
eBook - ePub
Fundamentals of Robotics
David Ardayfio
This is a test
- 448 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Fundamentals of Robotics
David Ardayfio
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Fundamentals of Robotics presents the basic concepts of robots to engineering and technology students and to practicing engineers who want to grasp the fundamentals in the growing field of robotics.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Fundamentals of Robotics als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Fundamentals of Robotics von David Ardayfio im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Tecnología e ingeniería & Ingeniería eléctrica y telecomunicaciones. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
1 Basic Components of Robot Arms
1.1 BASIC ARM TYPES
The identification of the various kinematic arrangements used in industrial robots is useful for manufacturers, users, and researchers. The working volume and dexterity, for example, of a robot are determined by the kinematic arrangements. From the user's point of view, a preliminary determination of the performance of a robot in the work environment based solely on geometry is possible by examination of the linkage type forming the structure of the robot.
Manipulators are typically located relative to ground by either a fixed base or a moving base. The first three links of the manipulator collectively form the manipulator arm. This arm is used for global positioning of the end of the manipulator within the work envelope. The hand is composed of the other links (up to three) and is used to define the orientation of the end of the manipulator. The hand also provides fine local positioning of the end of the manipulator. Detailed treatment of the hands and grippers used in manipulators can be found in Chapter 2. The present chapter discusses various arm types and other components of robot setups.
Two of the three types of connecting elements with one degree of freedom that can be used for connecting links in a robot are the prismatic and revolute pairs. The prismatic or sliding pair allows pure translation of one link with respect to another. The revolute or rotation pair provides pure rotation of one link on another.
