
eBook - ePub
Fundamentals of Robotics
David Ardayfio
This is a test
- 448 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Fundamentals of Robotics
David Ardayfio
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
Fundamentals of Robotics presents the basic concepts of robots to engineering and technology students and to practicing engineers who want to grasp the fundamentals in the growing field of robotics.
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Fundamentals of Robotics est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Fundamentals of Robotics par David Ardayfio en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Tecnología e ingeniería et Ingeniería eléctrica y telecomunicaciones. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
1 Basic Components of Robot Arms
1.1 BASIC ARM TYPES
The identification of the various kinematic arrangements used in industrial robots is useful for manufacturers, users, and researchers. The working volume and dexterity, for example, of a robot are determined by the kinematic arrangements. From the user's point of view, a preliminary determination of the performance of a robot in the work environment based solely on geometry is possible by examination of the linkage type forming the structure of the robot.
Manipulators are typically located relative to ground by either a fixed base or a moving base. The first three links of the manipulator collectively form the manipulator arm. This arm is used for global positioning of the end of the manipulator within the work envelope. The hand is composed of the other links (up to three) and is used to define the orientation of the end of the manipulator. The hand also provides fine local positioning of the end of the manipulator. Detailed treatment of the hands and grippers used in manipulators can be found in Chapter 2. The present chapter discusses various arm types and other components of robot setups.
Two of the three types of connecting elements with one degree of freedom that can be used for connecting links in a robot are the prismatic and revolute pairs. The prismatic or sliding pair allows pure translation of one link with respect to another. The revolute or rotation pair provides pure rotation of one link on another.
