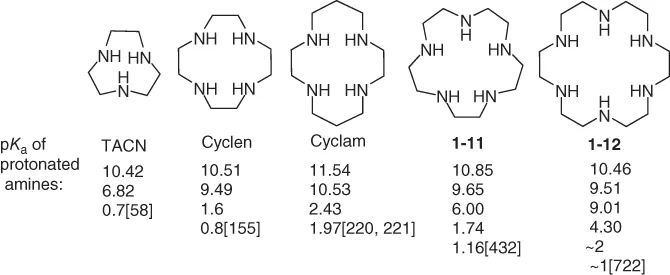
Except for the nitrogens on the aromatic ring, the amino groups on MPAs are mainly aliphatic secondary amines, which always have relatively strong basicity, and the pKa values of their protonated species are in the range of 9–11. However, the secondary amines on MPAs have a much wider pKa range. Generally, the first protonation steps of MPAs are much easier (pKa 9–11, similar to common secondary amines) than the last protonation steps (pKa 1–3, low basicity). This behavior might be attributable to charge-repulsion effects [1] due to the higher positive charge density on the cycle compared with open-chain polyamines. Some typical aliphatic MPAs with their pKa values for each amine are listed below; for detailed data, the reader may refer to the review by Izatt and coworkers [2]. The positive charge of MPAs under neutral conditions facilitates their interaction with negatively charged biomolecules such as nucleic acids and some proteins. MPA derivatives may bind to nucleic acids through electrostatic interaction, protect the nucleic acid cargo from degradation, and deliver the cargo to target cells or tissues (Chapter 4). Moreover, the wider pKa range of amines may afford the vector materials special pH buffering capability in the intracellular environment, leading to enhanced endosomal escape.
1.2.2 Coordination Property
Macrocyclic structures are extremely favorable for metal complexation. Similar to crown ethers, the nitrogens on MPAs may coordinate to metal ions of appropriate size. They show a pronounced ability to bind a wide variety of metals and, in many cases, undergo marked conformational changes during binding [3]. The increased stability of a metal coordination complex of a tetra-amine macrocyclic ligand over that of similar noncyclic tetra-amine ligands has been called the macrocyclic effect. 1,4,7-Triazacyclononane (TACN) has a smaller cavity, and the binding ability is weaker than that of cyclen or compound 1-11. Cyclen may coordinate well to first-row transition elements such as Cu2+ and Zn2+, and the resultant metal complexes are widely used as artificial nucleases (Chapter 3), chemical sensors (Chapter 6), ionophores (Chapter 7), or chemical catalysts. MPA 1-11 has a larger cycle, which facilitates its binding with larger metal ions such as Cd2+ and Hg2+. In addition, MPAs with a cavity larger than that of 1-11 may also coordinate with more than one first-row transition metal ion [2]. The analogs of 1-12 with 7–9 nitrogens can form dinuclear complexes, whereas those with 11 or 12 nitrogens can form even trinuclear complexes. In addition, pendant coordinating groups can also be attached to the nitrogens on the macrocycle, resulting in more extensive metal coordination properties and applications [4]. For example, some MPA derivatives with carboxylic groups on the arms may act as chelating agents to coordinate with lanthanide metal ions. For example, the Gd-complexes of cyclen derivatives are used intensively in the field of bio-imaging, as described in detail in Chapter 5.
Although most applications involving MPAs employ their metal complexes, the polyamine itself may also serve as a bioactive species. Certain ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Synthetic Methods for Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Chapter 3: Chemical Nucleases Based on Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Chapter 4: Derivatives of Macrocyclic Polyamines as Nanovector Materials
- Chapter 5: Macrocyclic Polyamine Derivatives for Bio-Imaging
- Chapter 6: Chemical Sensors Based on Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Chapter 7: Other Applications of Macrocyclic Polyamines
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Macrocyclic Polyamines by Xiaoqi Yu,Ji Zhang in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Organic Chemistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.