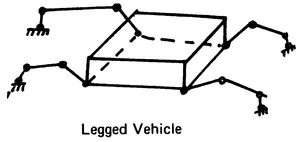
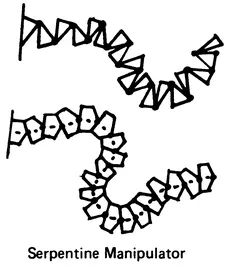
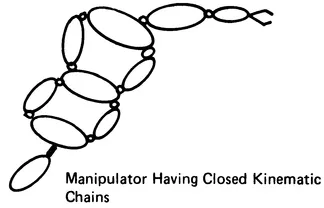
The structural arrangement of robot linkage systems (Figure 1.1) includes:
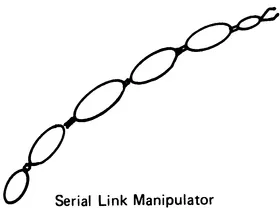
FIGURE 1.1 Types of robotic mechanisms.
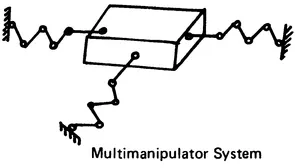
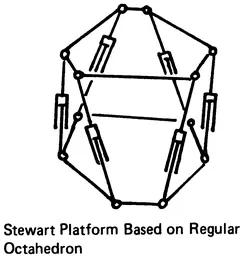
- Robot manipulators with simple serial kinematic chains
- Robot manipulators with tree structures
- Robot manipulators containing closed kinematic chains
- Legged locomotory vehicles
- Multimanipulator systems and dextrous manipulator grippers
- Parallel connection arrangements
- Multisegmented serpentine designs
Serial link robots (Figures 1.2 to 1.9) may be classified according to type and sequence of the kinematic arrangements of links with prismatic (P) and revolute (R) joints in four main categories:
- Cartesian (P1P2P3)
- Cylindrical (R3P2P3)
- Spherical (R1R2P3)
- Anthropomorphic (R1R2R3)
A cartesian robot, which is also called rectangular or rectilinear, has three translation joints. It generates a rectangular workspace with the three basic motions: base travel (P1), reach (P2) and elevation (P3). Some typical industrial robots of this classification are:
| Source | Model | Drive system |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Robotics (USA) | Cyro 750 | Electric DC |
| Anorad (USA) | Anorobot | Electric DC |
| FATA European Group (Italy) | Junior | Electric |
| Senior | Electric | |
| Hitachi (Japan) | Mr: Aros | Hydraulic |
| Matsushita Ind. (Japan) | RW2000 | Electric AC |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Ind. (Japan) | Robitus RC-RH | Hydraulic |
| Mouldmation (UK) | Mouldemate 1200 | Pneumatic |
| Oy W Roseniew (Finland) | Rb 17, 19 | Hydraulic |
| Renault (France) | G80 | Hydraulic |
| S.A. Distribel Robotechnic (Belgium) | Phoenix 3512S | Electric stepper |
| Volkswagenwerke AG (West Germany) | R100 | Electric DC |
| VFW (West Germany) | E440 | Electric DC |
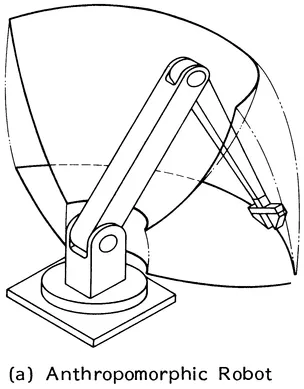
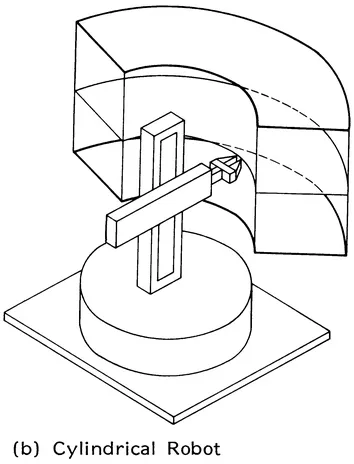
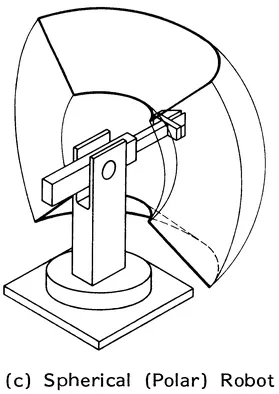
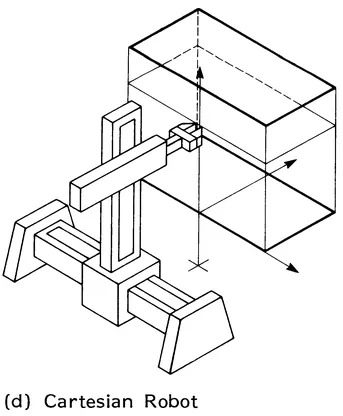