The structural arrangement of robot linkage systems (Figure 1.1) includes:
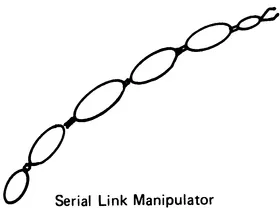
FIGURE 1.1 Types of robotic mechanisms.
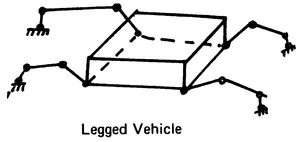
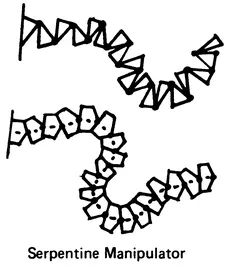
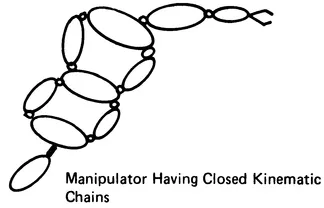
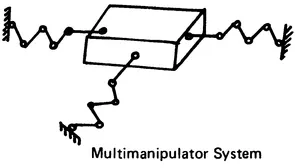
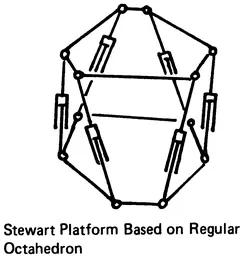
- Robot manipulators with simple serial kinematic chains
- Robot manipulators with tree structures
- Robot manipulators containing closed kinematic chains
- Legged locomotory vehicles
- Multimanipulator systems and dextrous manipulator grippers
- Parallel connection arrangements
- Multisegmented serpentine designs
Serial link robots (Figures 1.2 to 1.9) may be classified according to type and sequence of the kinematic arrangements of links with prismatic (P) and revolute (R) joints in four main categories:
- Cartesian (P1P2P3)
- Cylindrical (R3P2P3)
- Spherical (R1R2P3)
- Anthropomorphic (R1R2R3)
A cartesian robot, which is also called rectangular or rectilinear, has three translation joints. It generates a rectangular workspace with the three basic motions: base travel (P1), reach (P2) and elevation (P3). Some typical industrial robots of this classification are:
| Source | Model | Drive system |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Robotics (USA) | Cyro 750 | Electric DC |
| Anorad (USA) | Anorobot | Electric DC |
| FATA European Group (Italy) | Junior | Electric |
| Senior | Electric | |
| Hitachi (Japan) | Mr: Aros | Hydraulic |
| Matsushita Ind. (Japan) | RW2000 | Electric AC |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Ind. (Japan) | Robitus RC-RH | Hydraulic |
| Mouldmation (UK) | Mouldemate 1200 | Pneumatic |
| Oy W Roseniew (Finland) | Rb 17, 19 | Hydraulic |
| Renault (France) | G80 | Hydraulic |
| S.A. Distribel Robotechnic (Belgium) | Phoenix 3512S | Electric stepper |
| Volkswagenwerke AG (West Germany) | R100 | Electric DC |
| VFW (West Germany) | E440 | Electric DC |
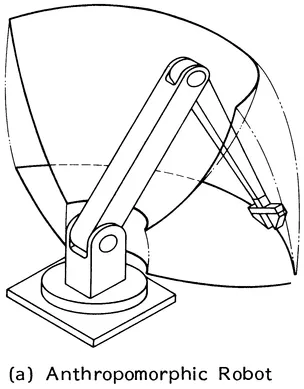
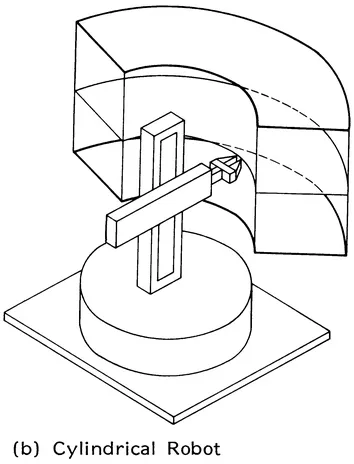
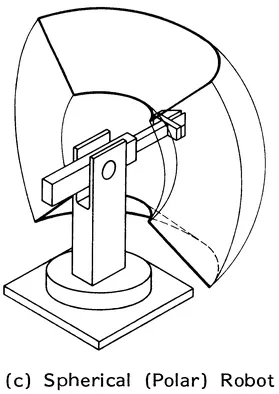
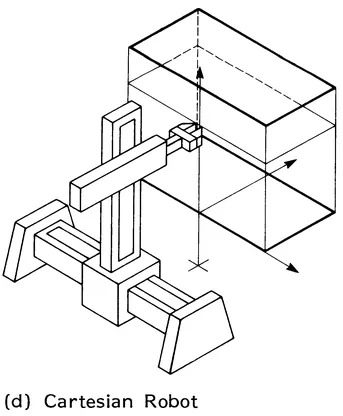
FIGURE 1.2 Basic configuration of serial robot arms and the associated workspace.
