
Warehouse Management with SAP ERP: Functionality and Technical Configuration
- 665 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Warehouse Management with SAP ERP: Functionality and Technical Configuration
About this book
Ensure an efficient and orderly Warehouse Management implementation with this comprehensive guide to SAP WM in SAP ERP! Learn to customize and use critical functionalities, like goods receipt and goods issue, as well as advanced technologies such as RFID, EDI, and mobile data entry. Covering everything from stock management to picking strategies, you'll master SAP WM. This new edition includes ITSmobile, connections with SAP ERP PP and QM, the warehouse activity monitor, and more. SAP WM Processes Grasp the essentials of warehouse management, including goods receipt, goods issue, replenishment, and putaway. Then master advanced topics such as hazardous materials management, cross-docking, and value-added services. SAP WM Configuration Understand the configuration details necessary to optimize your SAP WM implementation, from storage bins to yard management. Real World Scenarios Explore concrete business cases and examples to help you put expert tips into practice in your own warehouse.
Highlights:
- -Stock management
- -Goods receipt and goods issue
- -Replenishment
- -Picking strategies
- -Putaway strategies
- -Inventory management
- -Yard management
- -Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
- -Radio frequency identification (RFID)
- -ITSmobile
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1Basic Warehouse Functions
1.1Warehouse Structure
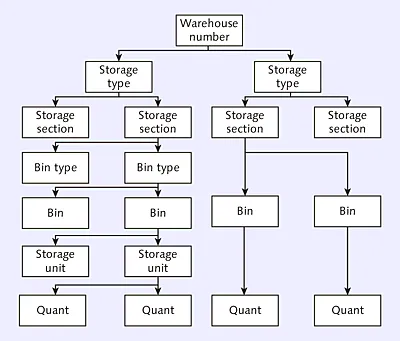
1.1.1Configuring a Warehouse
1.1.2Assignment of the Warehouse
- One plant and one storage location connected to one warehouse
- One plant and two or more storage locations, all connected to one warehouse
- One plant and one storage location connected to one warehouse and a second storage location not connected to the warehouse
- Two or more plants and two or more storage locations, all connected to one warehouse
Table of contents
- Dear Reader
- Notes on Usage
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 Basic Warehouse Functions
- 2 Stock Management
- 3 Warehouse Movements
- 4 Goods Receipts
- 5 Goods Issues
- 6 Stock Replenishment
- 7 Picking Strategies
- 8 Putaway Strategies
- 9 Integration
- 10 Inventory Procedures
- 11 Storage Unit Management
- 12 Hazardous Materials Management
- 13 Planning and Monitoring Workloads
- 14 Cross-Docking
- 15 Yard Management
- 16 Value-Added Services and Task and Resource Management
- 17 Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
- 18 Mobile Data Entry
- 19 Radio Frequency Identification Technology
- 20 ITSmobile
- 21 SAP Extended Warehouse Management
- A The Authors
- Index
- Service Pages
- Legal Notes
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app