FIGURE 1.2 Basic configuration of serial robot arms and the associated workspace.
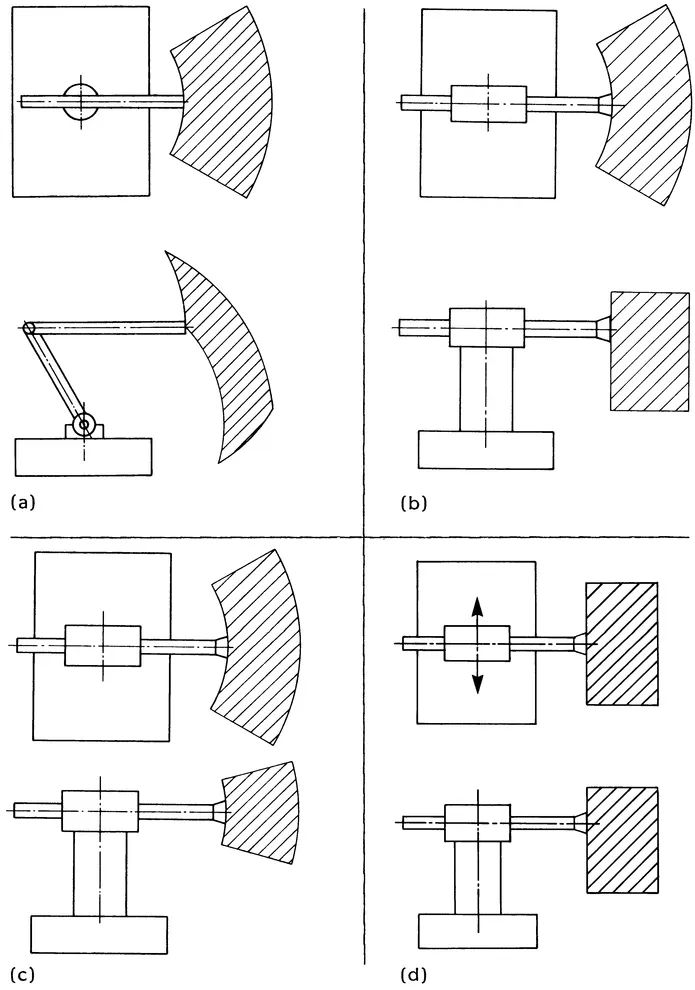
FIGURE 1.3 Orthographic projections of the workspace of tha basic robot configurations. (a) Anthropomorphic robot, (b) Cylindrical robot, (c) Polar robot, (d) Rectangular robot.
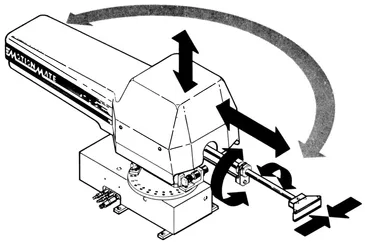
FIGURE 1.4 Configuration of a robot with cylindrical coordinate arm motions. (A) Base rotates with a motion range of 180°, which is adjustable in increments of 15°; (B) lift of 3 in.; (C) extends to 12 in.; (D) wrist rotates 90° or 180°; (E) grasp. (Courtesy of Sehrader-Bellows, a Division of Scovil.)
The cylindrical robot (Figure 1.4) has its basic motions in cylindrical coordinates: base rotation (R1), reach (R2), and elevation (P3). Examples of cylindrical robots are:
| Source | Model | Drive system |
|---|---|---|
| FAB Bilsing (Germany) | High speed | Hydraulic |
| Fanuc (Japan) | MO, Ml, M2 | Electric |
| Jobs (Italy) | JOBOT 10 | Electric |
| Kayaba Ind. (Japan) | KMR 200 | Hydraulic |
| KMR 300 | Hydraulic | |
| Lamberton Robotics (UK) | AA 150 | Electric |
| AA 700 | Electric | |
| AA 13... |
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Contents
- Introduction
- 1 Basic Components of Robot Arms
- 2 End Effectors
- 3 End-of-Arm Tooling and Workpiece Positioners
- 4 End-of-Arm Sensors
- 5 Robot Controllers
- 6 Nontextual Programming
- 7 Textual Programming
- 8 Robot Vision Systems
- 9 Robot Applications
- 10 Geometry of the Workspace
- 11 Kinematics and Trajectory Generation
- 12 Dynamics and Control
- Index
Zitierstile für Fundamentals of Robotics
APA 6 Citation
Ardayfio, D. (2020). Fundamentals of Robotics (1st ed.). CRC Press. Retrieved from https://www.perlego.com/book/1645669/fundamentals-of-robotics-pdf (Original work published 2020)
Chicago Citation
Ardayfio, David. (2020) 2020. Fundamentals of Robotics. 1st ed. CRC Press. https://www.perlego.com/book/1645669/fundamentals-of-robotics-pdf.
Harvard Citation
Ardayfio, D. (2020) Fundamentals of Robotics. 1st edn. CRC Press. Available at: https://www.perlego.com/book/1645669/fundamentals-of-robotics-pdf (Accessed: 14 October 2022).
MLA 7 Citation
Ardayfio, David. Fundamentals of Robotics. 1st ed. CRC Press, 2020. Web. 14 Oct. 2022.