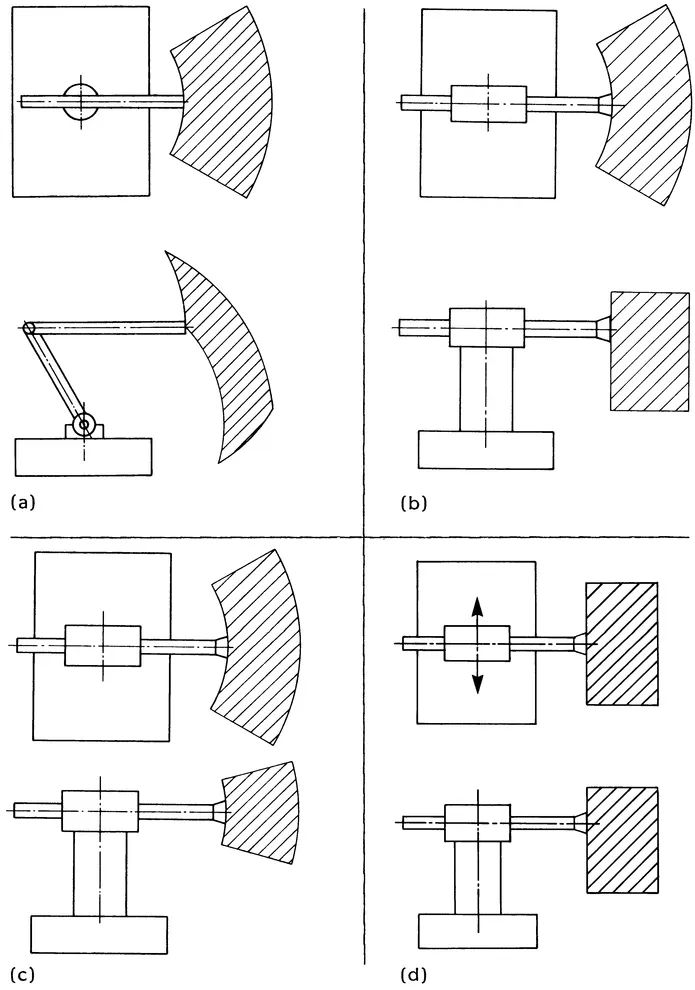
FIGURE 1.3 Orthographic projections of the workspace of tha basic robot configurations. (a) Anthropomorphic robot, (b) Cylindrical robot, (c) Polar robot, (d) Rectangular robot.
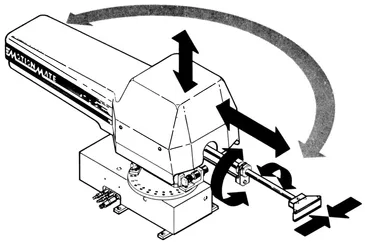
FIGURE 1.4 Configuration of a robot with cylindrical coordinate arm motions. (A) Base rotates with a motion range of 180°, which is adjustable in increments of 15°; (B) lift of 3 in.; (C) extends to 12 in.; (D) wrist rotates 90° or 180°; (E) grasp. (Courtesy of Sehrader-Bellows, a Division of Scovil.)
The cylindrical robot (Figure 1.4) has its basic motions in cylindrical coordinates: base rotation (R1), reach (R2), and elevation (P3). Examples of cylindrical robots are:
| Source | Model | Drive system |
|---|---|---|
| FAB Bilsing (Germany) | High speed | Hydraulic |
| Fanuc (Japan) | MO, Ml, M2 | Electric |
| Jobs (Italy) | JOBOT 10 | Electric |
| Kayaba Ind. (Japan) | KMR 200 | Hydraulic |
| KMR 300 | Hydraulic | |
| Lamberton Robotics (UK) | AA 150 | Electric |
| AA 700 | Electric | |
| AA 13... |
Table des matières
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Contents
- Introduction
- 1 Basic Components of Robot Arms
- 2 End Effectors
- 3 End-of-Arm Tooling and Workpiece Positioners
- 4 End-of-Arm Sensors
- 5 Robot Controllers
- 6 Nontextual Programming
- 7 Textual Programming
- 8 Robot Vision Systems
- 9 Robot Applications
- 10 Geometry of the Workspace
- 11 Kinematics and Trajectory Generation
- 12 Dynamics and Control
- Index
Normes de citation pour Fundamentals of Robotics
APA 6 Citation
Ardayfio, D. (2020). Fundamentals of Robotics (1st ed.). CRC Press. Retrieved from https://www.perlego.com/book/1645669/fundamentals-of-robotics-pdf (Original work published 2020)
Chicago Citation
Ardayfio, David. (2020) 2020. Fundamentals of Robotics. 1st ed. CRC Press. https://www.perlego.com/book/1645669/fundamentals-of-robotics-pdf.
Harvard Citation
Ardayfio, D. (2020) Fundamentals of Robotics. 1st edn. CRC Press. Available at: https://www.perlego.com/book/1645669/fundamentals-of-robotics-pdf (Accessed: 14 October 2022).
MLA 7 Citation
Ardayfio, David. Fundamentals of Robotics. 1st ed. CRC Press, 2020. Web. 14 Oct. 2022.